




1 package com.vince; 2 3 public class ThreadDemo1 { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 MyThread mt = new MyThread(); 6 //推荐: 7 MyRunnable mr = new MyRunnable(); 8 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr); 9 10 mt.start();//启动线程 11 t2.start(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 16 /* 17 实现线程的第一种方式:继承thread类 18 */ 19 20 class MyThread extends Thread{ 21 public void run(){ 22 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "-" + i); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 /* 29 实现线程的第二种方式:实现Runnable接口; 30 */ 31 class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ 32 public void run(){ 33 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "-" + i); 35 } 36 } 37 }


1 package com.vince; 2 3 4 /* 5 线程的休眠 6 在当前线程的执行中,暂停指定的毫秒数,释放CPU的时间片 7 */ 8 public class ThreadDemo1 { 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 MyThread mt = new MyThread(); 11 //推荐: 12 MyRunnable mr = new MyRunnable(); 13 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr); 14 15 mt.start();//启动线程 16 t2.start(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 21 /* 22 实现线程的第一种方式:继承thread类 23 */ 24 25 class MyThread extends Thread{ 26 public void run(){ 27 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 28 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "-" + i); 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(500); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 38 /* 39 实现线程的第二种方式:实现Runnable接口; 40 */ 41 class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ 42 public void run(){ 43 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 44 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "-" + i); 45 try { 46 Thread.sleep(500); 47 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 }


1 /* 2 join方法: 3 加入线程,让调用的线程先执行指定时间或执行完毕 4 */ 5 6 7 8 public class ThreadDemo2 { 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 MyRunable2 mr2 = new MyRunable2(); 11 Thread t = new Thread(mr2); 12 t.start(); 13 14 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--"+ i); 16 try { 17 Thread.sleep(300); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 if(i==20){ 22 // 1.1测试join的作用: 23 try { 24 t.join();//让t线程执行完毕 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 // t.interrupt();//中断线程,只是做了一个中断标记 29 } 30 31 } 32 33 } 34 } 35 36 37 class MyRunable2 implements Runnable{ 38 public void run(){ 39 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 40 // 1.2 41 if(Thread.interrupted()){ 42 //测试中断状态,此方法会把中断状态清除 43 break; 44 } 45 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + i); 46 try{ 47 Thread.sleep(300); 48 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 49 e.printStackTrace(); 50 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); 51 } 52 53 } 54 55 56 } 57 }
自定义中断:

1 /* 2 join方法: 3 加入线程,让调用的线程先执行指定时间或执行完毕 4 5 中断线程: 6 1.使用interrupt方法来中断线程,设置一个中断状态(标记) 7 2.自定义标记方法(推荐使用) 8 9 */ 10 11 12 13 public class ThreadDemo2 { 14 public static void main(String[] args){ 15 MyRunable2 mr2 = new MyRunable2(); 16 Thread t = new Thread(mr2); 17 // t.start(); 18 19 MyRunable3 mr3 = new MyRunable3(); 20 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr3); 21 t2.start(); 22 23 24 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 25 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--"+ i); 26 try { 27 Thread.sleep(300); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 if(i==20){ 32 // 1.1测试join的作用: 33 try { 34 t.join();//让t线程执行完毕 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 // t.interrupt();//中断线程,只是做了一个中断标记 39 mr3.flag = false; 40 } 41 42 } 43 44 } 45 } 46 47 48 class MyRunable2 implements Runnable{ 49 public void run(){ 50 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 51 // 1.2 52 if(Thread.interrupted()){ 53 //测试中断状态,此方法会把中断状态清除 54 break; 55 } 56 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + i); 57 try{ 58 Thread.sleep(300); 59 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); 62 } 63 64 } 65 66 67 } 68 } 69 70 class MyRunable3 implements Runnable{ 71 public boolean flag = true; 72 public MyRunable3(){ 73 flag = true; 74 } 75 public void run(){ 76 int i = 0; 77 while (flag){ 78 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=====" + (i++)); 79 try { 80 Thread.sleep(300); 81 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 82 e.printStackTrace(); 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 }


