锁(Locking)是数据库在并发访问时保证数据一致性和完整性的主要机制。在 MySQL 中,不同存储引擎使用不同的加锁方式;以 InnoDB 存储引擎为例探讨 MySQL 中的锁机制,其他存储引擎中的锁相对简单一些。
锁的分类
表级锁与行级锁
MySQL 中的锁可以按照粒度分为锁定整个表的表级锁(table-level locking)和锁定数据行的行级锁(row-level locking):
- 表级锁具有开销小、加锁快的特性;表级锁的锁定粒度较大,发生锁冲突的概率高,支持的并发度低;
- 行级锁具有开销大,加锁慢的特性;行级锁的锁定粒度较小,发生锁冲突的概率低,支持的并发度高。
InnoDB 存储引擎同时支持行级锁(row-level locking)和表级锁(table-level locking),默认情况下采用行级锁。
表级锁适用于并发较低、以查询为主的应用,例如中小型的网站;MyISAM 和 MEMORY 存储引擎采用表级锁。
行级锁适用于按索引条件高并发更新少量不同数据,同时又有并发查询的应用,例如 OLTP 系统;InnoDB 和 NDB 存储引擎实现了行级锁。
共享锁与排他锁
InnoDB 实现了以下两种类型的行锁:
- 共享锁(S):允许获得该锁的事务读取数据行(读锁),同时允许其他事务获得该数据行上的共享锁,并且阻止其他事务获得数据行上的共享锁。
- 排他锁(X):允许获得该锁的事务更新或删除数据行(写锁),同时阻止其他事务取得该数据行上的共享锁和排他锁。
这两种行锁之间的兼容性如下:
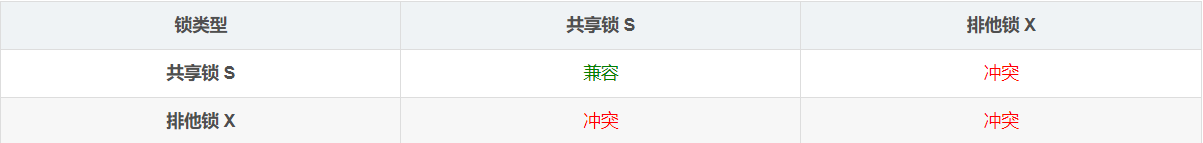
共享锁和共享锁可以兼容,排他锁和其它锁都不兼容。例如,事务 A 获取了一行数据的共享锁,事务 B 可以立即获得该数据行的共享锁,也就是锁兼容;但是此时事务 B 如果想获得该数据行的排他锁,则必须等待事务 A 释数据行上的共享锁,此种情况存在锁冲突。
默认情况下,数据库中的锁都可以自动获取;但是也可以手动为数据进行加锁。我们来看一个示例,首先创建一个表:
create table t( id int auto_increment primary key, c1 int, c2 int, c3 int ); create unique index idx_t_c1 on t(c1); create index idx_t_c2 on t(c2); insert into t(c1,c2,c3) values (1,1,1),(2,3,4),(3,6,9);
其中,id 是主键;c1 上创建了一个唯一索引;c2 上创建了一个非唯一索引;c3 上没有索引。接下来的示例都使用 MySQL 默认的隔离级别 Repeatable Read,除非另有说明。
然后创建两个数据库连接 T1 和 T2,先在 T1 中锁定一行数据:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t where id = 1 for share; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
我们在事务中使用select ... for share语句获得了数据行 id = 1 上的共享锁;对于 MySQL 8.0 之前的版本,可以使用select ... lock in share mode命令。由于 InnoDB 中的自动提交 autocommit 默认设置为 ON,我们必须在事务中为数据行加锁;或者将 autocommit 设置为 OFF。
然后在 T2 中执行以下语句:
-- T2 mysql> select * from t where id = 1 for share; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
结果显示,在 T2 中成功获取改行数据上的共享锁。然后尝试获取排他锁:
-- T2 mysql> select * from t where id = 1 for update; ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
使用select ... for update命令获取排他锁,此时该命令会一直处于等待状态并且最终超时。也就是说,共享锁和排他锁不兼容。
最后,在 T1 中提交或者回滚事务:
-- T1 mysql> commit;
意向锁
InnoDB 除了支持行级锁,还支持由 MySQL 服务层实现的表级锁(LOCK TABLES ... WRITE在指定的表加上表级排他锁)。当这两种锁同时存在时,可能导致冲突。例如,事务 A 获取了表中一行数据的读锁;然后事务 B 申请该表的写锁(例如修改表的结构)。如果事务 B 加锁成功,那么它就应该能修改表中的任意数据行,但是 A 持有的行锁不允许修改锁定的数据行。显然数据库需要避免这种问题,B 的加锁申请需要等待 A 释放行锁。
那么如何判断事务 B 是否应该获取表级锁呢?首先需要看该表是否已经被其他事务加上了表级锁,然后依次查看该表中的每一行是否已经被其他事务加上了行级锁。这种方式需要遍历整个表中的记录,效率很低。为此,InnoDB 引入了另外一种锁:意向锁(Intention Lock)。
意向锁属于表级锁,由 InnoDB 自动添加,不需要用户干预。意向锁也分为共享和排他两种方式:
- 意向共享锁(IS):事务在给数据行加行级共享锁之前,必须先取得该表的 IS 锁。
- 意向排他锁(IX):事务在给数据行加行级排他锁之前,必须先取得该表的 IX 锁。
此时,事务 A 必须先申请该表的意向共享锁,成功后再申请数据行的行锁。事务 B 申请表锁时,数据库查看该表是否已经被其他事务加上了表级锁;如果发现该表上存在意向共享锁,说明表中某些数据行上存在共享锁,事务 B 申请的写锁会被阻塞。
因此,意向锁是为了使得行锁和表锁能够共存,从而实现多粒度的锁机制。以下是表级锁和表级意向锁的兼容性:
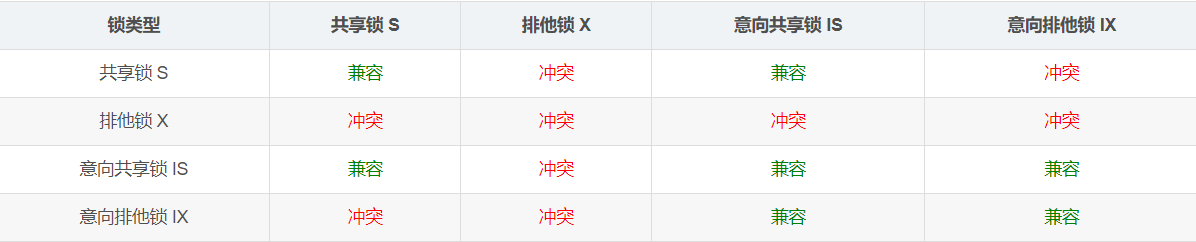
InnoDB 表存在两种表级锁,一种是LOCK TABLES语句手动指定的锁,另一种是由 InnoDB 自动添加的意向锁。
简单来说,意向锁和表锁之间只有共享锁兼容,意向锁和意向锁之间都可以兼容。意向锁的主要作用是表明某个事务正在或者即将锁定表中的数据行。
我们以意向排他锁 IX 为例,继续上面的实验。先在 T1 中执行以下加锁语句:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t where id = 1 for update; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
在事务中为表 t 中的数据行 id = 1 加上了排他锁,同时会为表 t 加上意向排他锁。然后在 T2 中执行以下语句:
-- T2 mysql> lock tables t read; -- lock tables t write;
