http://blog.51cto.com/3622288/1976834
find命令
find 命令使用来搜索文件的一个命令。
常见用法:-type -name -mtime -ctime -atime -mmin -exec {} ;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#name 的实例演示:[root@centos7 a]# find /tmp/a/ -name "1.txt"/tmp/a/1.txt#模糊搜索[root@centos7 a]# find /tmp/a/ -name "1*" # * 表示通配符/tmp/a/1.txt/tmp/a/1_2.txt/tmp/a/1_2.log/tmp/a/1.log/tmp/a/1 |
搜索指定类型为目录
|
1
2
|
[root@centos7 a]# find /tmp/a/ -type d -name "1*" #-type 表示类型 d 表示目录/tmp/a/1_2 |
搜索指定类型为文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@centos7 a]# find /tmp/a/ -type f -name "1*" # f 表示文件(file)/tmp/a/1.txt/tmp/a/1_2.txt/tmp/a/1_2.log/tmp/a/1.log/tmp/a/1 |
根据修改文件时间搜素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
[root@centos7 a]# find /tmp/a/ -type f -mtime -1 # -mtime 表示 修改的文件的时间/tmp/a/1.txt # -1 表示 一天内/tmp/a/2.txt # +1 表示 一天前/tmp/a/A/tmp/a/B/tmp/a/1_2.txt/tmp/a/1_2.log/tmp/a/1.log/tmp/a/1 |
根据inode号搜素文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#查询文件的inode号[root@centos7 a]# ls -i16777659 1.txt 16777659 2.txt #相同的inode号[root@centos7 a]# find /tmp/a/ -inum 16777659/tmp/a/1.txt/tmp/a/2.txt |
搜索几个小内的文件
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos7 ~]# find /tmp/ -type f -mmin -60 # -mmin 表示时间是按每分钟计算/tmp/a/1.txt # -60 表示 1小时=60min(分钟)/tmp/a/2.txt |
搜索的结果列出属性
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos7 ~]# find /tmp/ -type f -mmin -150 -exec ls -l {} ; -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 10月 27 22:39 /tmp/a/1.txt-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 10月 27 22:39 /tmp/a/2.txt |
批量修改文件名称
|
1
2
3
4
|
#格式: 路径 命令 修改后缀[root@centos7 ~]# find /tmp/ -type f -mmin -150 -exec mv {} {}.bak ;[root@centos7 ~]# ls /tmp/a/1.txt.bak 2.txt.bak |
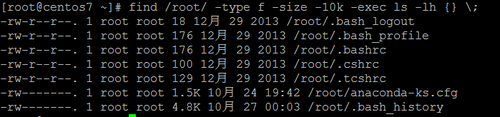
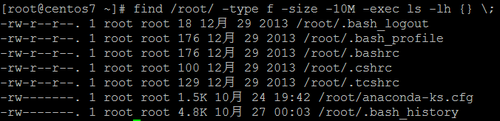
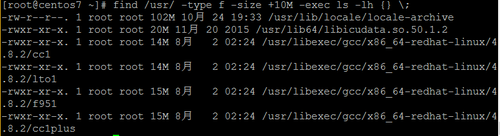
根据文件大小搜索
可以选择 10M
可以选择 +10M
stat 查看文件的具体信息
文件名后缀
1.linux系统是区分大小写的;
2.文件是有后缀的。windows系统也有,并且根据后缀名可以判断是否是.txt(文本编辑文件)或.exe(程序可执行文件)甚至.zip(压缩文件)等。而linux中是可以自定义的,所以如果1.txt可能不是文本文件;