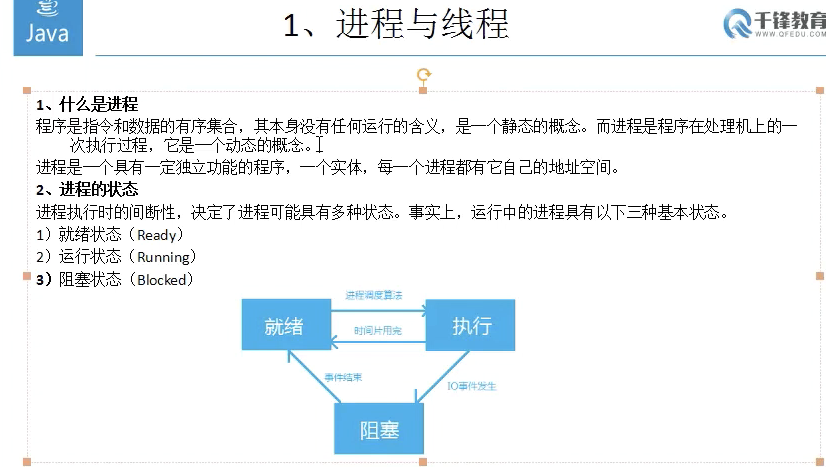
1 public class ThreadDemo3 { 2 public static void main(String [] args){ 3 MyRunnable4 mr4 = new MyRunnable4(); 4 Thread t = new Thread(mr4); 5 // 线程可以分成守护线程和用户线程,当进程中没有用户线程时,JVM会退出 6 t.setDaemon(true);//把线程设置为守护线程 7 t.start(); 8 9 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 10 System.out.println("main--:" + i); 11 try { 12 Thread.sleep(200); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 19 } 20 } 21 22 class MyRunnable4 implements Runnable{ 23 public void run(){ 24 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 25 System.out.println("--" + i); 26 try { 27 Thread.sleep(500); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }

1 public class ThreadDemo3 { 2 public static void main(String [] args){ 3 MyRunnable4 mr4 = new MyRunnable4(); 4 Thread t = new Thread(mr4); 5 // 线程可以分成守护线程和用户线程,当进程中没有用户线程时,JVM会退出 6 t.setDaemon(true);//把线程设置为守护线程 7 t.start(); 8 9 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 10 System.out.println("main--:" + i); 11 try { 12 Thread.sleep(200); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 if(i==5){ 17 Thread.yield();//让出本次cpu执行的时间片 18 } 19 } 20 21 22 } 23 } 24 25 class MyRunnable4 implements Runnable{ 26 public void run(){ 27 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 28 System.out.println("--" + i); 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(500); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 }
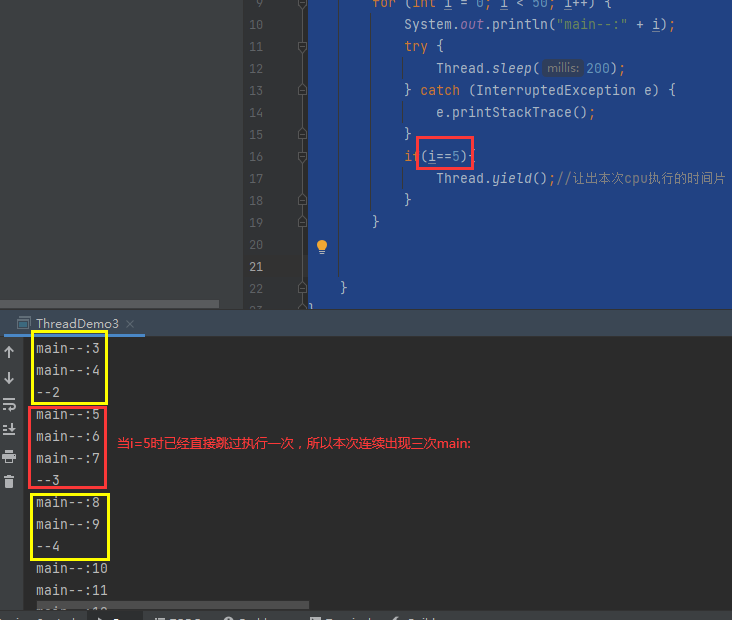



1 public class ThreadDemo4 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 MyRunnable5 mr5 = new MyRunnable5(); 5 6 Thread t1 = new Thread(mr5); 7 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr5); 8 t1.start(); 9 t2.start(); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{ 14 //两个线程共享一个数据:ticket 15 private int ticket = 10;//售票 16 public void run(){ 17 for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) { 18 if(ticket>0){ 19 ticket--; 20 21 try { 22 Thread.sleep(1000); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" +ticket +"张"); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------