lock tables ... read语句用于为表 t 加上表级共享锁;因为意向排他锁和表级共享锁冲突,所以 T2 一直等待 T1 释放锁。也可以使用lock tables ... write语句为表 t 加上表级排他锁;因为意向排他锁和表级排他锁冲突,所以该语句也会一直等待 T1 释放锁。
当我们在 T1 中提交或者回滚事务:
-- T1 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
T2 自动获得该表上的共享锁:
-- T2 Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 43.17 sec) mysql> unlock tables; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
以上的unlock tables语句用于释放该表上的排他锁。
我们再来验证一下两个意向排他锁之间锁的兼容性,先在 T1 中执行以下加锁语句:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t where id = 1 for update; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
T1 为表 t 加上了意向排他锁和数据行 id = 1 上的排他锁。然后在 T2 中执行以下语句:
-- T2 mysql> select * from t where id = 2 for update; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
T2 成功为数据行 id = 2 加上的排他锁,同时为表 t 加上了意向排他锁。也就是说,T1 和 T2 同时获得了表 t 上的意向排他锁,以及不同数据行上的行级排他锁。InnoDB 通过行级锁,实现了更细粒度的控制,能够支持更高的并发更新和查询。
最后在 T1 中提交或者回滚事务:
-- T1 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
行级锁实现
InnoDB 通过给索引上的索引记录加锁的方式实现行级锁。具体来说,InnoDB 实现了三种行锁的算法:记录锁(Record Lock)、间隙锁(Gap Lock)和 Next-key 锁(Next-key Lock)。
记录锁
记录锁(Record Lock)是针对索引记录(index record)的锁定。例如,SELECT * FROM t WHERE id = 1 FOR UPDATE;会阻止其他事务对表 t 中 id = 1 的数据执行插入、更新,以及删除操作。
通过主键操作单个值
id 是表 t 的主键,我们先在 T1 中执行以下命令:
-- T1 mysql> SET GLOBAL innodb_status_output=ON; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SET GLOBAL innodb_status_output_locks=ON; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE id = 1 FOR UPDATE; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
全局变量 innodb_status_output 和 innodb_status_output_locks 用于控制 InnoDB 标准监控和锁监控,我们利用监控查看锁的使用情况。然后 T1 锁定了 id = 1 的记录,此时 T2 无法修改该记录:
-- T2 mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE id = 1 for update; ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
使用SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令查看 InnoDB 监控中关于锁的事务数据,可以看到以下内容:
---TRANSACTION 43764, ACTIVE 4 sec 2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 1 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23734 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43764 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43764 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f0110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
日志显示存在 2 个锁结构,锁定了一个记录;表 t 上存在 IX 锁,主键索引上存在一个 X 记录锁,同时还显示了记录对应的数据值。注意but not gap,下文我们会介绍间隙锁(Gap Lock)。最后在 T1 中释放锁:
-- T1 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
通过唯一索引操作单个值
c1 字段上存在唯一索引,我们先在 T1 中执行以下命令:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE c1 = 1 FOR UPDATE; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
使用SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令查看 InnoDB 监控中关于锁的事务数据,可以看到以下内容:
---TRANSACTION 43761, ACTIVE 47 sec 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 2 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23722 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43761 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 5 n bits 72 index idx_t_c1 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43761 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43761 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f0110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
