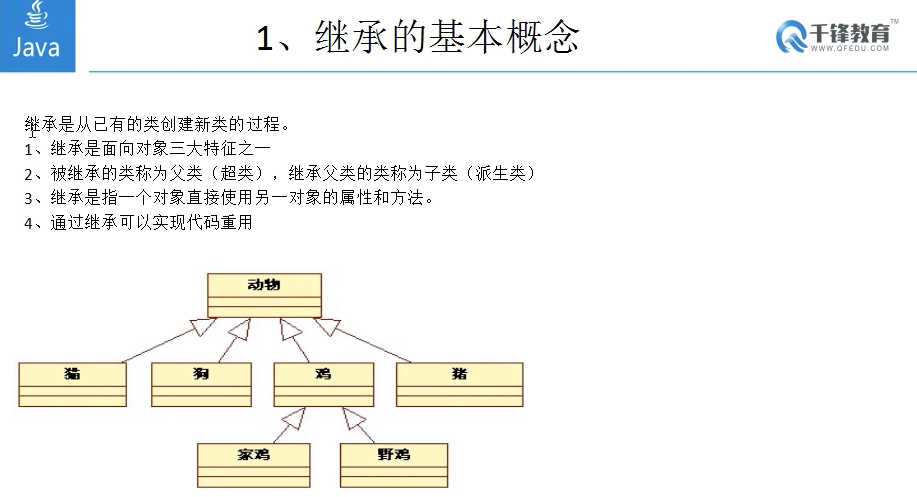



1 /** 2 继承:继承是从已有的类创建新类的过程。 3 继承一个父类,只能继承非私有的数据(属性和方法) 4 protected访问权限修饰符,在继承关系中使用,在父类中使用protected修饰的属性或方法可以被子类继承 5 创建子类对象时,父类的构造方法也会被调用,为什么? 6 因为子类要使用到父类的数据,那么就要通过父类的构造方法来初始化数据 7 //如果创建子类对象时使用默认的构造方法,那么父类的默认构造方法也会被调用 8 如果创建子类对象时会调用父类的默认构造方法 9 10 当父类中没有无参构造方法时,子类必须显示的调用父类的带参构造方法,怎么调用呢? 11 可以在子类中显示的使用super(...)调用父类的构造方法,只能出现在第一句 12 13 面试题 :overloading与overriding的区别? 14 overloading:方法的重载,发生在同一个类中,方法名相同,参数列表不同,返回值无关。 15 overriding:方法的重写,发生在子父类中,方法名相同,参数列表相同,返回值相同,子类的访问修饰符要大于或等于父类 16 的访问修饰符,子类的异常声明必须小于或等于父类的异常声明。如果方法被private,static,final修饰,那么不能被重写 17 18 */ 19 public class Test1{ 20 public static void main(String[] args){ 21 22 HomeDog homeDog = new HomeDog("旺财"); 23 homeDog.print(); 24 homeDog.eat(); 25 26 HuskyDog hd = new HuskyDog(); 27 hd.eat(); 28 29 } 30 } 31 32 class Dog{ 33 protected String name; 34 private String sex; 35 public Dog(String name,String sex){ 36 this.name = name; 37 this.sex = sex; 38 System.out.println("我是Dog的构造方法"); 39 } 40 protected void eat(){ 41 System.out.println("吃饭"); 42 } 43 } 44 class HomeDog extends Dog{ 45 public HomeDog(String name){ 46 super(name,"公");//只能在第一句 47 System.out.println("我是HomeDog的构造方法"); 48 } 49 protected void print(){ 50 //super.属性 表示调用父类的属性,如果是继承过来的属性,那么super可以省略 51 System.out.println(super.name+"我是一只家狗,wangwang"); 52 } 53 //重写父类的方法 54 public void eat(){ 55 super.eat();//调用父类的方法 56 System.out.println("我是家狗,我喜欢吃骨头"); 57 } 58 59 } 60 61 class HuskyDog extends Dog{ 62 public HuskyDog(){ 63 super("哈士奇","母"); 64 System.out.println("我是HuskyDog的构造方法"); 65 } 66 public void show(){ 67 System.out.println(name+"我是husky,我能跳舞"); 68 } 69 public void eat(){ 70 System.out.println("我是husky,我喜欢吃鸡肝"); 71 } 72 }



