一、什么是Feign?
Feign 的英文表意为“假装,伪装,变形”, 是一个http请求调用的轻量级框架,可以以Java接口注解的方式调用Http请求,而不用像Java中通过封装HTTP请求报文的方式直接调用。Feign通过处理注解,将请求模板化,当实际调用的时候,传入参数,根据参数再应用到请求上,进而转化成真正的请求,这种请求相对而言比较直观。
封装了Http调用流程,更适合面向接口化的变成习惯。
在服务调用的场景中,我们经常调用基于Http协议的服务,而我们经常使用到的框架可能有HttpURLConnection、Apache HttpComponnets、OkHttp3 、Netty等等,这些框架在基于自身的专注点提供了自身特性。而从角色划分上来看,他们的职能是一致的提供Http调用服务。具体流程如下:

二、Feign是如何设计的?
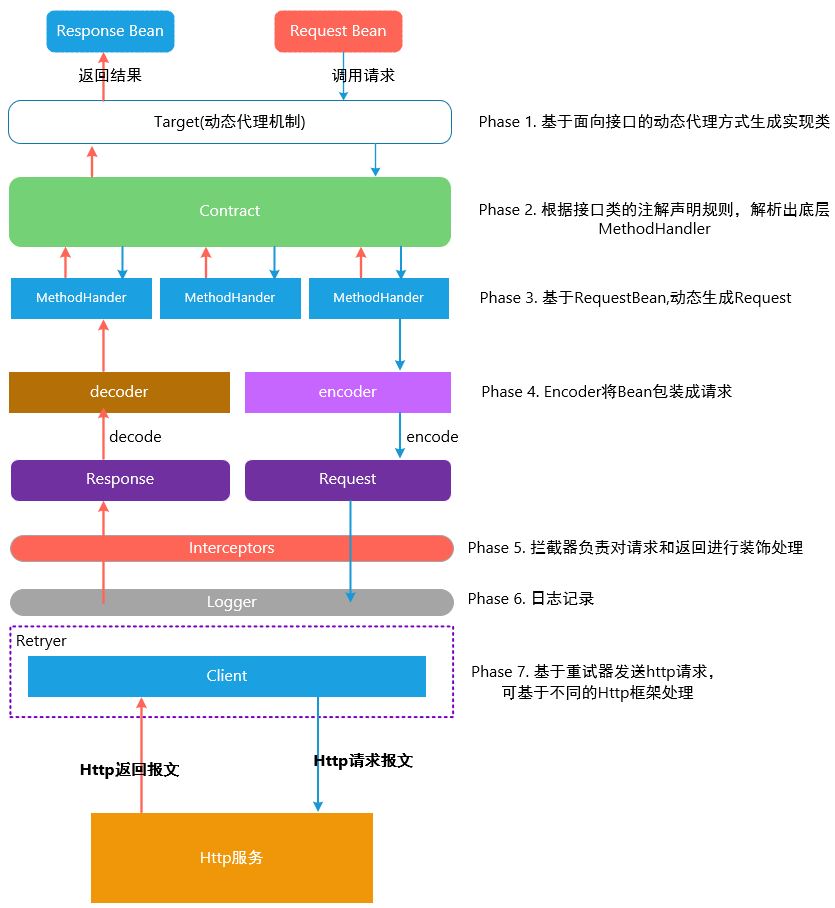
PHASE 1. 基于面向接口的动态代理方式生成实现类
在使用feign时,会定义对应的接口类,在接口类上使用Http相关的注解,标识HTTP请求参数信息,如下所示:
interface GitHub { @RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors") List<Contributor> contributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo); } public static class Contributor { String login; int contributions; } public class MyApp { public static void main(String... args) { GitHub github = Feign.builder() .decoder(new GsonDecoder()) .target(GitHub.class, "https://api.github.com"); // Fetch and print a list of the contributors to this library. List<Contributor> contributors = github.contributors("OpenFeign", "feign"); for (Contributor contributor : contributors) { System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")"); } } }
在Feign 底层,通过基于面向接口的动态代理方式生成实现类,将请求调用委托到动态代理实现类,基本原理如下所示:
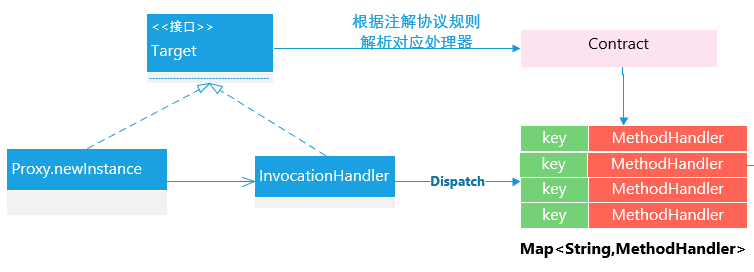
public class ReflectiveFeign extends Feign{ ///省略部分代码 @Override public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) { //根据接口类和Contract协议解析方式,解析接口类上的方法和注解,转换成内部的MethodHandler处理方式 Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target); Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>(); List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>(); for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) { if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { continue; } else if(Util.isDefault(method)) { DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method); defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler); methodToHandler.put(method, handler); } else { methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method))); } } InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler); // 基于Proxy.newProxyInstance 为接口类创建动态实现,将所有的请求转换给InvocationHandler 处理。 T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler); for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) { defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy); } return proxy; } //省略部分代码
PHASE 2. 根据Contract协议规则,解析接口类的注解信息,解析成内部表现:

Feign 定义了转换协议,定义如下:
/** * Defines what annotations and values are valid on interfaces. */ public interface Contract { /** * Called to parse the methods in the class that are linked to HTTP requests. * 传入接口定义,解析成相应的方法内部元数据表示 * @param targetType {@link feign.Target#type() type} of the Feign interface. */ // TODO: break this and correct spelling at some point List<MethodMetadata> parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class<?> targetType); }
2.1 默认Contract 实现
Feign 默认有一套自己的协议规范,规定了一些注解,可以映射成对应的Http请求,如官方的一个例子:
public interface GitHub { @RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors") List<Contributor> getContributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repository); class Contributor { String login; int contributions; } }
上述的例子中,尝试调用GitHub.getContributors("foo","myrepo")的的时候,会转换成如下的HTTP请求:
GET /repos/foo/myrepo/contributors
HOST XXXX.XXX.XXX
Feign 默认的协议规范
| 注解 | 接口Target | 使用说明 |
|---|---|---|
@RequestLine |
方法上 | 定义HttpMethod 和 UriTemplate. UriTemplate 中使用{} 包裹的表达式,可以通过在方法参数上使用@Param 自动注入 |
@Param |
方法参数 | 定义模板变量,模板变量的值可以使用名称的方式使用模板注入解析 |
@Headers |
