ES6中React生命周期
一。React生命周期
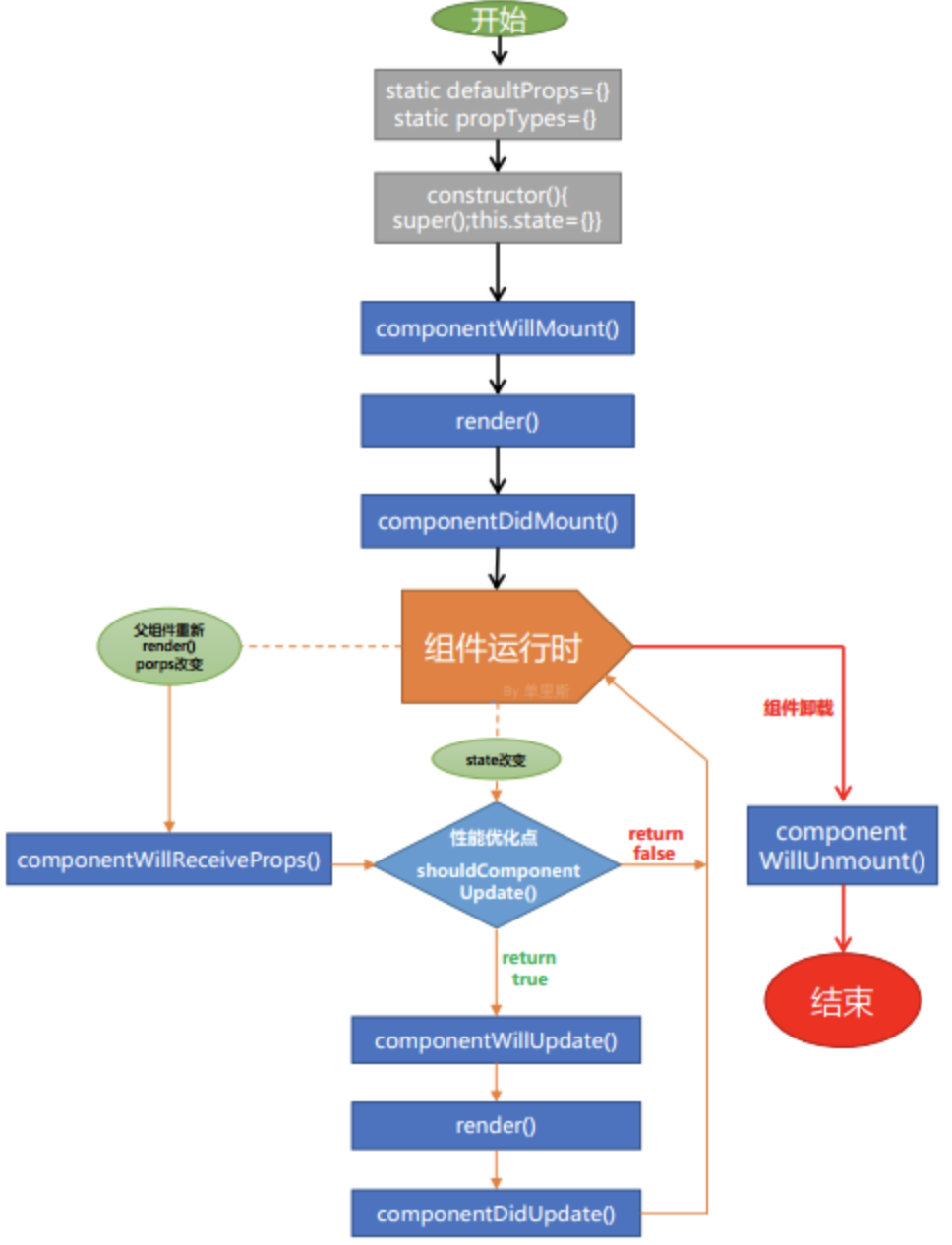
React生命周期主要包括三个阶段:初始化阶段、运行中阶段和销毁阶段。
在React不同的生命周期里,会依次触发不同的钩子函数。
二。React的生命周期函数
(一)、初始化阶段
1、设置组件的默认属性
static defaultProps = {
name: 'sls',
age:23
};
//or
Counter.defaltProps={name:'sls'}
复制代码2、设置组件的初始化状态
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {number: 0}
}
3、componentWillMount()
组件即将被渲染到页面之前触发,此时可以进行开启定时器、向服务器发送请求等操作
4、render()
组件渲染
5、componentDidMount()
组件已经被渲染到页面中后触发:此时页面中有了真正的DOM的元素,可以进行DOM相关的操作
(二)、运行中阶段
1、componentWillReceiveProps()
组件接收到属性时触发
2、shouldComponentUpdate()
当组件接收到新属性,或者组件的状态发生改变时触发。组件首次渲染时并不会触发
shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) {
if (newProps.number < 5) return true;
return false
}
//该钩子函数可以接收到两个参数,新的属性和状态,返回true/false来控制组件是否需要更新。
一般我们通过该函数来优化性能:
一个React项目需要更新一个小组件时,很可能需要父组件更新自己的状态。而一个父组件的重新更新会造成它旗下所有的子组件重新执行render()方法,形成新的虚拟DOM,再用diff算法对新旧虚拟DOM进行结构和属性的比较,决定组件是否需要重新渲染
无疑这样的操作会造成很多的性能浪费,所以我们开发者可以根据项目的业务逻辑,在
shouldComponentUpdate()中加入条件判断,从而优化性能
例如React中的就提供了一个
PureComponent的类,当我们的组件继承于它时,组件更新时就会默认先比较新旧属性和状态,从而决定组件是否更新。值得注意的是,PureComponent进行的是浅比较,所以组件状态或属性改变时,都需要返回一个新的对象或数组
3、componentWillUpdate()
组件即将被更新时触发
4、componentDidUpdate()
组件被更新完成后触发。页面中产生了新的DOM的元素,可以进行DOM操作
三、销毁阶段
1、componentWillUnmount()
组件被销毁时触发。这里我们可以进行一些清理操作,例如清理定时器,取消Redux的订阅事件等等。
演示React生命周期示例代码:

1 import React from 'react' 2 import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; 3 4 class SubCounter extends React.Component { 5 componentWillReceiveProps() { 6 console.log('9、子组件将要接收到新属性'); 7 } 8 9 shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) { 10 console.log('10、子组件是否需要更新'); 11 if (newProps.number < 5) return true; 12 return false 13 } 14 15 componentWillUpdate() { 16 console.log('11、子组件将要更新'); 17 } 18 19 componentDidUpdate() { 20 console.log('13、子组件更新完成'); 21 } 22 23 componentWillUnmount() { 24 console.log('14、子组件将卸载'); 25 } 26 27 render() { 28 console.log('12、子组件挂载中'); 29 return ( 30 <p>{this.props.number}</p> 31 ) 32 } 33 } 34 35 class Counter extends React.Component { 36 static defaultProps = { 37 //1、加载默认属性 38 name: 'sls', 39 age:23 40 }; 41 42 constructor() { 43 super(); 44 //2、加载默认状态 45 this.state = {number: 0} 46 } 47 48 componentWillMount() { 49 console.log('3、父组件挂载之前'); 50 } 51 52 componentDidMount() { 53 console.log('5、父组件挂载完成'); 54 } 55 56 shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) { 57 console.log('6、父组件是否需要更新'); 58 if (newState.number<15) return true; 59 return false 60 } 61 62 componentWillUpdate() { 63 console.log('7、父组件将要更新'); 64 } 65 66 componentDidUpdate() { 67 console.log('8、父组件更新完成'); 68 } 69 70 handleClick = () => { 71 this.setState({ 72 number: this.state.number + 1 73 }) 74 }; 75 76 render() { 77 console.log('4、render(父组件挂载)'); 78 return ( 79 <div> 80 <p>{this.state.number}</p> 81 <button onClick={this.handleClick}>+</button> 82 {this.state.number<10?<SubCounter number={this.state.number}/>:null} 83 </div> 84 ) 85 } 86 } 87 ReactDOM.render(<Counter/>, document.getElementById('root'));