日志显示存在 3 个锁结构,锁定了 2 个记录;表 t 上存在 IX 锁,索引 idx_t_c1 上存在一个 X 记录锁,主键索引上存在一个 X 记录锁。最后在 T1 中释放锁:
-- T1 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
记录锁永远都是锁定索引记录,锁定非聚集索引会先锁定聚集索引。如果表中没有定义索引,InnoDB 默认为表创建一个隐藏的聚簇索引,并且使用该索引锁定记录。
间隙锁
间隙锁(Gap Lock)锁定的是索引记录之间的间隙、第一个索引之前的间隙或者最后一个索引之后的间隙。例如,SELECT * FROM t WHERE c1 BETWEEN 1 and 10 FOR UPDATE;会阻止其他事务将 1 到 10 之间的任何值插入到 c1 字段中,即使该列不存在这样的数据;因为这些值都会被锁定。
通过主键操作范围值
首先在 T1 中执行以下命令锁住数据范围:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE id BETWEEN 1 and 10 FOR UPDATE; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | | 3 | 3 | 6 | 9 | +----+------+------+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
表 t 中只有 3 条记录,id = 4 的记录不存在;即便如此,T2 仍然无法插入该记录:
-- T2 mysql> insert into t(c1,c2,c3) values (4,8,12); ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
再次使用SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令查看 InnoDB 监控中关于锁的事务数据,可以看到以下内容:
---TRANSACTION 43765, ACTIVE 4 sec 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 4 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23741 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43765 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43765 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f0110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43765 lock_mode X Record lock, heap no 1 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 1; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 8; hex 73757072656d756d; asc supremum;; Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f011d; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f012a; asc *;; 3: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000009; asc ;;
日志显示存在 3 个锁结构,锁定了 4 个索引记录;表 t 上存在 IX 锁,主键索引上存在 1 个 X 记录锁(id = 1)和 3 个间隙锁((1, 2]、(2, 3]、supremum);其中 supremum 代表了大于 3 的间隙((3, positive infinity))。实际上这里的间隙锁属于 Next-key 锁,相当于间隙锁加记录锁,下文将会介绍。此时,我们可以插入 id 小于 1 的数据;但是不能插入 id 大于 10 的数据。
通过唯一索引操作范围值
首先在 T1 中执行以下命令锁住数据范围:
---TRANSACTION 43765, ACTIVE 4 sec 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 4 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23741 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43765 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43765 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f0110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 101 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43765 lock_mode X Record lock, heap no 1 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 1; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 8; hex 73757072656d756d; asc supremum;; Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f011d; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000aaec; asc ;; 2: len 7; hex 820000008f012a; asc *;; 3: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000009; asc ;;
再次使用SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令查看 InnoDB 监控中关于锁的事务数据,可以看到以下内容:
---TRANSACTION 43824, ACTIVE 153 sec 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 7 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23852 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43824 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 5 n bits 72 index idx_t_c1 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43824 lock_mode X Record lock, heap no 1 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 1; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 8; hex 73757072656d756d; asc supremum;; Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43824 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a70110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a7011d; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a7012a; asc *;; 3: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000009; asc ;;
日志显示存在 3 个锁结构,锁定了 7 个索引记录;表 t 上存在 IX 锁,索引 idx_t_c1 上存在 4 个间隙锁((negative infinity, 1]、(1, 2]、(2, 3]、supremum),其中 supremum 代表了大于 3 的间隙((3, positive infinity));主键索引上存在 3 个 X 记录锁,锁定了 3 个主键值。实际上这里的间隙锁属于 Next-key 锁,相当于间隙锁加记录锁,后面将会介绍。此时,我们无法插入任何数据。
间隙可能会包含单个索引值、多个索引值或者没有索引值。间隙锁是性能和并发之间的一种权衡,只会在某些事务隔离级别(Repeatable Read)使用。
使用唯一索引来搜索单个值的语句不会使用间隙锁(不包括搜索条件只包含多列唯一索引中部分列的情况;在这种情况下,仍然会使用间隙锁)。例如,SELECT * FROM t WHERE id = 1 FOR UPDATE;只会对 id = 1 的索引记录加上记录锁,而不关心其他事务是否会在前面的间隙中插入数据。但是,如果 id 列上没有索引或者创建的是非唯一索引,则该语句会锁定前面的间隙。
需要注意的是,不同事务可以获取一个间隙上互相冲突的锁。例如,事务 A 在一个间隙上获取了共享的间隙锁(间隙 S 锁),事务 B 可以在同一间隙上获取排他的间隙锁(间隙 X 锁)。允许存在互相冲突的间隙锁的原因在于,如果从索引中清除某个记录,必须合并不同事务在记录上获取的间隙锁。
InnoDB 间隙锁的唯一目的是阻止其他事务在间隙中插入数据。间隙锁可以共存,一个事务的间隙锁不会阻止另一个事务在同一个间隙上获取间隙锁。共享间隙锁和排他间隙锁之间没有区别,彼此不冲突,它们的作用相同。
间隙锁可以显式禁用,例如将事务隔离级别设置为 READ COMMITTED。此时,查找和索引扫描不会使用间隙锁,间隙锁只用于外键约束和重复键的检查。
使用 READ COMMITTED 隔离级别还会带来其他影响,MySQL 在判断 WHERE 条件之后会释放不满足条件的数据行上的记录锁。对于 UPDATE 语句,InnoDB 执行“半一致”读取;以便将数据的最新版本返回给 MySQL,MySQL 就可以确定该行是否满足 UPDATE 中的 WHERE 条件。
Next-key 锁
Next-key 锁(Next-key Lock)相当于一个索引记录锁加上该记录之前的一个间隙锁。
InnoDB 实现行级锁的方式如下:当搜索或扫描表索引时,在遇到的索引记录上设置共享锁或排它锁。因此,InnoDB 行级锁实际上是索引记录锁。一个索引记录上的 next-key 锁也会影响该索引记录之前的“间隙”,如果一个会话在索引中的记录 R 上有共享锁或排它锁,则另一个会话不能在 R 之前的间隙中插入新的索引记录。
假设一个索引中包含数据 10、11、13 和 20。该索引中可能的 next-key 锁包含以下范围,其中圆括号表示排除端点值,方括号表示包含端点值:
(negative infinity, 10] (10, 11] (11, 13] (13, 20] (20, positive infinity) -- 显示为 supermum
对于最后一个间隔,next-key 锁将会锁定最大索引值(20)之后的间隙;伪记录“supermum”的值大于索引中任何值,它不是真正的索引记录。(10, 11) 是一个间隙锁的锁定范围,(10, 11] 是一个 next-key 锁的锁定范围。默认隔离级别(REPEATABLE READ )下,InnoDB 通过 next-key 锁进行查找和索引扫描,用于防止幻读;因为它会锁定范围值,不会导致两次查询结果的数量不同。
通过普通索引操作单个值
c2 字段上存在非唯一索引,我们先在 T1 中执行以下命令:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE c2 = 1 FOR UPDATE; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
使用SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令查看 InnoDB 监控中关于锁的事务数据,可以看到以下内容:
---TRANSACTION 43830, ACTIVE 6 sec 4 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 3 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23871 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43830 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 6 n bits 72 index idx_t_c2 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43830 lock_mode X Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43830 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a70110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 6 n bits 72 index idx_t_c2 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43830 lock_mode X locks gap before rec Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
