前 言
JRedu
Android今天接着上次没有时间说完的AngularJS来接着讲。
| 一、 Android AngularJS中的服务 |
1.1Service
(1)内置服务:
要使用服务必须要把服务名通过controller的构造函数的参数注入进来!!!
系统内置的服务,同意使用$开头,服务中的属性和方法统一使用$$开头!!!自定义服务时,需要注意与系统服务的写法区分开
$location:返回当前页面的URL地址信息,第一个对象
$http:向服务器发送请求,类似于JQuery中的ajax
$timeout:相当于setTimeout():
$interval:相当于setInterval ();
angular.module("app",[])
.controller("ctrl",function($scope,$location,$timeout,
$interval,hexafy){
$scope.local = $location.$$host;
$timeout(function(){
$scope.time = "我是两秒之后出现的";
},2000);
$scope.num = 0;
$interval(function(){
$scope.num++;
},1000);
$scope.gongneng = hexafy.gongneng;
$scope.num1 = hexafy.func(10);
})

(2)自定义服务
第一个参数是服务名
第二个参数是自定义服务的构造函数。我们自定义的服务,本质是一个对象
对象的属性:可以在构造函数中,使用this.属性 表示;
对象的方法,可以在构造函数中,使用this.方法 表示
将十进制数转化为16进制
.service("hexafy",function(){
this.gongneng = "将十进制数转化为16进制";
this.func = function(num){
return num.toString(16);
}
})

使用过滤器实现同样功能
<p>{{10|filter1}}</p>
.filter("filter1",function(){
return function(num){
return num.toString(16);
}
})
结果为a
在过滤器中调用服务!!!
也必须在声明过滤器的外层构造中,注入名称!!
<p>{{11|filter2}}</p>
.filter("filter2",function(hexafy,$location){
return function(num){
return num.toString(16);
}
})
结果为b
1.2Factory
自定义服务
factory服务在使用上与service服务内有太大差别
唯一不同的是,是声明服务时,factory服务是在函数中先声明号一个对象,然后使用return将对象返回
而servicce服务,则是直接在函数中使用this将属性和方法添加到对象上面
<h1>{{gongneng}}</h1>
<p>10进制转化为16{{num1}}</p>
angular.module("app",[])
.controller("ctrl",function($scope,hexafy){
$scope.gongneng = hexafy.gongneng;
$scope.num1 = hexafy.func(10);
})
