Java第九次作业
(一)学习总结
1.用思维导图对java多线程的学习内容进行总结。
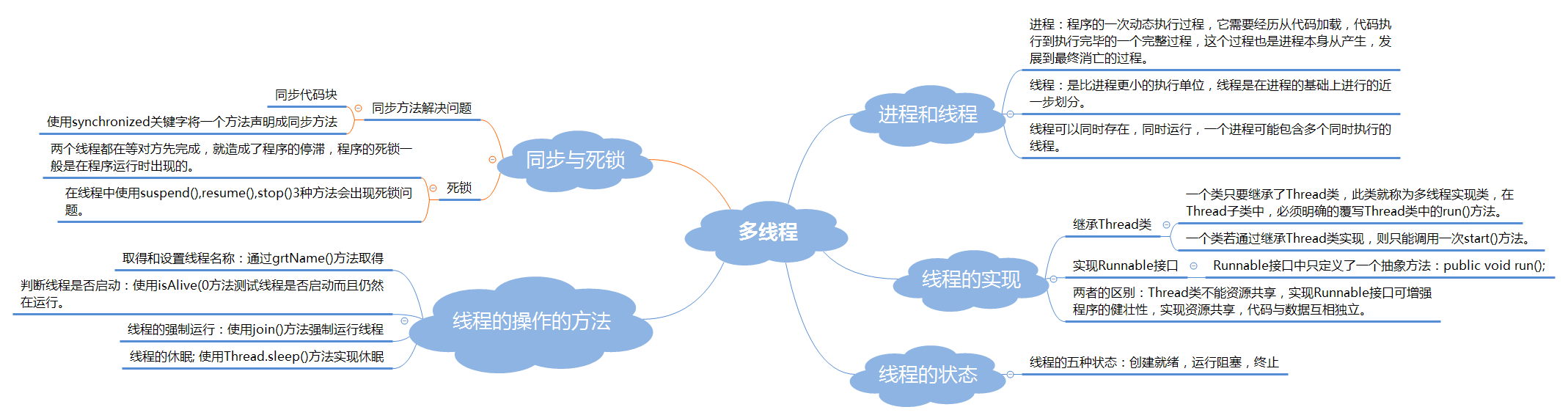
参考资料: XMind。
2.下面是一个单线程实现的龟兔赛跑游戏。
public class TortoiseHareRace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int totalStep = 10;
int tortoiseStep = 0;
int hareStep = 0;
boolean[] flags = {true,false};
System.out.println("龟兔赛跑开始了...");
while(tortoiseStep < totalStep && hareStep < totalStep){
tortoiseStep++;
System.out.println("乌龟跑了"+tortoiseStep+"步...");
boolean isHareSleep = flags[((int)(Math.random()*10))%2];
if(isHareSleep){
System.out.println("兔子睡着了zzzz");
}else{
hareStep += 2;
System.out.println("兔子跑了"+hareStep+"步...");
}
}
}
}
阅读程序,采用实现Runnable接口的方式用多线程实现这个小游戏。下面给出主线程类,补充Tortoise线程类和Hare线程类。
package 作业;
public class TortoiseHareRace1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tortoise tortoise = new Tortoise();
Hare hare = new Hare();
Thread tortoiseThread = new Thread(tortoise);
Thread hareThread = new Thread(hare);
tortoiseThread.start();
hareThread.start();
}
}
class Tortoise implements Runnable {
private int totalStep=10;
private int tortoiseStep = 0;
public Tortoise(){}
private boolean flags =true;
public Tortoise(int totalStep,int tortoiseStep){
this.totalStep=totalStep;
this.tortoiseStep=tortoiseStep;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("龟兔赛跑开始了...");
while (flags) {
if (tortoiseStep < totalStep) {
tortoiseStep+=totalStep;
System.out.println("小乌龟走了"+tortoiseStep+"步了");
} if(totalStep<=10) {
System.out.println("小乌龟到达终点");
flags=false;
}
}
}
}
class Hare implements Runnable {
private int hareStep;
private int tootalStep=10;
private boolean[] flags = {true,false};
public Hare(){}
public Hare(int hareStep,int tootalStep) {
this.hareStep = hareStep;
this.tootalStep= tootalStep;
}
public void run() {
while (flags != null) {
if (hareStep < tootalStep) {
boolean isHareSleep = flags[((int)(Math.random()*10))%2];
if(isHareSleep){//兔子睡觉了
System.out.println("小兔子睡觉啦");
}else{
hareStep += 2;
System.out.println("兔子跑了"+hareStep+"步...");
}
} if(tootalStep<=10) {
System.out.println("兔子到达终点");
}
}
}
}
3.下面的程序是模拟了生产者——消费者问题,生产者生产10个数,消费者依次消费10个数,运行程序,看结果是否正常?存在什么问题?说明原因。使用synchronized, wait, notify解决程序出现的问题。写出修改的部分程序即可。
修改后的程序为:
package 作业;
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Clerk clerk;
public Consumer(Clerk clerk) {
this.clerk = clerk;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("消费者开始消耗整数......");
// 消耗10个整数
