传统BIO编程
网络编程的基本模型是Client-Server模型,也就是两个进程之间相互通信,其中服务端提供位置信息(绑定的IP地址和监听端口),客户端通过连接操作向服务端监听的端口发起连接请求,通过三次握手建立连接,如果连接成功,双方就可以通过网络套接字(Socket)进行通信。
在传统的BIO编程中,ServerSocket负责绑定IP地址,启动端口监听,Socket负责发起连接请求,连接成功之后,双方通过输入和输出流进行同步阻塞通信。
下面通过TimeServer的一个例子,回顾和熟悉BIO编程
BIO通信模型图
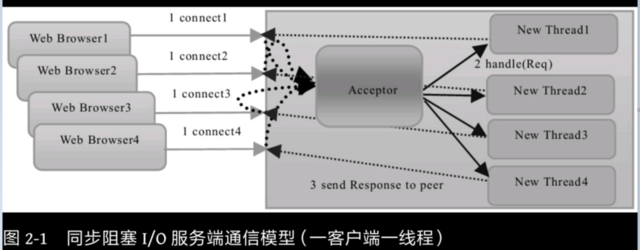
可以看到再改模型中,有一个Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,并为每个请求创建一个新的线程进行处理。
我们可以发现该模型最大问题就是缺乏弹性伸缩能力,服务端和客户端线程个数是1比1的关系。
BIO的TimeServer
package nio.bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* Created by jj on 2018/12/23.
*/
public class TimeServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length >0){
try{
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
}
}
ServerSocket server = null;
try{
server = new ServerSocket(port);
Socket socket = null;
while (true){
socket = server.accept();
new Thread(new TimeServerHandler(socket)).start();
}
}finally {
if (server!= null){
server.close();
server = null;
}
}
}
}
如果没有客户端请求,则阻塞在server.accept操作上,如果有,则创建一个TimeServerHandler的Runnable线程,处理客户端的Socket链路
下面,我们看一下TimeServerHandler
public class TimeServerHandler implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public TimeServerHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
public void run() {
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try{
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(this.socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(this.socket.getOutputStream(),true);
String curentTime = null;
String body = null;
while (true){
body = in.readLine();
if (body == null)
break;
System.out.println("the time server receive order:" + body);
curentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body)?new Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()
).toString():"BAD ORDER";
out.println(curentTime);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (in != null){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (out != null){
out.close();
out = null;
}
if (this.socket !=null){
try {
this.socket.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
this.socket = null;
}
}
}
}
可以看到run中的功能为读取客户端请求,并通过PrintWriter返回给客户端相应。
下面我们看一下客户端的代码
public class TimeClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
}
Socket socket = null;
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try{
socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",port);
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(),true);
out.println("QUERY TIME ORDER");
String resp = in.readLine();
System.out.print(resp);
}finally {
if (out != null){
out.close();
out = null;
}
if (in != null){
in.close();
in = null;
}
if (socket != null){
socket.close();
socket = null;
}
}
}
}