类上或者方法上 | 定义头部模板变量,使用@Param 注解提供参数值的注入。如果该注解添加在接口类上,则所有的请求都会携带对应的Header信息;如果在方法上,则只会添加到对应的方法请求上 |
@QueryMap |
方法上 | 定义一个键值对或者 pojo,参数值将会被转换成URL上的 query 字符串上 |
@HeaderMap |
方法上 | 定义一个HeaderMap, 与 UrlTemplate 和HeaderTemplate 类型,可以使用@Param 注解提供参数值 |
2.2 基于Spring MVC的协议规范SpringMvcContract:
当前Spring Cloud 微服务解决方案中,为了降低学习成本,采用了Spring MVC的部分注解来完成请求协议解析,也就是说 ,写客户端请求接口和像写服务端代码一样:客户端和服务端可以通过SDK的方式进行约定,客户端只需要引入服务端发布的SDK API,就可以使用面向接口的编码方式对接服务:

当然,目前的Spring MVC的注解并不是可以完全使用的,有一些注解并不支持,如@GetMapping,@PutMapping 等,仅支持使用@RequestMapping 等,另外注解继承性方面也有些问题;具体限制细节,每个版本能会有些出入,可以参考上述的代码实现,比较简单。
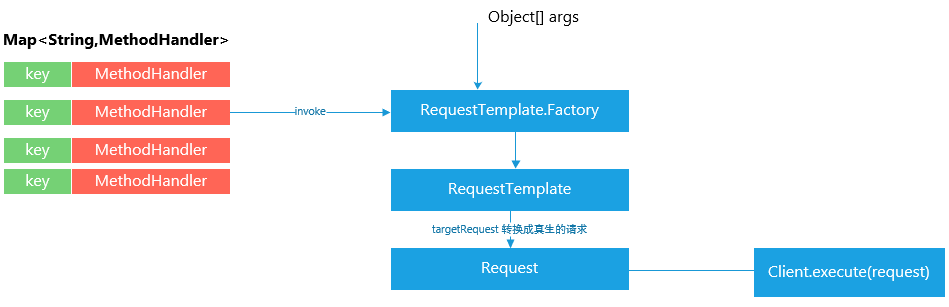
PHASE 3. 基于 RequestBean,动态生成Request
根据传入的Bean对象和注解信息,从中提取出相应的值,来构造Http Request 对象:
PHASE 4. 使用Encoder 将Bean转换成 Http报文正文(消息解析和转码逻辑)
Feign 最终会将请求转换成Http 消息发送出去,传入的请求对象最终会解析成消息体,如下所示:

public interface Encoder { /** Type literal for {@code Map<String, ?>}, indicating the object to encode is a form. */ Type MAP_STRING_WILDCARD = Util.MAP_STRING_WILDCARD; /** * Converts objects to an appropriate representation in the template. * 将实体对象转换成Http请求的消息正文中 * @param object what to encode as the request body. * @param bodyType the type the object should be encoded as. {@link #MAP_STRING_WILDCARD} * indicates form encoding. * @param template the request template to populate. * @throws EncodeException when encoding failed due to a checked exception. */ void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) throws EncodeException; /** * Default implementation of {@code Encoder}. */ class Default implements Encoder { @Override public void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) { if (bodyType == String.class) { template.body(object.toString()); } else if (bodyType == byte[].class) { template.body((byte[]) object, null); } else if (object != null) { throw new EncodeException( format("%s is not a type supported by this encoder.", object.getClass())); } } } }
目前Feign 有以下实现:
| Encoder/ Decoder 实现 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| JacksonEncoder,JacksonDecoder | 基于 Jackson 格式的持久化转换协议 |
| GsonEncoder,GsonDecoder | 基于Google GSON 格式的持久化转换协议 |
| SaxEncoder,SaxDecoder | 基于XML 格式的Sax 库持久化转换协议 |
| JAXBEncoder,JAXBDecoder | 基于XML 格式的JAXB 库持久化转换协议 |
| ResponseEntityEncoder,ResponseEntityDecoder | Spring MVC 基于 ResponseEntity< T > 返回格式的转换协议 |
| SpringEncoder,SpringDecoder | 基于Spring MVC HttpMessageConverters 一套机制实现的转换协议 ,应用于Spring Cloud 体系中 |
PHASE 5. 拦截器负责对请求和返回进行装饰处理
在请求转换的过程中,Feign 抽象出来了拦截器接口,用于用户自定义对请求的操作
public interface RequestInterceptor { /** * 可以在构造RequestTemplate 请求时,增加或者修改Header, Method, Body 等信息 * Called for every request. Add data using methods on the supplied {@link RequestTemplate}. */ void apply(RequestTemplate template); }
public class FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor extends BaseRequestInterceptor { /** * Creates new instance of {@link FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor}. * * @param properties the encoding properties */ protected FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor(FeignClientEncodingProperties properties) { super(properties); } /** * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override public void apply(RequestTemplate template) { // 在Header 头部添加相应的数据信息 addHeader(template, HttpEncoding.ACCEPT_ENCODING_HEADER, HttpEncoding.GZIP_ENCODING, HttpEncoding.DEFLATE_ENCODING); } }
PHASE 6. 日志记录
在发送和接收请求的时候,Feign定义了统一的日志门面来输出日志信息 , 并且将日志的输出定义了四个等级:
|
级别 |
说明 |
|---|---|
|
NONE |
不做任何记录 |
|
BASIC |
只记录输出Http 方法名称、请求URL、返回状态码和执行时间 |
|
HEADERS |
记录输出Http 方法名称、请求URL、返回状态码和执行时间 和 Header 信息 |