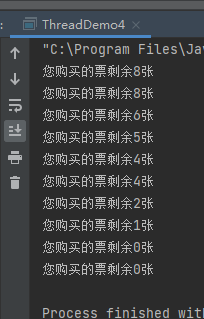
1 /* 2 1.多线程共享数据时,会发生线程不安全的情况 3 2.多线程共享数据必须使用同步 4 */ 5 6 7 8 public class ThreadDemo4 { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args){ 11 MyRunnable5 mr5 = new MyRunnable5(); 12 13 Thread t1 = new Thread(mr5); 14 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr5); 15 t1.start(); 16 t2.start(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{ 21 //两个线程共享一个数据:ticket 22 private int ticket = 10;//售票 23 private Object obj = new Object(); 24 public void run(){ 25 for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) { 26 synchronized (obj) { 27 if (ticket > 0) { 28 ticket--; 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(1000); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 }
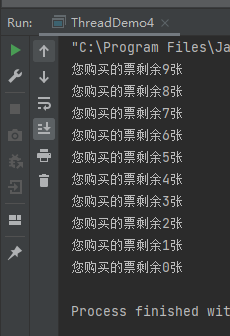


1 /* 2 1.多线程共享数据时,会发生线程不安全的情况 3 2.多线程共享数据必须使用同步 4 */ 5 6 7 public class ThreadDemo4 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 MyRunnable5 mr5 = new MyRunnable5(); 11 12 Thread t1 = new Thread(mr5); 13 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr5); 14 t1.start(); 15 t2.start(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 //class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{ 20 // //两个线程共享一个数据:ticket 21 // private int ticket = 10;//售票 22 // private Object obj = new Object();//同步锁 23 // public void run(){ 24 // for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) { 25 // synchronized (this) { 26 // if (ticket > 0) { 27 // ticket--; 28 // try { 29 // Thread.sleep(1000); 30 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { 31 // e.printStackTrace(); 32 // } 33 // System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 34 // } 35 // } 36 // } 37 // } 38 39 40 class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable { 41 //两个线程共享一个数据:ticket 42 private int ticket = 10;//售票 43 private Object obj = new Object();//同步锁 44 45 public void run() { 46 for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) { 47 // if (ticket > 0) { 48 // synchronized (this) { 49 // if (ticket > 0) { 50 // ticket--; 51 // try { 52 // Thread.sleep(1000); 53 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { 54 // e.printStackTrace(); 55 // } 56 // System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 57 // } 58 method(); 59 // } 60 } 61 } 62 // 同步方法:同步的对象是当前对象(this) 63 private synchronized void method() { 64 if (ticket >0) { 65 ticket--; 66 try { 67 Thread.sleep(1000); 68 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 69 e.printStackTrace(); 70 } 71 System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 72 } 73 } 74 75 76 }

1 /* 2 1.多线程共享数据时,会发生线程不安全的情况 3 2.多线程共享数据必须使用同步 4 3.实现同步的三种方法: 5 1.使用同步代码块 6 2.使用同步方法 7 3.使用Lock(更灵活的代码控制) 8 */ 9 10 11 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 12 13 public class ThreadDemo4 { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 MyRunnable5 mr5 = new MyRunnable5(); 17 18 Thread t1 = new Thread(mr5); 19 Thread t2 = new Thread(mr5); 20 t1.start(); 21 t2.start(); 22 } 23 } 24 25 //class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{ 26 // //两个线程共享一个数据:ticket 27 // private int ticket = 10;//售票 28 // private Object obj = new Object();//同步锁 29 // public void run(){ 30 // for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) { 31 // synchronized (this) { 32 // if (ticket > 0) { 33 // ticket--; 34 // try { 35 // Thread.sleep(1000); 36 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 // e.printStackTrace(); 38 // } 39 // System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 40 // } 41 // } 42 // } 43 // } 44 45 46 class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable { 47 //互斥锁 48 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 49 //两个线程共享一个数据:ticket 50 private int ticket = 10;//售票 51 private Object obj = new Object();//同步锁 52 53 public void run() { 54 for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) { 55 // if (ticket > 0) { 56 // synchronized (this) { 57 // if (ticket > 0) { 58 // ticket--; 59 // try { 60 // Thread.sleep(1000); 61 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { 62 // e.printStackTrace(); 63 // } 64 // System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 65 // } 66 method(); 67 // } 68 } 69 } 70 71 // 同步方法:同步的对象是当前对象(this) 72 private synchronized void method() { 73 if (ticket >0) { 74 ticket--; 75 try { 76 Thread.sleep(1000); 77 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 78 e.printStackTrace(); 79 } 80 System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 81 } 82 } 83 84 //Lock实现同步 85 private synchronized void method2() { 86 lock.lock();//锁 87 try{ 88 if (ticket >0) { 89 ticket--; 90 try { 91 Thread.sleep(1000); 92 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 93 e.printStackTrace(); 94 } 95 System.out.println("您购买的票剩余" + ticket + "张"); 96 } 97 }finally{ 98 lock.unlock();//释放锁 99 } 100 101 } 102 103 }



