在Angular中可以自定义带参数的管道;只要遵循下面三条规则:
- 利用@pipe装饰器声明管道的名字
- 实现PipeTransform接口
- 如果是全局使用,则 include your pipe in the
declarationsarray of theAppModule; 如果想要局部使用, 则 provide it in theprovidersarray of yourNgModule.
如下:
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'myFilter',
pure: true // default
})
export class MyFilterPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, filterKey: any) {
if (!filterKey['name']) {
return value;
}
return value.filter(item => item.name === filterKey.name && item.sex === filterKey.sex );
}
}
同时,Angular中,pipe分为 pure pipe (纯管道) 和 impure pipe (非纯管道)。纯管道和非纯管道是相对于管道所传的参数(如上例的 filterKey)而言的。如果管道是纯管道,则管道的触发只会针对基本类型的参数的变化或者引用类型引用的变化( a primitive input value (String, Number, Boolean, Symbol) or a changed object reference (Date, Array, Function, Object));然而, 对于非纯管道,不管是基本类型参数的改变还是引用类型内部数据变化(而非引用变化)都可以触发管道。
举例:
html:
<div class="test"> <table class="a-table"> <thead class="a-thead"> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Sex</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody class="a-tbody"> <ng-container *ngFor="let student of students|myFilter: filterObj"> <tr> <td> {{ student.name }}</td> <td> {{ student.sex }}</td> </tr> </ng-container> </tbody> </table> <div class="a-p-20"> <label class="a-form-label">带参的纯管道:过滤male/female</label> <!-- <input class="a-text-input" #filterKey /> --> </div> <div class="a-p-20"> <label class="a-form-label">过滤 name</label> <input class="a-text-input" #name /> </div> <div class="a-p-20"> <label class="a-form-label">过滤 sex</label> <input class="a-text-input" #sex /> </div> <button class="a-btn a-btn-secondary a-btn-lg" (click)="constructFilterObj(name.value, sex.value)">Go Filter</button> </div>
angular ts:
private students: any[]; // 需要被管道处理的数据 private filterObj = Object.create({}); // 对象: 创建一个空对象并作为传给管道的参数, this.students = [ { name:'Tom', sex: 'male' }, { name:'Jerry', sex: 'male' }, { name:'Alice', sex: 'female' }, { name:'Henry', sex: 'male' } ]; }); ............ constructFilterObj(name: string, sex: string) { // 该方法用于构造传给管道的参数 filterObj this.filterObj['name'] = name; this.filterObj['sex'] = sex; }
纯管道:
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'myFilter',
pure: true // default
})
export class MyFilterPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, filterKey: any) {
if (!filterKey['name']) {
return value;
}
return value.filter(item => item.name === filterKey.name && item.sex === filterKey.sex );
}
}
结果:
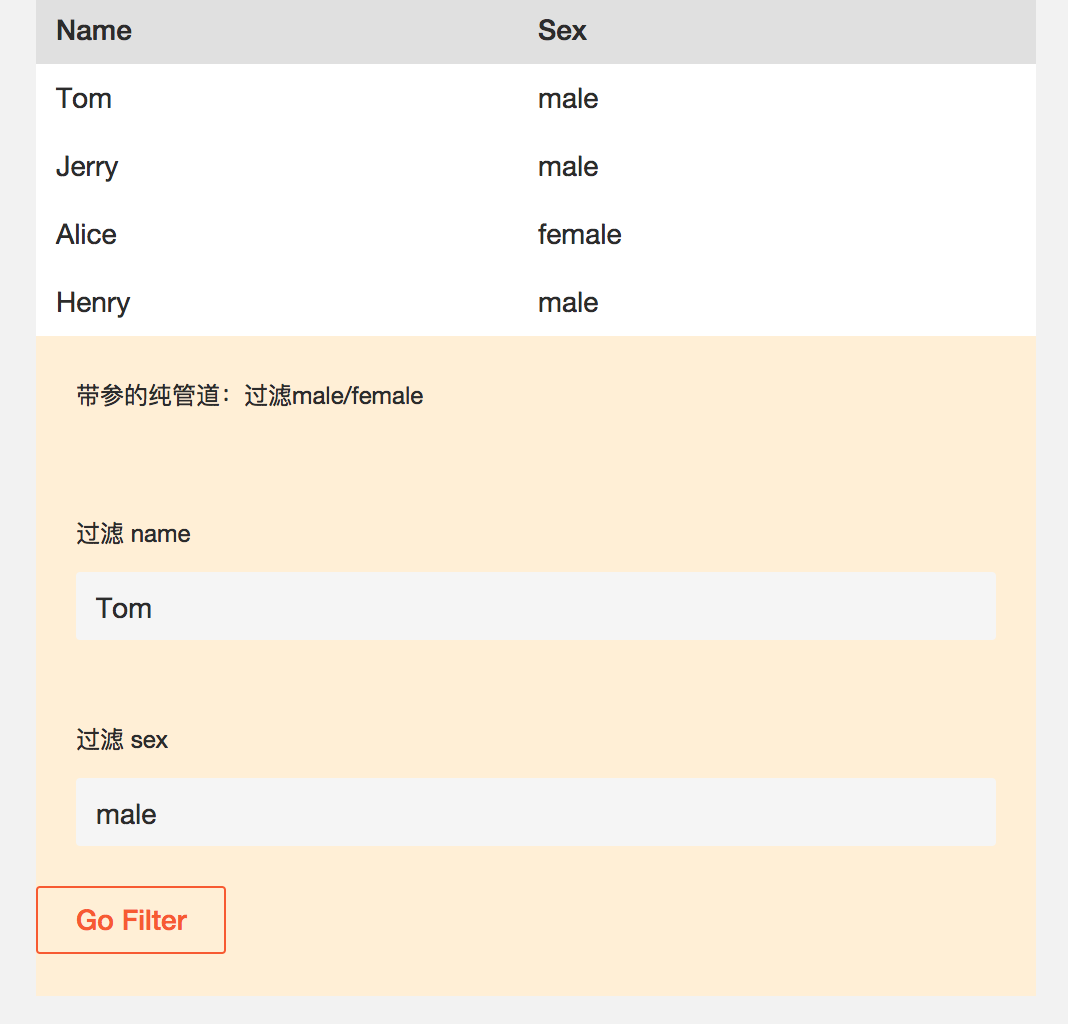
当输入 Tom, male;管道并没有把Tom给筛选出来。原因是: filterObj 初始化是一个空对象 filterObj = Object.create({}); 当点击 Go Filter button, 我们可以看到程序只是更改了filterObj的内容,而非引用。所以,对于纯管道来说,它是检测不到这个输入的变化的,因此数据不会被过滤。
当将该管道改为非纯管道后,过滤就起作用了
非纯管道:
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'myFilter',
pure: false // 非纯管道
})
export class MyFilterPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, filterKey: any) {
if (!filterKey['name']) {
return value;
}
return value.filter(item => item.name === filterKey.name && item.sex === filterKey.sex );
}
}
结果:

可以看到, Tom被过滤出来了