这篇文章的数据库操作方式是使用JPA。
而且是简单的说明,更多的介绍,在本标签下,后续会再说明一些细节。
一:操作数据库起步
1.Spring-Data-Jpa
JPA定义了对象持久化的标准。
目前实现了有Hibernate,TopLink
2.pom添加依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> 4 </dependency> 5 6 <dependency> 7 <groupId>mysql</groupId> 8 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> 9 </dependency>
3.对jps进行配置
1 spring: 2 profiles: 3 active: dev 4 datasource: 5 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 6 url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3308/people?useSSL=false 7 username: root 8 password: 123456 9 jpa: 10 hibernate: 11 ddl-auto: create 12 show-sql: true
4.新建一个people的数据库
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS yiibaidb DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
不然,程序会报未发现数据库。
但是,表不需要新建,这个通过类就可以生成。
5.student的类
可以映射成数据库的字段。
Entity注解表示:类对应一个数据库的一个表。
1 package com.caojun.springboot; 2 3 import javax.persistence.Entity; 4 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; 5 import javax.persistence.Id; 6 7 @Entity 8 public class Student { 9 10 @Id 11 @GeneratedValue 12 private Integer id; 13 private String name; 14 private Integer age; 15 16 public Student(){ 17 18 } 19 20 public Integer getId() { 21 return id; 22 } 23 24 public void setId(Integer id) { 25 this.id = id; 26 } 27 28 public String getName() { 29 return name; 30 } 31 32 public void setName(String name) { 33 this.name = name; 34 } 35 36 public Integer getAge() { 37 return age; 38 } 39 40 public void setAge(Integer age) { 41 this.age = age; 42 } 43 }