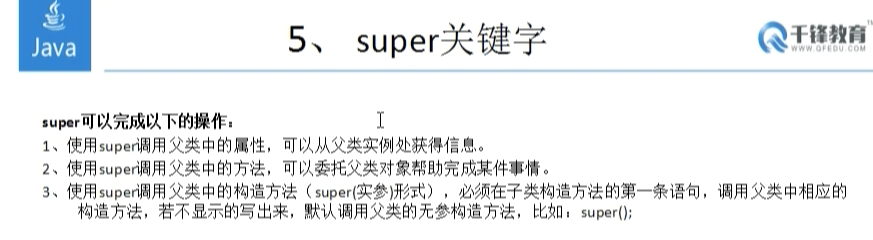




1 /** 2 final关键字 3 1、使用final声明一个属性,就是常量,常量的命名规则建议使用全大写,常量必须在定义时或在构造器中初始化 4 2、使用final声明的方法,不能被子类重写,只能被继承 5 3、使用final关键字声明一个类,该类就转变为最终类,没有子类的类,fianl修饰的类无法被继承。 6 */ 7 public class Test3{ 8 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 11 System.out.println(Constant.PERSON_NUM); 12 13 FinalClass fc = new FinalClass(); 14 fc.setLength(10); 15 } 16 } 17 18 //常量类(工具类):在实际项目开发中,常量类通常用于定义项目中一些公共的,不变的,数据 19 20 final class Constant{ 21 public static final int PERSON_NUM = 10; //人数 22 public static final String SERVER_ROOT_URL = "http://www.baidu.com"; 23 public static final String CACHE_PATH = "data_cache"; 24 25 } 26 27 class FinalClass{ 28 public final int DAY_NUMBER;//工作天数 29 30 public FinalClass(){ 31 DAY_NUMBER = 22; 32 } 33 34 public final void print(){ 35 System.out.println("我是final方法"); 36 } 37 38 public void setLength(final int size){ 39 final int x = 20; 40 size++; 41 System.out.println(size); 42 } 43 } 44 45 class SubClass extends FinalClass{ 46 /*public void print(){ 47 System.out.println("我是final方法"); 48 }*/ 49 }
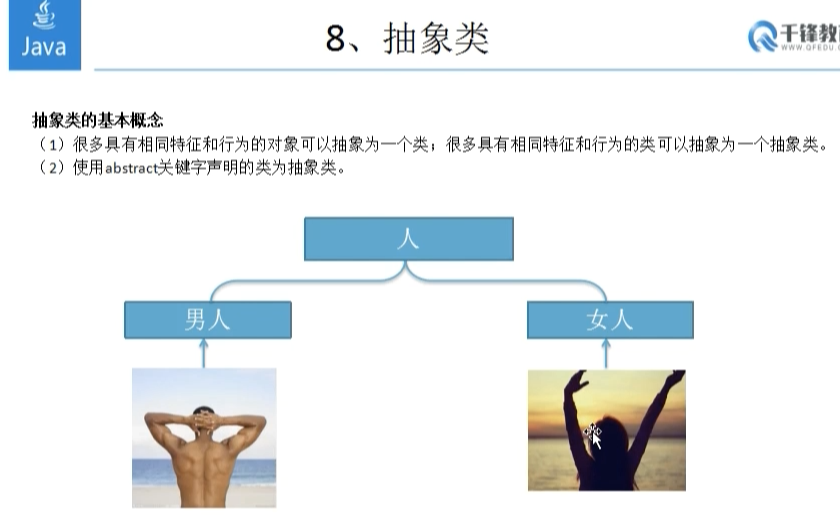



