ThreadLocal的工作原理
场景
假设一个用户是一个线程。他们都对数据库进行操作,这个时候就会每个用户就会从数据源中开启一个事务以确保能够顺利的打开或者关闭事务。那么如何保证用户与用户之间的数据库连接不发生冲突呢?就是用ThreadLocal。
原理解释
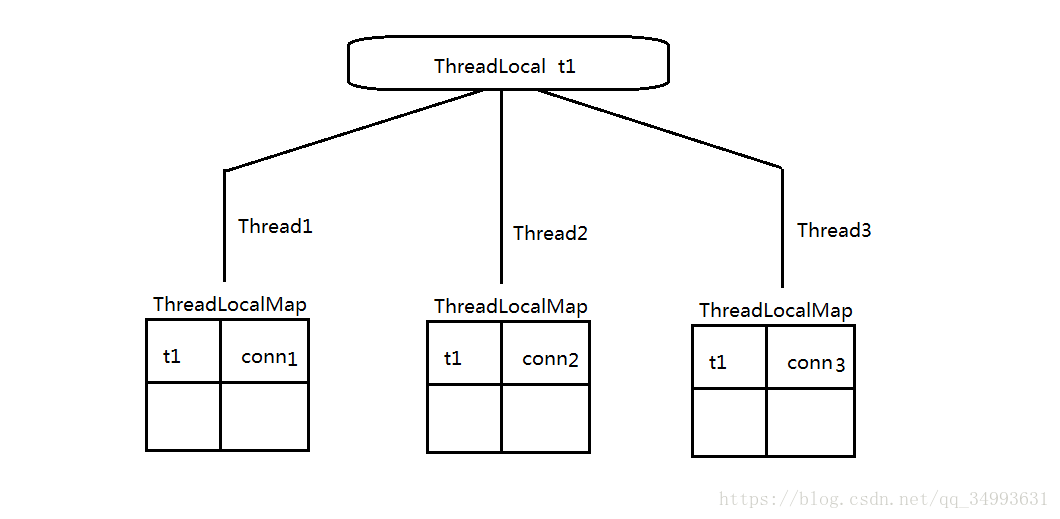
这里先交代一下,每一个线程都有自己的一个Map集合叫做ThreadLocalMap他是线程的一个静态内部类它就是用来保存连接的集合,ThreadLocal是一个工具类它负责将一个连接放入到每一个线程的Map集合中。具体来说就是每来一个用户,数据源就会创建一个连接Connection然后ThreadLocal工具类会将这个新创建的Connection添加到新来用户的Map集合中,并且以Map<ThreadLocal,Object>的方式存入。又因为这个Map是每一个线程(用户)所特有的,所以每个线程会从自己的Map中拿出属于自己的Connection,这样用户之间的Connection就不会发生混乱。
底层源码
当我们要将一个conn放入对应的线程中时调用threadLocal.set()代码如下:
|
public void set(T value) {
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> Thread t = Thread.currentThread();</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> if (map != null)</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> map.set(this, value);</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> else</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> createMap(t, value);</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> }</strong></span></strong></p>
</td>
</tr></tbody></table><p style="margin-left:0pt;"> </p>
当我们想要得到每个线程的conn时:
|
public T get() {
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> Thread t = Thread.currentThread();</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> if (map != null) {</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> if (e != null)</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> return (T)e.value;</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> }</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> return setInitialValue();</strong></span></strong></p>
<p style="margin-left:0pt;"><strong><span style="color:#000000;"><strong> }</strong></span></strong></p>
</td>
</tr></tbody></table><p style="margin-left:0pt;"><span style="color:#000000;">不难发现,get和set操作都是对当前线程做操作。</span></p>
这就是著名的ThreadLocal。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34993631/article/details/82343689
相关阅读:
[Spring开发]获取上下文对象
[Dubbo开发]Dubbo日志插件实现(打包)
[Dubbo开发]Dubbo日志插件实现(未打包)
[Java开发]打印当前路径到控制台
[Dubbo开发]Dubbo拦截器(Filter)初探
[Dubbo开发]配置简单的生产者和消费者
[Dubbo开发]Zookeeper配置
[Dubbo开发]Maven安装与配置
EL表达式的特性
oracle中rownum的使用
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jpfss/p/9913319.html
Copyright © 2020-2023
润新知
|
|