.factory("hexafy",function(){
var obj = {
gongneng : "将十进制数转换为十六进制",
func : function(num){
return num.toString(16);
}
}
return obj;
})

1.3provider
自定义服务
(1)在AngularJS中,service服务,factory服务都是基于provider服务实现的
(2)字定义provider时,可以使用this.$get方法,接受一个函数,函数里面采用与factory完全相同的写法!!!
例子:
.provider("hexafy",function(){
this.$get = function(){
var obj = {
gongneng : "333",
}
return obj;
}
})

(3)在三种服务中,provider服务是唯一一个可以写进config配置阶段的服务
所以说,如果服务需要在配置阶段,也就是在声明controller之前执行的话,则可以使用provider,否则一般使用service或者factory
angular.module("app",[])
.config(function($provide){
$provide.provider("hexafy",function(){
this.$get = function(){
var obj = {
gongneng : "444",
}
return obj;
}
})
})
注意:
.config() 表示配置阶段,在声明controller之前执行。可以用于声明一些在controller中需要使用全局变量、方法、服务等。。。
在配置阶段声明provider服务,需要在config中注入系统对象$provide
| 二、AngularJS中的$http.html |
正常写的方式:
angular.module("app",[])
.controller("ctrl",function($scope,$http){
$http({
method:'GET',//请求的方法
url:'h51701.json'//请求的地址
}).then(function(obj){
//请求成功的回调函数
$scope.data = obj.data;
},function(){
//请求失败的回调函数
alert("n");
});
$scope.classes = [
{name:"张三",age:12,score:44},
{name:"张诶",age:15,score:80},
{name:"刘青",age:11,score:23},
{name:"55",age:15,score:99},
{name:"小刘",age:13,score:54},
]
})
简写方式:
可以直接简写为get或者post方式:
$http.get('/someUrl', ).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
$http.post('/someUrl', data, config).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
$http.post('127.0.0')
.then(function(){
alert("y");
},function(){
alert("n");
})
再加上之前的HTML:
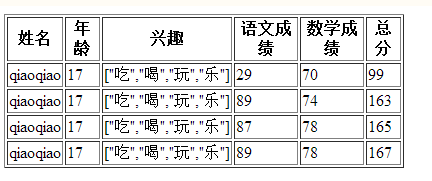
<table border="1" width="400px">
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>兴趣 </th>
<th>语文成绩</th>
<th>数学成绩</th>
<th>总分</th>
</tr><!-- |filter:search |filterByName:name "-->
<tr ng-repeat="item in data | orderBy : 'score.math'">
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.age}}</td>
<td>{{item.hobby}}</td>
<td>{{item.score.chinese}}</td>
<td>{{item.score.math}}</td>
<td>{{item.score.chinese+item.score.math}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
以及一个josn文件
[
{
"name": "qiaoqiao",
"age": 17,
"hobby": [
"吃",
"喝",
"玩",
"乐"
],
"score":{
"math":74,
"chinese":89
}
},
{
"name": "qiaoqiao",
"age": 17,
"hobby": [
"吃",
"喝",
"玩",
"乐"
],
"score":{
"math":78,
"chinese":87
}
},
{
"name": "qiaoqiao",
"age": 17,
"hobby": [
"吃",
"喝",
"玩",
"乐"
],
"score":{
"math":70,
"chinese":29
}
},
{
"name": "qiaoqiao",
"age": 17,
"hobby": [
"吃",
"喝",
"玩",
"乐"
],
"score":{
"math":78,
"chinese":89
}
}
]
最终的结果为:
| 三、AngularJS中的select和表格.html |
(1)使用数组作为数据源
a、item表示数组中的每一项!
b、循环出的option中,value的值,默认为item
c、option显示出的内容(<option></option>标签中的文字)是由item.site for决定的!
(2)以对象作为数据源
a、 (key,value) 第一项表示对象的键,第二项表示对象的值;
b、 option的value,永远都是对象的值!
c、 option显示出的内容(<option></option>标签中的文字)是由...for 决定的!也就是说 for前面是什么,option标签中就是什么。
(3)【ng-options 和 ng-repeat】
a、ng-options使用时,是将指令添加在select上;
ng-repeat使用时,试讲指令添加在option上;
b、 ng-options使用时,必须同步给select标签绑定ng-model;
ng-repeat使用时,不一定需要绑定ng-model
c、 ng-options使用时,我们只需要关心for前面的部分,即option标签中显示的文字;
而option的value会自动分配,不由我们决定。
