欢迎各路大神临幸寒舍
以下节点标签为people,friend,用户自己也可以设置成其他标签,查询时需要用到标签。这个标签可以类比为关系数据库中的表名
创建节点、关系
创建节点(小明):create (n:people{name:’小明’,age:’18’,sex:’男’}) return n;
创建节点(小红): create (n:people{name:’小红’,age:’18’,sex:’女’}) return n;
创建关系(小明送礼物给小红):小明节点id为0,小红节点id为1
start a =node(0),b=node(1) create (a)-[n:gift]->(b)return n
属性查询
- 查询18岁的人
Match (n: people) where n.age = 18 return n- 查询大于18岁的人
Match (n: people) where n.age > 18 return n- 查询大于等于18岁的人
Match (n: people) where n.age >= 18 return n- 查询不等于18岁的人
Match (n: people) where n.age <> 18 return n关系查询
- 正向查询
查询小明送礼物给了哪些人,有两种写法:(以下例子类似)
1. Match (n:people)-[: gift]->(end:people) where n.name='小明' return end
2. Match (n:people{name: '小明'})-[:gift]->(end:people) return end
- 反向查询
查询哪些人送了礼物给小明
Match (n:people{name: '小明'})<-[:gift]-(end:people) return end- 无方向查询
查询和小明有礼物来往的人
Match (n:people{name: '小明'})-[:gift]-(end:people) return endID查询
在neo4j中,每一个节点,会自动有一个唯一Id。
查找id为1的节点,有两种方式:
1. Start n = node(1) return n
2. Match (n:people) where ID(n)=1 return n
级次查询(树形遍历)
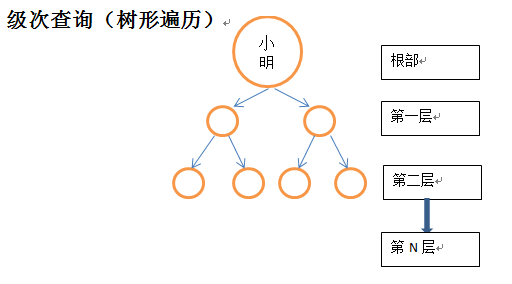
以根部为条件,查询第二层的节点
Match (start:people{name:’小明’})-[:gift*2..2]->(end:people) return end以根部为条件,查询第一层和第二层的节点
Match (start:people{name:’小明’})-[:gift*1..2]->(end:people) return end以根部为条件,按级次查询出所有直接或间接获得过小明的礼物的人
Match (start:people{name:’小明’})-[:gift*]->(end:people) return endDelete
删除2个节点之间的关系:
Match (x:people{name:’小明’})-[r:gift]->(y:people{name:’小红’}) delete r删除节点,会删除和该节点有关的所有关系:
Match (n:people{name:’小红’}) delete nCount
(不按属性)查询标签(people)中一共有多少节点(人):
Match (n:people) return count(n)(按属性)查询标签(people)中年龄为18岁的一共有多少节点(人):
三种写法:
1. Match (n:people) where n.age=18 return count(n)
2. Match (n:people{age:’18’}) return count(n)
3. Match (n:people) return count(n.age=18)Limit
查询标签(people)中的10个节点(人):
Match (n:people) return n limit 10Distinct
查询标签(people)中所有的不同的age:
Match (n:people) return distinct(n.age)Order by
根据标签(people)中的name 排序:
Match(n:people) return n order by name (默认升序)
Match(n:people) return n order by name asc (升序)
Match(n:people) return n order by name desc (降序)
Union all (Union)
求并集,不去重(去重用Union):
Match(n:people) where n.age=18 return n.name as name
Union all
Match(n:friend) where n.age=18 return n.name as name
In
查询id为0,5,8的节点:
Match (n) where ID(n) IN[0,5,8] return n Exists
判断节点是否存在 name这个属性:
Match (n) where exists(n.name) return n With
查询name以‘小’开头的节点:
Match (n) where n.name starts with ‘小’ return n 查询name以‘明’结尾的节点:
Match (n) where n.name ends with ‘明’ return nContains
查询name中含有 ‘小’的节点
Match (n) where n.name Contains ‘小’ return n 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/free8666/article/details/52909523