1 /** 2 抽象类:用abstract关键字声明的类称为抽象类, 3 很多具有相同特征和行为的对象可以抽象为一个类, 4 很多具有相同特征和行为的类可以抽象为一个抽象类 5 6 1、抽象类可以没有抽象方法,有抽象方法的类必须是抽象类 7 2、非抽象类继承抽象类必须实现所有抽象方法 8 3、抽象类可以继承抽象类,可以不实现父类抽象方法。 9 4、抽象类可以有方法实现和属性 10 5、抽象类不能被实例化 11 6、抽象类不能声明为final 12 7、抽象类可以有构造方法 13 14 15 */ 16 public class Test4{ 17 public static void main(String[] args){ 18 Man man = new Man(); 19 man.move(); 20 man.eat(); 21 22 Women women = new Women(); 23 women.move(); 24 women.eat(); 25 26 //Animal a = new Animal(); 27 28 } 29 } 30 31 abstract class Animal{ 32 public abstract void move();//方法的声明,抽象方法只有声明,没有实现 33 34 } 35 36 abstract class Person extends Animal{ 37 public abstract void eat(); 38 public void sleep(){ 39 System.out.println("睡觉"); 40 } 41 } 42 43 //继承抽象类的具体类必须实现所有抽象方法 44 class Man extends Person{ 45 46 public void move(){ 47 System.out.println("我是男人,我爱跑步"); 48 } 49 public void eat(){ 50 System.out.println("我是男人,我爱吃肉"); 51 } 52 } 53 54 class Women extends Person{ 55 public void move(){ 56 System.out.println("我是女人,我爱逛街"); 57 } 58 public void eat(){ 59 System.out.println("我是女人,我爱吃香蕉"); 60 } 61 }




 \
\

1 /* 2 * OO设计原则: 3 * 4 * 1、面向接口编程(面向抽象编程) 5 * 6 * 2、封装变化 ex:save方法是可以变的,单独拿出来封装 7 * 8 * 3、多用组合,少用继承;继承的多那么重写的方法就会很多,继承少慎用 9 * 10 * 11 * 12 * 把可变的行为抽象出来,这样的好处是这些行为可以在真正使用时 13 * 14 */ 15 16 public class Test8 { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 BaseService user = new UserService(); 19 //user.setISave(new FileSave()); 20 user.setISave(new NetSave()); 21 user.add("user"); 22 } 23 } 24 25 //把可变的行为抽象出来,定义一系列的算法 26 //↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓111111111111↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓ 27 //========================================================== 28 interface ISave{ 29 //可变的是save,把可变的东西单独拿出来封装,这就是封装变法 30 public void save(String data); 31 } 32 33 class FileSave implements ISave{ 34 public void save(String data) { 35 System.out.println("把数据保存到文件中..." + data); 36 } 37 } 38 39 class NetSave implements ISave{ 40 public void save(String data) { 41 System.out.println("把数据保存到网络上..." + data); 42 } 43 } 44 //============================================================ 45 46 //↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓22222222222222↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓ 47 abstract class BaseService{ 48 //BaseService来组合ISave 49 //把接口作为类的属性来定义,然后提供一个set方法或者是构造方法都行 50 private ISave iSave; 51 public void setISave(ISave iSave) { 52 this.iSave = iSave; 53 } 54 55 public void add(String data) { 56 System.out.println("检查数据合法性..."); 57 iSave.save(data); 58 System.out.println("数据保存完毕..."); 59 } 60 } 61 62 class UserService extends BaseService{ 63 //UserService到main里面 64 }