(使用数组作为数据源是,value就是数组的每一项;使用对象作为数据源是,value永远都是对象的值)
ng-repeat使用,除了要指定option标签中显示的文字,还需要手动指定value中的内容,如果没有指定则默认没有value;
<table width="400" border="1">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="item in options">
<!--ng-repeat遍历是,$index 表示当前的行索引!-->
<td>{{$index + 1}}</td>
<td>{{item}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script src="js/angular.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
angular.module("app",[])
.controller("ctrl",function($scope){
$scope.options = ["张三","李四","王二麻子","赵六","李二狗"];
$scope.sites = [
{site : "Google", url : "http://www.google.com"},
{site : "Runoob", url : "http://www.runoob.com"},
{site : "Taobao", url : "http://www.taobao.com"}
];
$scope.sitess = {
site01 : "Google",
site02 : "Runoob",
site03 : "Taobao"
}
})
</script>

| 四、AngularJS中的DOM与事件.html |
(1)DOM
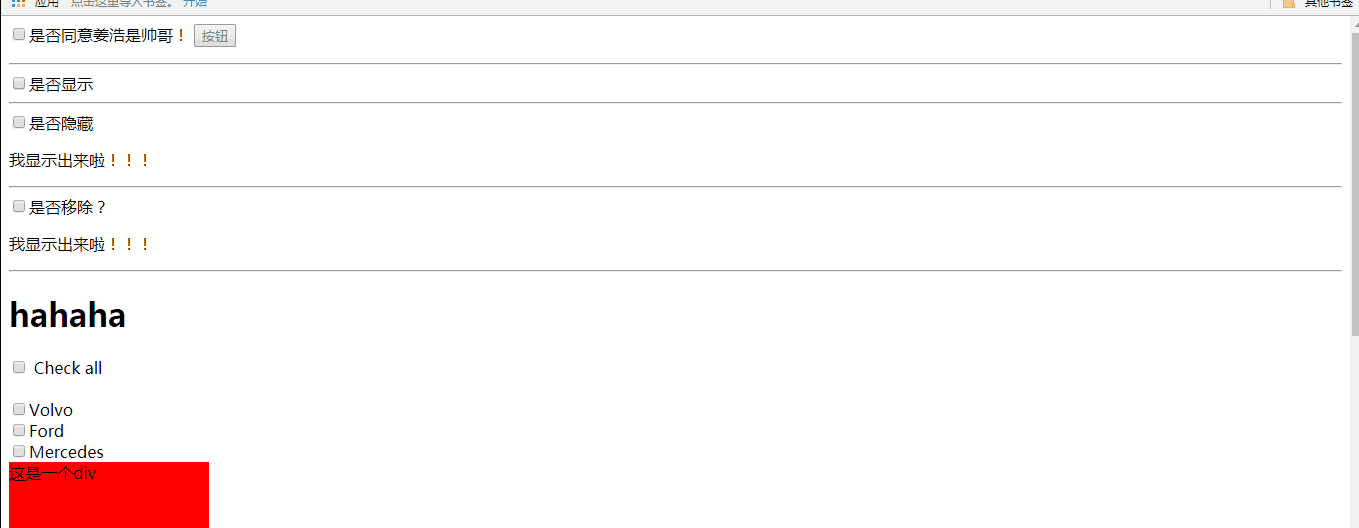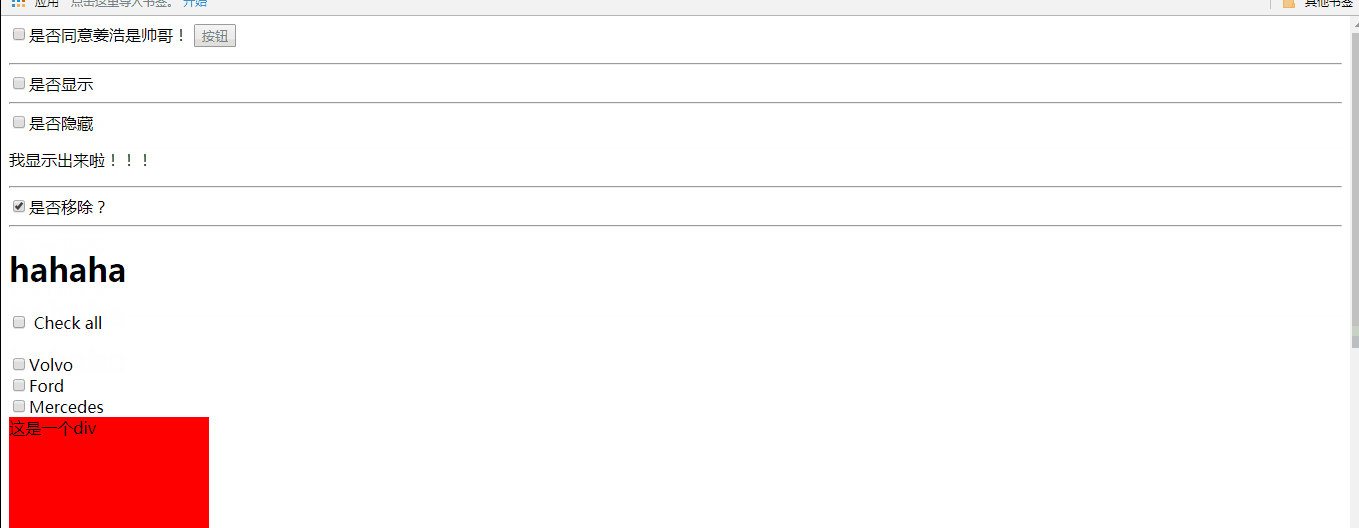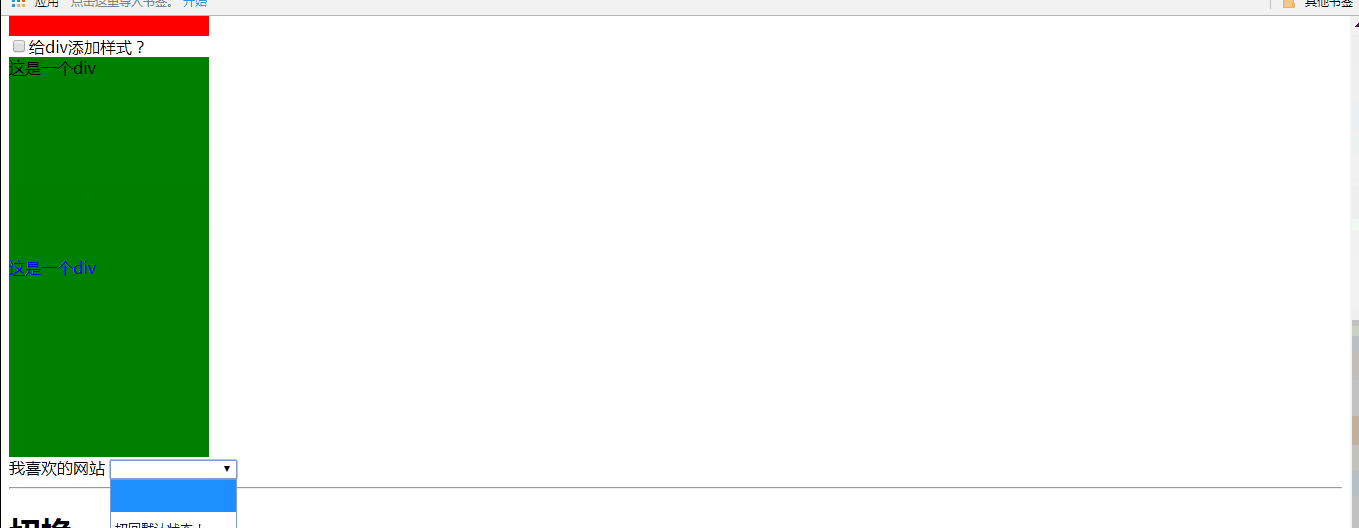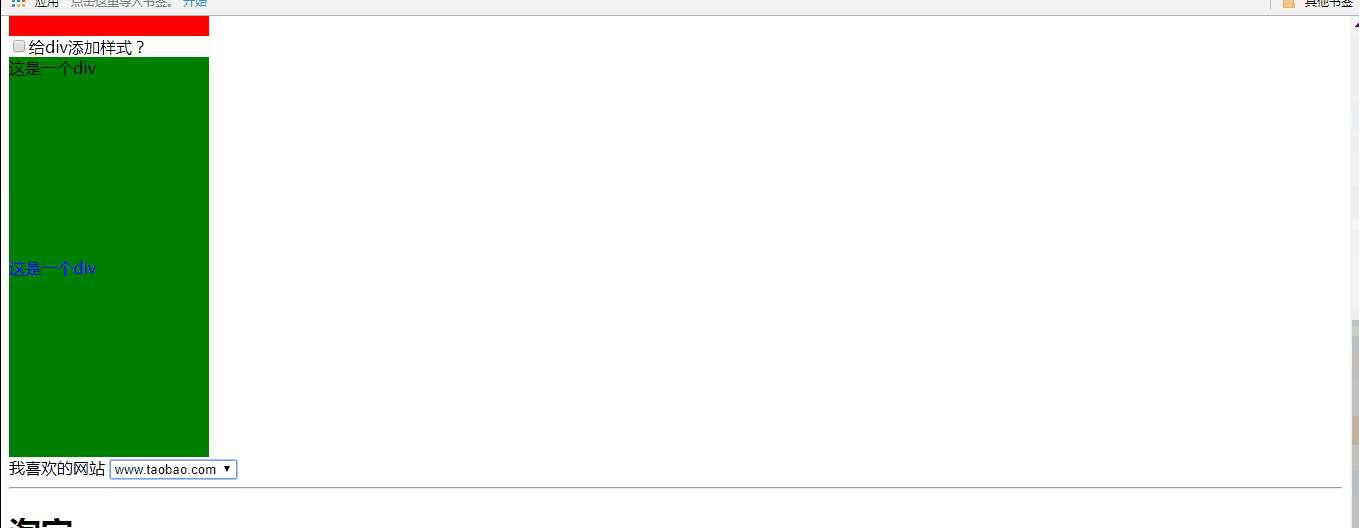
a、ng-show是否显示 传入true表示显示,否则false隐藏
b、ng-hide是否隐藏 传入true表示隐藏,否则false显示
c、ng-if:是否移除元素
当传入true显示,传入false是移除
效果与ng-show相同,但是ng-show和ng-hide只是隐藏元素,而ng-if是将元素从DOM中移除
d、ng-bind-html:相当于innerHTML
ng-bind:相当于innerText
注意:要使用ng-bind-html,必须导入/angular-sanitize.js文件进行安全验证。
同时需要在声明模块的时候,在数组中注入安全严重模块'ngSanitize'
e、ng-checkerd 设置复选框或单选框的选中状态
传入true设置当前复选框被选中
f、ng-class:用于设置给div添加class类。
可选值有以下几种情况:
①可以使字符串。表示直接给元素添加对应的class。多个class直接用空格分隔
②可以使对象。对象的键表示class名字,对象的值为true或false,当值为true时表示添加对应的class