|
FULL |
记录Request 和Response的Header,Body和一些请求元数据 |
public abstract class Logger { protected static String methodTag(String configKey) { return new StringBuilder().append('[').append(configKey.substring(0, configKey.indexOf('('))) .append("] ").toString(); } /** * Override to log requests and responses using your own implementation. Messages will be http * request and response text. * * @param configKey value of {@link Feign#configKey(Class, java.lang.reflect.Method)} * @param format {@link java.util.Formatter format string} * @param args arguments applied to {@code format} */ protected abstract void log(String configKey, String format, Object... args); protected void logRequest(String configKey, Level logLevel, Request request) { log(configKey, "---> %s %s HTTP/1.1", request.method(), request.url()); if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.HEADERS.ordinal()) { for (String field : request.headers().keySet()) { for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(request.headers(), field)) { log(configKey, "%s: %s", field, value); } } int bodyLength = 0; if (request.body() != null) { bodyLength = request.body().length; if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) { String bodyText = request.charset() != null ? new String(request.body(), request.charset()) : null; log(configKey, ""); // CRLF log(configKey, "%s", bodyText != null ? bodyText : "Binary data"); } } log(configKey, "---> END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength); } } protected void logRetry(String configKey, Level logLevel) { log(configKey, "---> RETRYING"); } protected Response logAndRebufferResponse(String configKey, Level logLevel, Response response, long elapsedTime) throws IOException { String reason = response.reason() != null && logLevel.compareTo(Level.NONE) > 0 ? " " + response.reason() : ""; int status = response.status(); log(configKey, "<--- HTTP/1.1 %s%s (%sms)", status, reason, elapsedTime); if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.HEADERS.ordinal()) { for (String field : response.headers().keySet()) { for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(response.headers(), field)) { log(configKey, "%s: %s", field, value); } } int bodyLength = 0; if (response.body() != null && !(status == 204 || status == 205)) { // HTTP 204 No Content "...response MUST NOT include a message-body" // HTTP 205 Reset Content "...response MUST NOT include an entity" if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) { log(configKey, ""); // CRLF } byte[] bodyData = Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream()); bodyLength = bodyData.length; if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal() && bodyLength > 0) { log(configKey, "%s", decodeOrDefault(bodyData, UTF_8, "Binary data")); } log(configKey, "<--- END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength); return response.toBuilder().body(bodyData).build(); } else { log(configKey, "<--- END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength); } } return response; } protected IOException logIOException(String configKey, Level logLevel, IOException ioe, long elapsedTime) { log(configKey, "<--- ERROR %s: %s (%sms)", ioe.getClass().getSimpleName(), ioe.getMessage(), elapsedTime); if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) { StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); ioe.printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(sw)); log(configKey, sw.toString()); log(configKey, "<--- END ERROR"); } return ioe; }