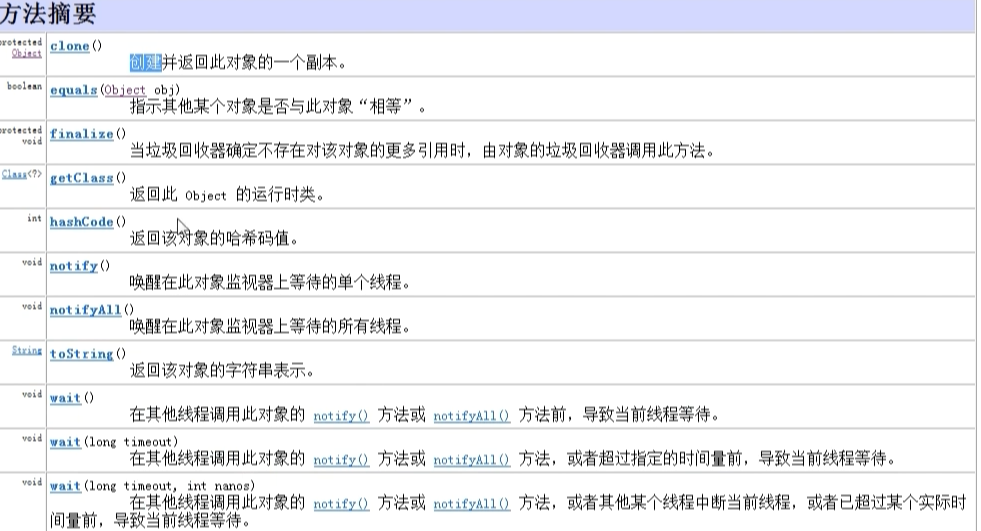



1 /** 2 Object对象 3 */ 4 public class Test9{ 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 Student s = new Student(1,"飞飞",18); 7 System.out.println(s); 8 Student s2 = new Student(1,"飞飞",18); 9 boolean b = s.equals(s2); 10 System.out.println("student equals "+b); 11 12 String str1 = new String("备备"); 13 String str2 = new String("备备"); 14 System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); 15 16 System.out.println(s.getClass()==s2.getClass()); 17 18 19 } 20 } 21 22 class Student{ 23 private String name; 24 private int sid; 25 private int age; 26 public Student(){} 27 public Student(int sid,String name,int age){ 28 this.sid = sid; 29 this.name = name; 30 this.age = age; 31 } 32 //重写Object类中的toString方法 33 public String toString(){ 34 return "sid="+sid+",name="+name+",age="+age; 35 } 36 37 //重写equals方法,来实现两个对象的比较 38 public boolean equals(Object obj){ 39 if(this==obj){ 40 return true; 41 } 42 if(obj instanceof Student){ 43 Student s = (Student)obj; 44 if(!this.name.equals(s.name)){ 45 return false; 46 } 47 if(this.sid!=s.sid){ 48 return false; 49 } 50 if(this.age!=s.age){ 51 return false; 52 } 53 return true; 54 } 55 return false; 56 } 57 }

1 /* public class Test10{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 //使用者和被使用者两者之间,耦合,产生了依赖,当 被使用者 改变时,会影响使用者 4 //使用工厂模式来降低两者之间的依赖 5 Product phone = new Phone(); 6 phone.work(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 11 interface Product{ 12 public void work(); 13 } 14 15 class Phone implements Product{ 16 public void work(){ 17 System.out.println("手机开始工作..."); 18 } 19 } 20 21 class Computer implements Product{ 22 public void work(){ 23 System.out.println("电脑开始工作...") 24 } 25 } */ 26 27 //简单的工厂设计模式: 28 29 public class Test10{ 30 public static void main(String[] args){ 31 //使用者和被使用者两者之间,耦合,产生了依赖,当 被使用者 改变时,会影响使用者 32 //使用工厂模式来降低两者之间的依赖 33 //Product phone = new Phone(); 34 Product phone = ProductFactory.getProduct("phone"); 35 if(null!=phone){ 36 phone.work(); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 //工厂类: 42 class ProductFactory{ 43 public Product getProduct(String name){ 44 if("phone".equals(name)){ 45 return new Phone(); 46 }else if("computer".equals(name)){ 47 return new Computer(); 48 }else{ 49 return null; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 54 interface Product{ 55 public void work(); 56 } 57 58 class Phone implements Product{ 59 public void work(){ 60 System.out.println("手机开始工作..."); 61 } 62 } 63 64 class Computer implements Product{ 65 public void work(){ 66 System.out.println("电脑开始工作...") 67 } 68 }