1 package com.vince; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by vince on 2017/6/5. 5 * 线程死锁:在一个同步方法中调用了另一个对象的同步方法,可能产生死锁 6 * 7 */ 8 public class DeadThreadDemo { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 new DeadThread(); 12 } 13 14 } 15 16 //顾客 17 class Customer{ 18 public synchronized void say(Waiter w){ 19 System.out.println("顾客说:先吃饭再买单!"); 20 w.doService(); 21 } 22 23 public synchronized void doService(){ 24 System.out.println("同意了,买完单再吃饭!"); 25 } 26 } 27 //服务员 28 class Waiter{ 29 public synchronized void say(Customer c){ 30 System.out.println("服务员说:先买单再吃饭!"); 31 c.doService(); 32 } 33 public synchronized void doService(){ 34 System.out.println("同意了,吃完饭再买单!"); 35 } 36 } 37 38 39 //死锁线程 40 class DeadThread implements Runnable{ 41 Customer c = new Customer(); 42 Waiter w = new Waiter(); 43 public DeadThread(){ 44 new Thread(this).start(); 45 w.say(c); 46 } 47 @Override 48 public void run() { 49 c.say(w); 50 } 51 }

1 package com.vince; 2 3 public class ProducterCustomerDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Food food = new Food(); 6 Producter p = new Producter(food); 7 Customers c = new Customers(food); 8 Thread t1 = new Thread(p); 9 Thread t2 = new Thread(c); 10 t1.start(); 11 t2.start(); 12 13 } 14 } 15 16 /* 17 消费者 18 */ 19 class Customers implements Runnable{ 20 private Food food; 21 public Customers(Food food){ 22 this.food = food; 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public void run() { 27 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 28 food.get(); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 33 34 /* 35 生产者 36 */ 37 class Producter implements Runnable{ 38 private Food food; 39 40 public Producter(Food food){ 41 this.food = food; 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public void run() { 46 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 47 if (i%2 ==0){ 48 food.set("锅包肉","酸甜口味"); 49 }else { 50 food.set("佛跳墙","大补"); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 57 class Food{ 58 private String name; 59 private String desc; 60 private boolean flag = true;//true表示可以生产,flase表示可以消费 61 public Food() { 62 63 } 64 65 66 /** 67 * 生产产品 68 * @return 69 */ 70 71 public synchronized void set(String name,String desc){ 72 this.setName(name); 73 try { 74 Thread.sleep(500); 75 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 76 e.printStackTrace(); 77 } 78 this.setDesc(desc); 79 } 80 81 /** 82 * 消费产品 83 */ 84 public synchronized void get(){ 85 try { 86 Thread.sleep(500); 87 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 88 e.printStackTrace(); 89 } 90 System.out.println(this.getName()+"->"+this.getDesc()); 91 } 92 93 94 public String getDesc() { 95 return desc; 96 } 97 98 public void setDesc(String desc) { 99 this.desc = desc; 100 } 101 102 103 104 public String getName() { 105 return name; 106 } 107 108 public void setName(String name) { 109 this.name = name; 110 } 111 112 @Override 113 public String toString() { 114 return "Food{" + 115 "name='" + name + '\'' + 116 ", desc='" + desc + '\'' + 117 '}'; 118 } 119 120 public Food(String name,String desc) { 121 this.name = name; 122 this.desc = desc; 123 } 124 }
