图Lasso求逆协方差矩阵(Graphical Lasso for inverse covariance matrix)
作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
1. 图Lasso方法的基本理论




2. 坐标下降算法


3. 图Lasso算法


4. MATLAB程序
数据见参考文献[2]
4.1 方法一
demo.m
load SP500 data = normlization(data); S = cov(data); %样本协方差 [X, W] = glasso_1(double(S), 0.5); %X:sigma^(-1), W:sigma [~, idx] = sort(info(:,3)); colormap gray imagesc(X(idx, idx) == 0) axis off %% Data Normalization function data = normlization(data) data = bsxfun(@minus, data, mean(data)); data = bsxfun(@rdivide, data, std(data)); end
glasso_1.m
function [X, W] = glasso_1(S, lambda)
%% Graphical Lasso - Friedman et. al, Biostatistics, 2008
% Input:
% S - 样本的协方差矩阵
% lambda - 罚参数
% Output:
% X - 精度矩阵 sigma^(-1)
% W - 协方差矩阵 sigma
%%
p = size(S,1); %数据维度
W = S + lambda * eye(p); %W=S+λI
beta = zeros(p) - lambda * eye(p); %β=-λI
eps = 1e-4;
finished = false(p); %finished:p*p的逻辑0矩阵
while true
for j = 1 : p
idx = 1 : p; idx(j) = [];
beta(idx, j) = lasso(W(idx, idx), S(idx, j), lambda, beta(idx, j));
W(idx, j) = W(idx,idx) * beta(idx, j); %W=W*β
W(j, idx) = W(idx, j);
end
index = (beta == 0);
finished(index) = (abs(W(index) - S(index)) <= lambda);
finished(~index) = (abs(W(~index) -S(~index) + lambda * sign(beta(~index))) < eps);
if finished
break;
end
end
X = zeros(p);
for j = 1 : p
idx = 1 : p; idx(j) = [];
X(j,j) = 1 / (W(j,j) - dot(W(idx,j), beta(idx,j)));
X(idx, j) = -1 * X(j, j) * beta(idx,j);
end
% X = sparse(X);
end
lasso.m
function w = lasso(A, b, lambda, w)
% Lasso
p = size(A,1);
df = A * w - b;
eps = 1e-4;
finished = false(1, p);
while true
for j = 1 : p
wtmp = w(j);
w(j) = soft(wtmp - df(j) / A(j,j), lambda / A(j,j));
if w(j) ~= wtmp
df = df + (w(j) - wtmp) * A(:, j); % update df
end
end
index = (w == 0);
finished(index) = (abs(df(index)) <= lambda);
finished(~index) = (abs(df(~index) + lambda * sign(w(~index))) < eps);
if finished
break;
end
end
end
%% Soft thresholding
function x = soft(x, lambda)
x = sign(x) * max(0, abs(x) - lambda);
end
结果
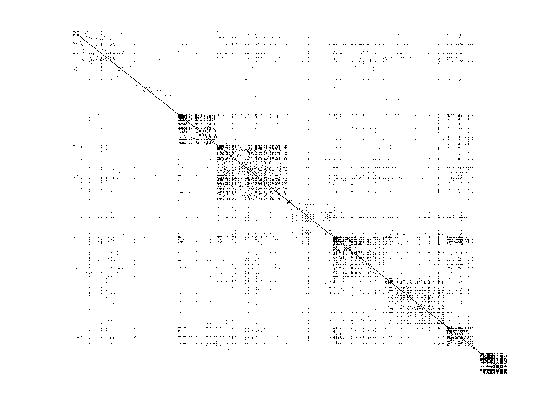
注意:罚参数lamda的设定对逆协方差的稀疏性的影响很大,可以用交叉验证方式得到。
4.2 方法二
graphicalLasso.m
function [Theta, W] = graphicalLasso(S, rho, maxIt, tol)
% http://www.ece.ubc.ca/~xiaohuic/code/glasso/glasso.htm
% Solve the graphical Lasso
% minimize_{Theta > 0} tr(S*Theta) - logdet(Theta) + rho * ||Theta||_1
% Ref: Friedman et al. (2007) Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the
% graphical lasso. Biostatistics.
% Note: This function needs to call an algorithm that solves the Lasso
% problem. Here, we choose to use to the function *lassoShooting* (shooting
% algorithm) for this purpose. However, any Lasso algorithm in the