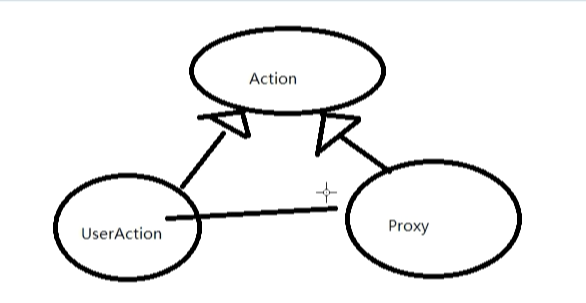
1 /** 2 代理模式(Proxy):为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。 3 代理模式说白了就是“真实对象”的代表,在访问对象时引入一定程度的间接性, 4 因为这种间接性可以附加多种用途。 5 6 */ 7 public class Test11{ 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 Action userAction = new UserAction(); 10 ActionProxy proxy = new ActionProxy(userAction); 11 proxy.doAction(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class ActionProxy implements Action{ 16 17 private Action target;//被代理的对象 18 19 public ActionProxy(Action target){ 20 this.target = target; 21 } 22 23 //执行操作 24 public void doAction(){ 25 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 26 27 target.doAction();//执行真正的业务 28 29 30 long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 31 System.out.println("共耗时:"+(endTime-startTime)); 32 } 33 } 34 35 interface Action{ 36 public void doAction(); 37 } 38 39 class UserAction implements Action{ 40 public void doAction(){ 41 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ 42 System.out.println("用户开始工作..."); 43 } 44 45 } 46 }
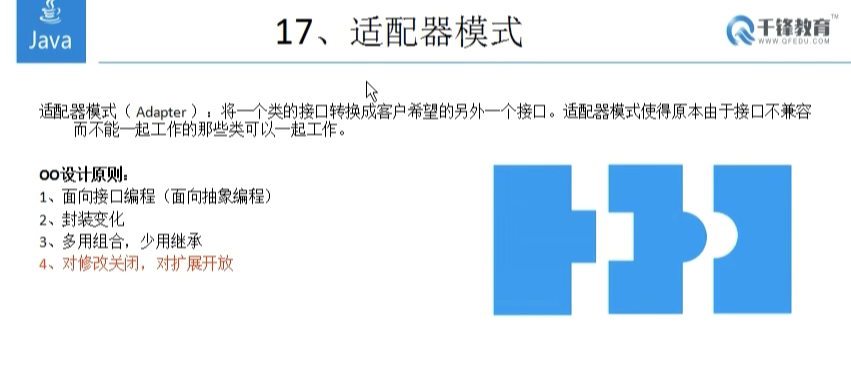
1 /* public class Test12{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 PowerA powerA = new PowerA(); 4 work(powerA); 5 } 6 7 public static void work(PowerA a){ 8 System.out.println("正在连接..."); 9 a.insert(); 10 System.out.println("工作结束..."); 11 } 12 } 13 14 interface PowerA{ 15 public void insert(); 16 } 17 18 class PowerAImpl implements PowerA{ 19 public void insert(){ 20 System.out,println("电源A开始工作"); 21 } 22 } */ 23 24 //================================================== 25 26 public class Test12{ 27 public static void main(String[] args){ 28 PowerA powerA = new PowerAImpl(); 29 //work(powerA); 30 31 PowerB powerB = new PowerAImpl(); 32 //work(powerB); 33 Adapter adapter = new Adapter(powerB); 34 work(adapter); 35 36 } 37 38 public static void work(PowerA a){ 39 System.out.println("正在连接..."); 40 a.insert(); 41 System.out.println("工作结束..."); 42 } 43 } 44 45 //适配器 46 interface Animal{ 47 public void sing(); 48 public void cry(); 49 public vodi run(); 50 public void swim(); 51 } 52 53 abstract class AnimalFunction{ 54 public void sing(){} 55 public void cry(){} 56 public vodi run(){} 57 public void swim(){} 58 } 59 60 61 class Dog extends AnimalFunction{ 62 //class Dog implements Animal{ 63 public void sing(){} 64 public void cry(){} 65 public vodi run(){ 66 System.out.println("我是疯狗,疯狂的跑"); 67 } 68 public void swim(){} 69 } 70 71 72 //适配器:==================================== 73 class Adapter implements PowerA{ 74 private PowerB powerB; 75 public Adapter(PowerB powerB){ 76 this.powerB = powerB; 77 } 78 public void insert(){ 79 powerB.connect(); 80 } 81 } 82 //=========================================== 83 84 interface PowerB{ 85 public void connect(); 86 } 87 class PowerBImpl implements PowerB{ 88 public void connect(){ 89 System.out.println("电源B开始工作"); 90 } 91 } 92 93 interface PowerA{ 94 public void insert(); 95 } 96 97 class PowerAImpl implements PowerA{ 98 public void insert(){ 99 System.out,println("电源A开始工作"); 100 } 101 }

