1. 概要
回溯算法实际上一个类似枚举的搜索尝试过程,主要是在搜索尝试过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。回溯法是一种选优搜索法,按选优条件向前搜索,以达到目标。但当探索到某一步时,发现原先选择并不优或达不到目标,就退回一步重新选择,这种走不通就退回再走的技术为回溯法,而满足回溯条件的某个状态的点称为“回溯点”。许多复杂的,规模较大的问题都可以使用回溯法,有“通用解题方法”的美称。
2. 原理
我们通过皇后问题来讲解回溯算法。
回溯算法经典案例皇后问题:
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的n皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个明确的n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例: 输入: 4
// 解法 1 // 解法 2

解释: 4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
回溯算法原理图解:

如何判断皇后是否会被攻击: 横排,竖排好判断,对角线如何判断
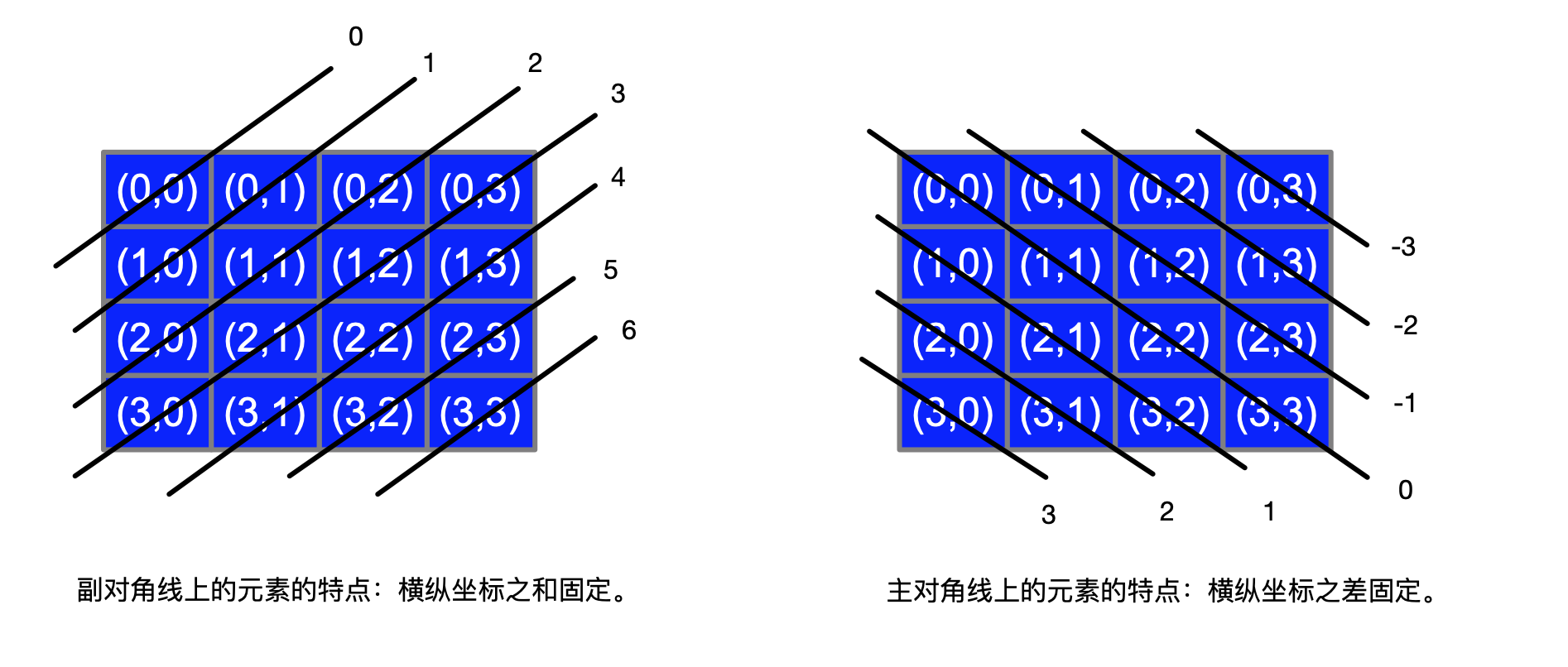
根据图解找到对角线规律。
3 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Subject98 { //竖排被占登记,用于判断是否能够被竖排攻击 int rows[]; // // "从左到右对角线" 登记,用于判断是否能够被竖排攻击 int hills[]; // "从右到左对角线" 登记,用于判断是否能够被竖排攻击 int dales[]; int n; // output List<List<String>> output = new ArrayList(); // 皇后的位置 int queens[]; public static void main(String[] args) { List<List<String>> listList = new Subject98().solveNQueens(6); System.out.println(listList); } /** * 判断该位置是否会被攻击 * @param row * @param col * @return */ public boolean isNotUnderAttack(int row, int col) { int res = rows[col] + hills[row - col + n - 1] + dales[row + col]; return (res == 0) ? true : false; } /** * 将皇后放入该位置 * @param row * @param col */ public void placeQueen(int row, int col) { queens[row] = col; //将皇后位置放入 rows[col] = 1; //竖排攻击位置 hills[row - col + n - 1] = 1; // "从左到右对角线" 攻击位置 dales[row + col] = 1; //"从右到左对角线" 攻击位置 } /** * 回溯皇后位置 * @param row * @param col */ public void removeQueen(int row, int col) { queens[row] = 0; rows[col] = 0; hills[row - col + n - 1] = 0; dales[row + col] = 0; } /** * 将满足条件的皇后位置放入output中 */ public void addSolution() { List<String> solution = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int col = queens[i]; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) sb.append("."); sb.append("Q"); for(int j = 0; j < n - col - 1; ++j) sb.append("."); solution.add(sb.toString()); } output.add(solution); } public void backtrack(int row) { for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) { if (isNotUnderAttack(row, col)) { placeQueen(row, col); // 皇后数量是否满足,满足则输出 if (row + 1 == n) addSolution(); // 不满足则继续 else backtrack(row + 1); // 回溯。 removeQueen(row, col); } } } public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) { this.n = n; rows = new int[n]; hills = new int[2 * n - 1]; dales = new int[2 * n - 1]; queens = new int[n]; backtrack(0); return output; } }