③可以是数组。数组中的值可以是字符串或对象,判断规则同上
g、ng-switch 根据变量的值,选择不同的ng-switch-when来显示,当没有合适的选项时,显示ng-switch-default
(2)事件
AngularJs中的事件
AngularJS中的事件 只能触发绑定在AngularJs作用域上面的属性和方法

| 五、AngularJS表单和输入验证.html |
(1)表单中,常用的验证操作:
$dirty 表单有填写记录
$valid 字段内容合法的
$invalid 字段内容是非法的
$pristine 表单没有填写记录
$error 表单验证不通过的错误信息
(2)验证时,必须给 form 和 input 设置 name 属性
给form 和 input 设置了 name 后,会自动将表单信息绑定到$scope作用域中,
所以,可以直接使用formName.inputName.$验证操作,得到验证结果
例如:
formName.inputName.$dirty = "true";
表示表单被填写过
formName.inputName.$invalid = "true";
表示表单输入内容不合法
formName.inputName.$error.required = "true";
表示设置了必填,但是没有输入
注意:$error 支持的验证: required/minlength/maxlength/partten/email/number/date/url等
(3)为了避免AngularJs 的验证与HTML5 的表单验证冲突,比如说type="email",required等,
h5也会进行验证,可以给form添加 novalidate 属性,禁用 h5 的验证功能
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>AngularJs中的表单和输入验证</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap.css" />
<style type="text/css">
.row{
margin: 10px 0;
}
.col-xs-5{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body ng-app="app" ng-controller="ctrl">
<div class="container" style=" 400px; margin: 0 auto; padding: 0;">
<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">
<div class="panel-title" style="text-align: center;">用户注册</div>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<form class="form-horizontal" name="form" novalidate>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">用户名</div>
<div class="col-xs-9">
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="name" ng-model="user.name