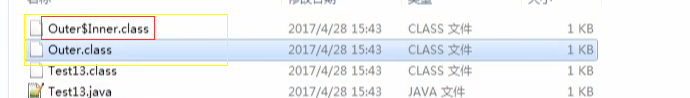
 自动生成两个class文件
自动生成两个class文件
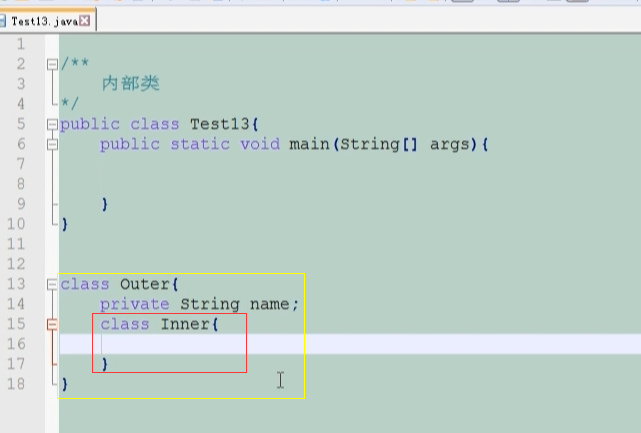
1 /* 2 内部类 3 1、成员内部类:直接在类中定义的类 4 2、方法内部类:在一个类中的方法内定义一个类 5 (1)方法内部类只能在定义该内部类的方法内实例化,不可以在此方法外对其实例化 6 (2)方法内部类对象不能使用该内部类所在方法的非final局部变量。 7 3、静态内部类,在类中定义一个静态修饰的内部类, 8 静态的含义是该内部类可以像其他静态成员一样,没有外部类对象时,也能够访问它。 9 静态嵌套类仅能访问外部类的静态成员和方法。 10 4、匿名内部类就是没有名字的内部类。 11 匿名内部类的三种情况: 12 (1)继承式的匿名内部类 13 (2)接口式的匿名内部类 14 (3)参数式的匿名内部类 15 //*/// 16 17 /* public class Test13{ 18 public static void main(String[] args){ 19 20 Outer outer = new Outer(); 21 //在外部创建成员内部类的实例,因为成员内部类需要依赖外部类的对象; 22 //通常情况下,我们不建议这样来实例化内部类的对象↓ 23 Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner(); 24 inner.print(); 25 26 } 27 } 28 29 class Outer{ 30 31 private String name; 32 33 //成员内部类 34 class Inner{ 35 public void print(){ 36 System.out.println("inner"); 37 } 38 } 39 40 } */ 41 42 43 //========================================================================= 44 public class Test13{ 45 public static void main(String[] args){ 46 47 Outer outer = new Outer(); 48 //在外部创建成员内部类的实例,因为成员内部类需要依赖外部类的对象; 49 //通常情况下,我们不建议这样来实例化内部类的对象↓ 50 /* Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner(); 51 inner.print(); */ 52 53 //改进:↓ 54 outer.innerPrint(); 55 } 56 } 57 58 class Outer{ 59 60 private String name; 61 //建议再外部类中定义一个方法,对外提供访问内部类的接口: 62 //改进:↓ 63 public void innerPrint(){ 64 Inner inner = new Inner(); 65 inner.print(); 66 } 67 68 //成员内部类 69 //改进:↓本来是class Inner变成私有的:private class Inner 70 private class Inner{ 71 public void print(){ 72 System.out.println("inner"); 73 } 74 } 75 76 }