6.自动生成数据库
7.注意点
配置文件的ddi-auto:create
意思的每次启动的时候都会把数据库清空。
ddl-auto:update
如果没有表,会自动创建,但是如果里面有数据,就不会清空数据。
二:操作数据的API
1.新建类(继续使用上面的Student.java类)
2.新建接口
1 package com.caojun.springboot; 2 3 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; 4 5 public interface StudentResitory extends JpaRepository<Student,Integer> { 6 }
3.新建controller类
查询数据库中的所有
1 package com.caojun.springboot; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 4 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; 5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 6 7 import java.util.List; 8 9 @RestController 10 public class StudentController { 11 12 @Autowired 13 private StudentResitory studentResitory; 14 15 /** 16 * 查询数据库中的所有 17 * @return 18 */ 19 @GetMapping(value = "/hello") 20 public List<Student> getStuList(){ 21 return studentResitory.findAll(); 22 } 23 }
4.效果
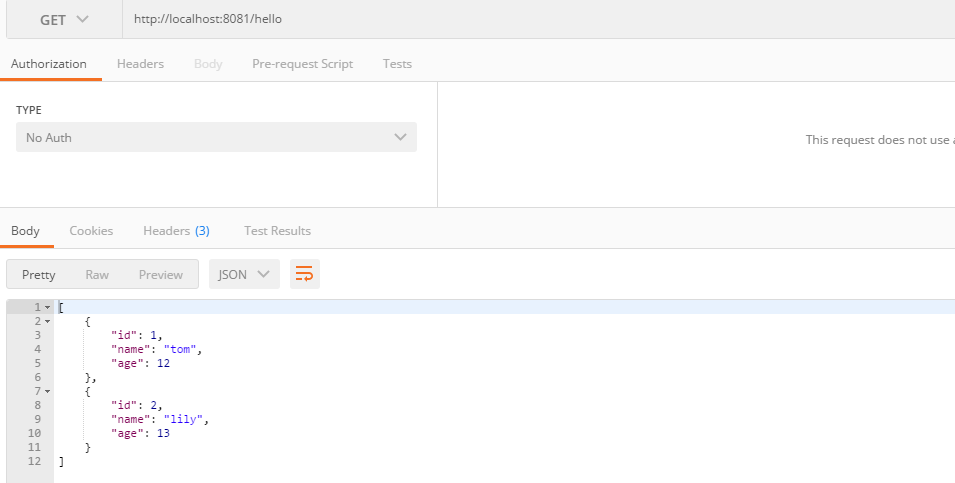
5.添加一个学生记录
1 /** 2 * 添加一个学生记录 3 */ 4 @PostMapping(value = "/hello") 5 public Student addStu(@RequestParam("name") String name,@RequestParam("age") Integer age){ 6 Student stu=new Student(); 7 stu.setName(name); 8 stu.setAge(age); 9 return studentResitory.save(stu); 10 }
6.效果
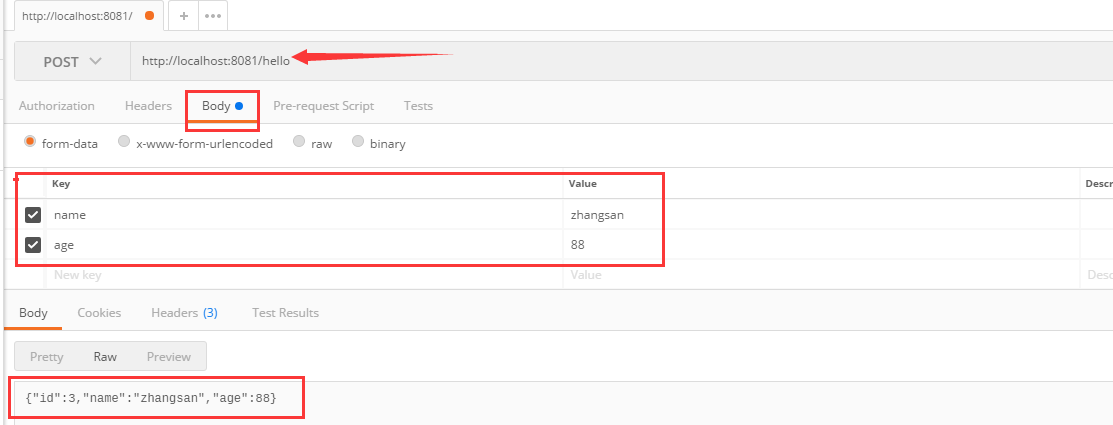
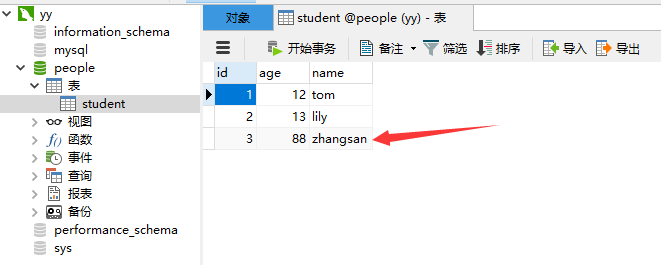
7.查询一个人,根据id
