c#异步编程-线程
近期会分享自己学习c#异步编程系列的文章,如果能帮助大家希望多多关注文章末尾的微信公众号和知乎三连。各位举手之劳是对我更新技术文章最大的支持。
1.线程
- 线程是一个可执行的路径,它可以独立于其他线程执行。
- 每个线程都在操作系统的进程内执行,而操作系统进程提供了程序运行的独立环境。
- 单线程应用,在进程的独立环境里只跑一个线程,所以该线程拥有独占权。
- 多线程应用,单个进程中会跑多个线程,他们会共享当前的执行环境(内存)等。
- 进程和线程的对应关系,一个进程可以拥有多个线程,多个线程只能属于一个进程。 例如:一个非常耗时的操作(读数据库、复杂耗时的计算),如果只用主线程执行UI线程会“假死”专业术语叫线程阻塞。这时候的解决办法就是单独开一个线程去执行这个耗时操作。这个时候处理的数据就可被称作是共享状态。
示例代码如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(PrintValue);
t.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread.");
}
}
static void PrintValue()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}效果:
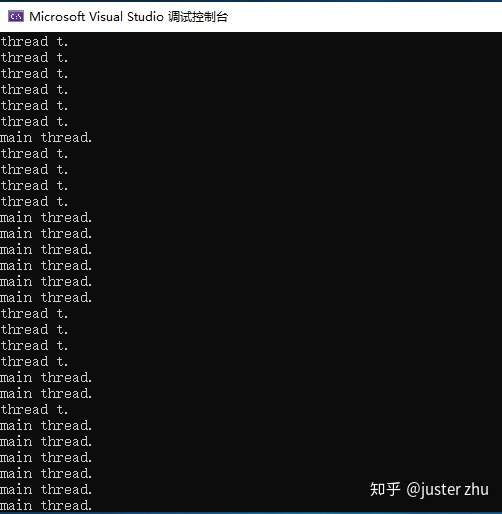
- 在单核计算机上,操作系统必须为每个线程分派“时间片”(在windows中通常为20毫秒)来模拟并发,从而导致重复的"main thread."和"thread t."输出。
- 在多核或多处理计算机上,这两个线程可以真正的并行执行(也可能受到计算机上其他活动进程的竞争)。
- 线程抢占:A线程的执行与另外一个线程上代码的执行交织的那一刻。可被成为线程抢占。
线程属性:
- 线程一旦开始执行,isAlive就是True,线程结束就编程false。
- 线程结束的条件就是:线程构造函数传入的委托结束了执行。
- 线程一旦结束,就无法再重启,因为线程需要执行的代码执行完成之后会自动销毁。
- 每个线程都有Name属性,通常用于调试。每个线程的Name只能设置一次,以后更改会抛出异常。
- 静态的Thread.CurrentThread属性,会返回当前执行的线程。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main_Thread";
Thread t = new Thread(PrintValue);
t.Name = "T_Thread";
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread.");
}
}
static void PrintValue()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}2.Thread.Join 和 Thread.Sleep
Join();
- 调用Join方法,就可以等待另一个线程结束。也叫阻塞线程
示例代码如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region Join and Sleep
Thread t = new Thread(PrintValue);
t.Start();
t.Join();//等待PrintValue执行完成
Console.WriteLine("End.");
#endregion
}
static void PrintValue()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}- 调用join的时候,可以设置一个超时,用毫秒或者TimeSpan都可以。
- 如果返回true,那就是线程结束;如果超时,则返回false。
static Thread t1, t2;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
t1 = new Thread(ThreadTest);
t1.Name = "t1";
t1.Start();
t2 = new Thread(ThreadTest);
t2.Name = "t2";
t2.Start();
}
private static void ThreadTest()
{
Console.WriteLine("Current thread:{0}",Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
if (Thread.CurrentThread.Name == "t1" && t2.ThreadState != ThreadState.Unstarted)
{
if (t2.Join(1000))
{
Console.WriteLine("t2 join 2000ms.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("the time out.");
}
}
Thread.Sleep(4000);
Console.WriteLine("thread 1:{0}", t1.ThreadState);
Console.WriteLine("thread 2:{0}", t2.ThreadState);
}效果:

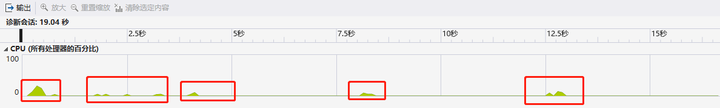
Sleep() - Thread.Sleep()方法会暂停当前的线程,并等一段时间。期间是不占用cpu资源的。
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("i");
}
Thread.Sleep(4000);
}验证: 在每次i循环的时候会占用CPU输出10000次,然后休息4秒再继续循环。这时候分析图如下:
3.前台线程和后台线程
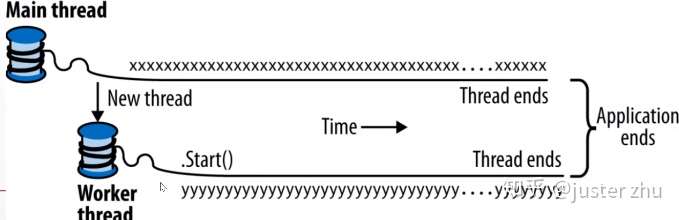
前台线程:
- 该线程在没有执行完成函数代码时,在程序关闭时是不会退出进程的。
Thread t1 = new Thread(PrintValue);
t1.IsBackground = true;
t1.Start();
static void PrintValue()
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}效果:
后台线程:
- 该线程不管有没有执行完成函数代码,都会直接退出进程。
Thread t1 = new Thread(PrintValue);
t1.IsBackground = false;
t1.Start();
static void PrintValue()
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}4.线程优先级
线程优先级决定了相对于操作系统中其他活跃线程所占的执行时间,提升指定线程优先级如果该线程处理任务比较重则会降低其他线程优先级会导致其他抢占不到CPU处理时间片,。
Thread t1 = new Thread(() => { Console.ReadLine(); });
t1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
t1.Start();ThreadPriority枚举如下:
//
// 摘要:
// Specifies the scheduling priority of a System.Threading.Thread.
public enum ThreadPriority
{
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with any other priority.
Lowest = 0,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with Normal priority
// and before those with Lowest priority.
BelowNormal = 1,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with AboveNormal priority
// and before those with BelowNormal priority. Threads have Normal priority by default.
Normal = 2,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with Highest priority
// and before those with Normal priority.
AboveNormal = 3,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled before threads with any other priority.
Highest = 4
}如果想让某线程的优先级比其他进程中的线程高,那么就必须提升进程的优先级。
- 使用system.Diagnostics下的Process类。
using(Process p = Process.GetCurrentProcess()) p.PriorityClass = ProcessPriorityClass.High; - 这可以很好的用于只做少量工作且需要较低延迟的非UI进程。
- 对于需要大量计算的程序(wpf、winfrom等),提高进程优先级可能会降低其他进程抢占不到CPU处理时间片,从而降低整个计算机的速度。
- E-Mail:zhuzhen723723@outlook.com
- QQ: 580749909(技术交流群)
- Blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/justzhuzhu/
- Git: https://github.com/JusterZhu
- 微信公众号