" required ng-minlength="6" ng-maxlength="12" />
<p style="color: red; margin: 0;" ng-show="form.name
.$invalid && form.name
.$dirty">
<span ng-show="form.name
.$error.required">用户名必须填写</span>
<span ng-show="form.name
.$error.minlength">用户名长度最小为6位</span>
<span ng-show="form.name
.$error.maxlength">用户名长度最大为12位</span>
</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">邮箱</div>
<div class="col-xs-9">
<input type="email" class="form-control" name="email" ng-model="user.email" required />
<p style="color: red; margin: 0;" ng-show="form.email.$invalid && form.email.$dirty">
<span ng-show="form.email.$error.required">邮箱必须填写</span>
<span ng-show="form.email.$error.email">邮箱不合法</span>
</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">密码</div>
<div class="col-xs-9">
<input type="password" class="form-control" name="pwd" ng-model="user.pwd" pattern="^w{6,18}$" required />
<p style="color: red; margin: 0;" ng-show="form.pwd.$invalid && form.pwd.$dirty">
<span ng-show="form.pwd.$error.pattern">密码只能有6~18位的字母、数字、下划线组成</span>
</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">确认密码</div>
<div class="col-xs-9">
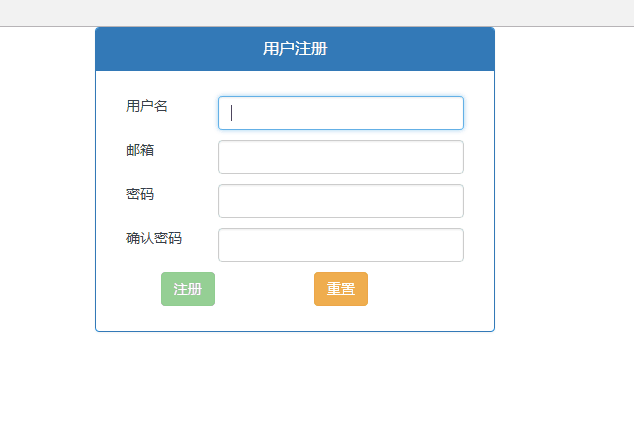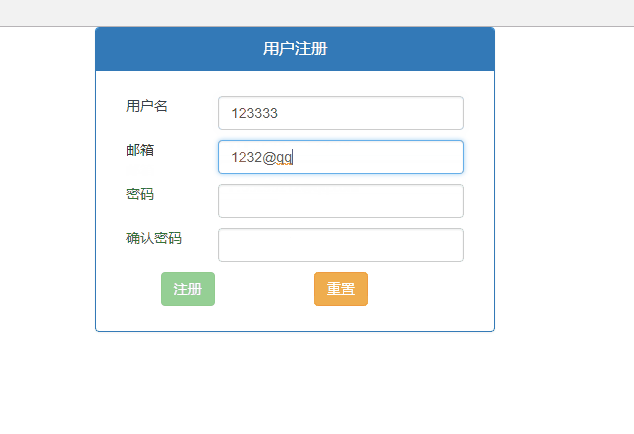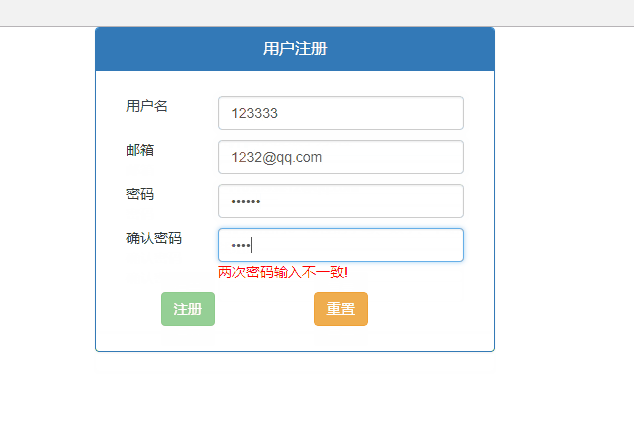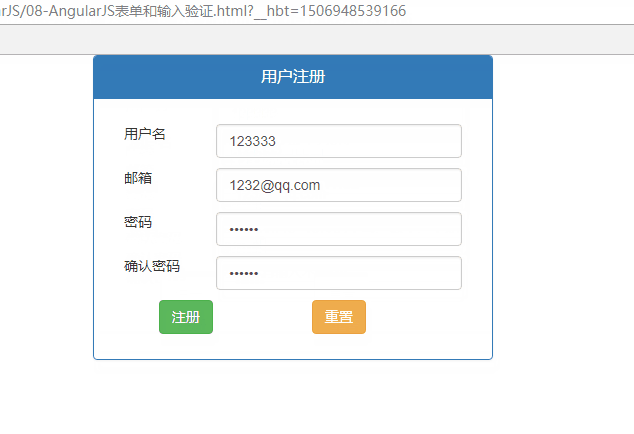
<input type="password" class="form-control" name="repwd" ng-model="user.repwd" required />
<p style="color: red; margin: 0;" ng-show="form.repwd.$dirty && user.pwd != user.repwd">
两次密码输入不一致!