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
// 等待随机时间
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 3000));
}
catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
clerk.getProduct();// 从店员处取走整数
}
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable {
private Clerk clerk;
public Producer(Clerk clerk) {
this.clerk = clerk;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println( "生产者开始生产整数......");
// 生产1到10的整数
for(int product = 1; product <= 10; product++) {
try {
Thread.sleep((int) Math.random() * 3000);
}
catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
clerk.setProduct(product); // 将产品交给店员
}
}
}
public class ProductTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clerk clerk = new Clerk();
Thread consumerThread = new Thread(new Consumer(clerk));
Thread producerThread = new Thread(new Producer(clerk));
consumerThread.start();
producerThread.start();
}
}
class Clerk {
private int product = -1; // -1 表示目前没有产品
private int call;
// 这个方法由生产者呼叫
public synchronized void setProduct(int product) {
if (this.product != -1) {
try {
super.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.product = product;
System.out.printf("生产者设定 (%d)%n", call);
getProduct();
this.product = -1;
super.notify();
}
// 这个方法由消费者呼叫
public synchronized int getProduct() {
if (this.product == -1) {
try {
super.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int call = this.product;
System.out.printf("消费者取走 (%d)%n", call);
this.product = -1;
super.notify();
return this.product;
}
}
3.其他需要总结的内容。
- int flag = (int)(Math.random()*2+1);生成1-2的随机数;
2.集合类的特点:
(1)集合类中只容纳对象名(指向对象的地址)
(2)集合类中容纳的元素都是Object类型,一旦把一个对象置入集合类中,它的类信息将丢失
(3)集合类的大小可改变
3.LinkedList类提供了使用双向链表实现数据存储的方法,可按序号检索数据,并能够进行向前或向后遍历 - 集合输出
(1)Iterator:迭代输出,是使用最多的输出方式;
(2)ListIterator:是Iterator的子接口,专门用于输出List中的内容;
foreach:JDK (2)可以输出数组或集合。 - Map中每项都是成对出现的
- 经常使用Properties集合存取应用的配置项
7.线程
(1) 等待:public final void wait()
中断当前线程的运行,使该线程等待。
(2)唤醒:public final void notify()
唤醒第一个等待的线程
(3)唤醒:public final void notifyAll()
唤醒全部等待的线程
(二)实验总结
实验内容:
1.模拟三个老师同时分发80分作业,每个老师相当于一个线程。
程序设计思路:创建三个线程,使用同步方法创建MyThread类
MyThread my=new MyThread();
new Thread(my,"李老师").start();
new Thread(my,"王老师").start();
new Thread(my,"张老师").start();
2.模拟一个银行存款的程序。假设有两个储户都去银行往同一个账户进行存款,一次存100,每人存三次。要求储户每存一次钱,账户余额增加100,并在控制台输出当前账户的余额。
程序设计思路:创建银行类储存钱,创建用户类实现Runnable接口,在测试类中同时启动两个用户的线程
(三)代码托管
- 码云commit历史截图