% penelized form will work.
%
% Input:
% S -- sample covariance matrix
% rho -- regularization parameter
% maxIt -- maximum number of iterations
% tol -- convergence tolerance level
%
% Output:
% Theta -- inverse covariance matrix estimate
% W -- regularized covariance matrix estimate, W = Theta^-1
p = size(S,1);
if nargin < 4, tol = 1e-6; end
if nargin < 3, maxIt = 1e2; end
% Initialization
W = S + rho * eye(p); % diagonal of W remains unchanged
W_old = W;
i = 0;
% Graphical Lasso loop
while i < maxIt,
i = i+1;
for j = p:-1:1,
jminus = setdiff(1:p,j);
[V D] = eig(W(jminus,jminus));
d = diag(D);
X = V * diag(sqrt(d)) * V'; % W_11^(1/2)
Y = V * diag(1./sqrt(d)) * V' * S(jminus,j); % W_11^(-1/2) * s_12
b = lassoShooting(X, Y, rho, maxIt, tol);
W(jminus,j) = W(jminus,jminus) * b;
W(j,jminus) = W(jminus,j)';
end
% Stop criterion
if norm(W-W_old,1) < tol,
break;
end
W_old = W;
end
if i == maxIt,
fprintf('%s
', 'Maximum number of iteration reached, glasso may not converge.');
end
Theta = W^-1;
% Shooting algorithm for Lasso (unstandardized version)
function b = lassoShooting(X, Y, lambda, maxIt, tol),
if nargin < 4, tol = 1e-6; end
if nargin < 3, maxIt = 1e2; end
% Initialization
[n,p] = size(X);
if p > n,
b = zeros(p,1); % From the null model, if p > n
else
b = X Y; % From the OLS estimate, if p <= n
end
b_old = b;
i = 0;
% Precompute X'X and X'Y
XTX = X'*X;
XTY = X'*Y;
% Shooting loop
while i < maxIt,
i = i+1;
for j = 1:p,
jminus = setdiff(1:p,j);
S0 = XTX(j,jminus)*b(jminus) - XTY(j); % S0 = X(:,j)'*(X(:,jminus)*b(jminus)-Y)
if S0 > lambda,
b(j) = (lambda-S0) / norm(X(:,j),2)^2;
elseif S0 < -lambda,
b(j) = -(lambda+S0) / norm(X(:,j),2)^2;
else
b(j) = 0;
end
end
delta = norm(b-b_old,1); % Norm change during successive iterations
if delta < tol, break; end
b_old = b;
end
if i == maxIt,
fprintf('%s
', 'Maximum number of iteration reached, shooting may not converge.');
end
结果
>> A=[5.9436 0.0676 0.5844 -0.0143
0.0676 0.5347 -0.0797 -0.0115
0.5844 -0.0797 6.3648 -0.1302
-0.0143 -0.0115 -0.1302 0.2389
];
>> [Theta, W] = graphicalLasso(A, 1e-4)
Theta =
0.1701 -0.0238 -0.0159 0.0003
-0.0238 1.8792 0.0278 0.1034
-0.0159 0.0278 0.1607 0.0879
0.0003 0.1034 0.0879 4.2369
W =
5.9437 0.0675 0.5843 -0.0142
0.0675 0.5348 -0.0796 -0.0114
0.5843 -0.0796 6.3649 -0.1301
-0.0142 -0.0114 -0.1301 0.2390
5. 补充:近端梯度下降(Proximal Gradient Descent, PGD)求解Lasso问题


6. 参考文献
[1] 林祝莹. 图Lasso及相关方法的研究与应用[D].燕山大学,2016.
[2] Graphical Lasso for sparse inverse covariance selection
[3] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 清华大学出版社, 2016.
[4] Graphical lasso in R and Matlab
[5] Graphical Lasso