</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-5">
<input type="submit" value="注册" class="btn btn-success" ng-disabled="form.$invalid || user.pwd != user.repwd" />
</div>
<div class="col-xs-5">
<input type="reset" value="重置" class="btn btn-warning" />
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/angular.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
angular.module("app",[]).controller("ctrl",function(){
})
</script>
</html>
| 六、AngularJS中的路由.html |
(1)在AngularJS中使用路由:
a、 导入路由文件:angular-route.js
b、 在主模块中注入"ngRoute"。 rg:angular.module("app",["ngRoute"])
c、 将超链接改写为路由格式。 "#/标记"
<a href="#/">首页</a> 首页直接使用 #/ 表示
<a href="#/page1">page1</a> 其他页面"#/标记" 表示
d、 在config配置阶段,注入$routeProvider,进行路由配置:
e、 在页面的合适位置,添加ng-view,用于承载路由打开的页面:
<div ng-view></div> 或 <ng-view></ng-view>
(2)【路由对象中接受的可选参数:】
① template: 自定义HTML模板,会直接将这段HTML记载到ng-view中;
② templateUrl: 导入外部的HTML模板文件。 为了避免冲突,外部的HTML应该是一个代码片段,即只保留body以内的部分。
③ controller: 在当前HTML模板上,执行的controller函数。会生出新的作用域$scope.
可以接受字符串(声明好的controller名字),也可以直接接受函数。
注意: 使用ng-view打开的页面,controller中的作用域是属于当前页面作用域的子作用域!!
依然符合Angular中父子作用域"能读不能写"的要求!
所以: 如果需要在ng-view中修改当前作用域的变量,必须把这个变量声明为对象的属性!!
④ redirectTo:重定向。一般用于.otherwise()中,用于重定向回首页
(3)AngularJS允许用户自定义指令!!
例如: <div ng-view></div> 或 <ng-view></ng-view>
a、 使用.directive()声明一个自定义指令;
b、 定义指令时,指令名必须使用驼峰命名法; 而调用指令时,用"-"链接
.directive("jiangHao") → <jiang-hao><jiang-hao>
.directive("jianghao") → <jianghao><jianghao>
c、 定义指令时,对象中使用的属性:
① template: 调用指令时,生成的模板
② restrict: 用于声明指令允许的调用方式:
E→允许标签名表明 A→允许属性调用 C→允许类名调用 M→允许注释调用
默认值为:EA
如果需要注释调用,必须再添加一个属性:replace:true,而且注释调用前必须添加"directive:" eg:<!-- directive: jiang-hao -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
ul{
overflow: hidden;
}
li{
width: 100px;
height: 40px;
text-align: center;
float: left;
line-height: 40px;
list-style: none;
cursor: pointer;
}
li a{
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
}
li:hover{
background-color: yellow;
}
#div1{
width: 1000px;
height: 500px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 2px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body ng-app="app" ng-controller="ctrl">
<ul>
<li><a href="#/">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="#/page1">page1</a></li>
<li><a href="#/page2">page2</a></li>
<li><a href="#/page3">page3</a></li>
<li><a href="#/page4">page4</a></li>
</ul>
<input type="text" ng-model="test" />
<p>{{test}}</p>
<p>{{obj.test}}</p>
<div id="div1" ng-view></div>
<!--<ng-view></ng-view>-->
<jiang-hao></jiang-hao>
<div jiang-hao></div>
<div class="jiang-hao"></div>
<!-- directive:jiang-hao -->
</body>
<script src="js/angular.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="js/angular-route.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
angular.module("app",["ngRoute"])
.config(function($routeProvider){
$routeProvider
.when("/",{template:'<h1 style="color:red;">这是首页</h1>'})
.when("/page1",{templateUrl:"AngularJS动画.html",controller:"ctrl1"})
.when("/page2",{templateUrl:"AngularJS动画.html",controller:function($scope){
$scope.text = "这是ctrl不知道是几控制器!!"
}})
.when("/page3",{templateUrl:"AngularJS动画.html"})
.when("/page4",{})
.otherwise({redirectTo:"/"})
})
.controller("ctrl",function($scope){
$scope.test = "这是一段测试文字!";
$scope.obj = {
test:"这是一个测试对象!"
}
})
.controller("ctrl1",function($scope){
$scope.text = "这是ctrl1控制器!";
})
.directive("jiangHao",function(){
return {
restrict : "EACM",
replace:true,
template:"<h1>这是一个自定义指令</h1>",
}
})
</script>
</html>