1 /** 2 * 查询一个学生,根据字段id 3 */ 4 @GetMapping(value = "/hello/{id}") 5 public Student getStu(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ 6 return studentResitory.findOne(id); 7 }
8.效果
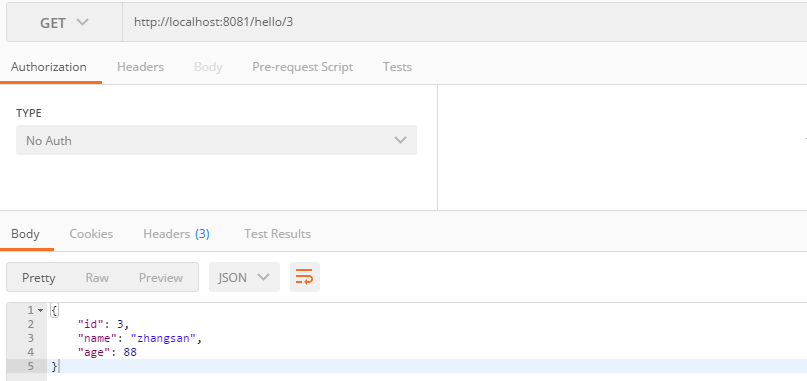
9.更新
1 /** 2 * 更新数据库 3 */ 4 @PutMapping(value = "/hello/{id}") 5 public Student updateStu(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, 6 @RequestParam("name") String name, 7 @RequestParam("age") Integer age ){ 8 Student stu=new Student(); 9 stu.setId(id); 10 stu.setName(name); 11 stu.setAge(age); 12 return studentResitory.save(stu); 13 }
10.效果

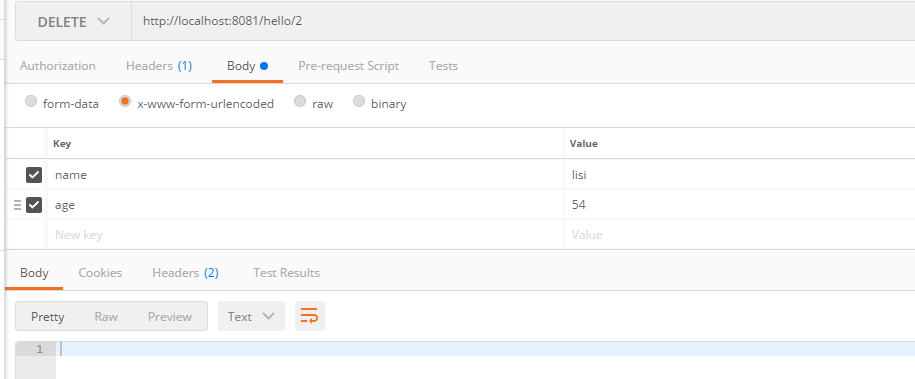
11.删除
1 /** 2 * 删除数据 3 */ 4 @DeleteMapping(value = "/hello/{id}") 5 public void deleteStu(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ 6 studentResitory.delete(id); 7 }
12.效果
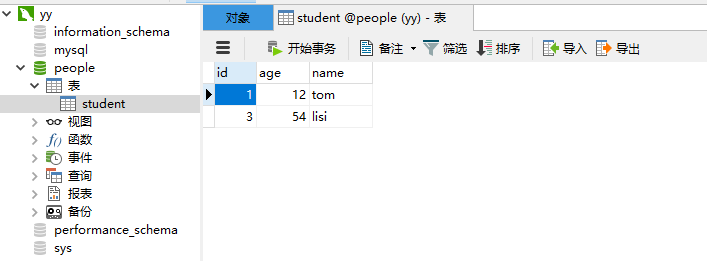
三:扩展
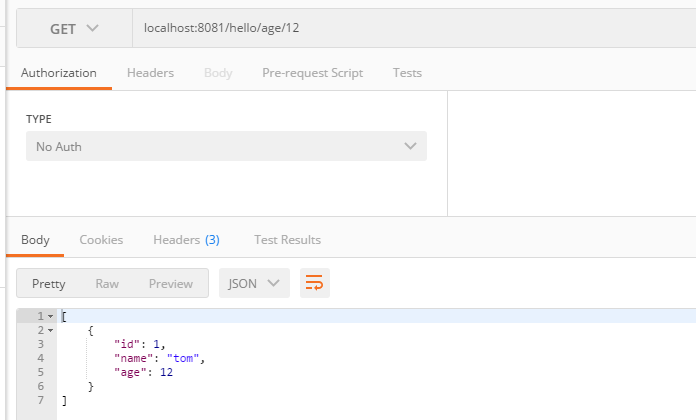
1.通过年龄还来查询
2.扩展接口
这个方法名比较有讲究。
1 package com.caojun.springboot; 2 3 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; 4 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 public interface StudentResitory extends JpaRepository<Student,Integer> { 8 9 //根据年龄来查询数据 10 public List<Student> findByAge(Integer age); 11 }
3.程序
1 /** 2 * 根据年龄进行查询 3 */ 4 @GetMapping(value = "/hello/age/{age}") 5 public List<Student> getStuList(@PathVariable("age") Integer age){ 6 return studentResitory.findByAge(age); 7 }
4.效果