日志显示存在 4 个锁结构,锁定了 3 个索引项;表 t 上存在 IX 锁,索引 idx_t_c2 上存在一个 next-key 锁(c2 = 1,锁定了 (negative infinity, 1])和一个 X 间隙锁((1, 3)),主键索引上存在一个 X 记录锁(id = 1)。
此时其他事务无法在 c2 中插入小于 3 的值,但是可以插入大于等于 3 的值。最后在 T1 中释放锁:
-- T1 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
如果索引有唯一属性,则 InnnoDB 会自动将 next-key 锁降级为记录锁。我们在前面已经给出了记录锁的示例。
通过普通索引操作范围值
如果利用 c2 字段作为条件操作范围值,加锁情况与通过唯一索引(c1)操作范围值相同。可以参考上文示例。
无索引操作单个值或范围值
c3 字段上没有索引,我们先在 T1 中执行以下命令:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE c3 = 1 FOR UPDATE; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
使用SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令查看 InnoDB 监控中关于锁的事务数据,可以看到以下内容:
---TRANSACTION 43848, ACTIVE 5 sec 2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 4 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23917 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43848 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 4 n bits 80 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43848 lock_mode X Record lock, heap no 1 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 1; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 8; hex 73757072656d756d; asc supremum;; Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a70110; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a7011d; asc ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;; Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a7012a; asc *;; 3: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000009; asc ;;
日志显示存在 2 个锁结构,锁定了 4 个索引项;表 t 上存在 IX 锁,主键索引上存在 4 个 next-key 锁,锁定了所有的主键范围。此时其他事务无法插入任何数据。
最后在 T1 中释放锁:
-- T1 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
如果我们将语句修改为SELECT * FROM t WHERE c3 between 1 and 10 FOR UPDATE;,通过无索引的字段操作范围值,也会锁定主键的所有范围。这也就是为什么 MySQL 推荐通过索引操作数据,最好是主键。
插入意向锁
插入意向锁(Insert Intention Lock)是在插入数据行之前,由 INSERT 操作设置的一种间隙锁。插入意向锁表示一种插入的意图,如果插入到相同间隙中的多个事务没有插入相同位置,则不需要互相等待。假设存在索引记录 4 和 7。两个事务分别尝试插入 5 和 6,它们在获取行排他锁之前,分别使用插入意向锁来锁定 4 到 7 之间的间隙;但是不会相互阻塞,因为插入的是不同的行。
在 T1 中对 c2 大于 3 的索引记录设置排它锁,这个排它锁包含记录 6 之前的间隙锁:
-- T1 mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM t WHERE c2 > 3 FOR UPDATE; +----+------+------+------+ | id | c1 | c2 | c3 | +----+------+------+------+ | 3 | 3 | 6 | 9 | +----+------+------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
使用 SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令可以显示锁事务数据:
---TRANSACTION 43853, ACTIVE 38 sec 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 3 row lock(s) MySQL thread id 103, OS thread handle 140437513750272, query id 23931 localhost root TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43850 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 6 n bits 72 index idx_t_c2 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43850 lock_mode X Record lock, heap no 1 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 1; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 8; hex 73757072656d756d; asc supremum;; Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 4 n bits 80 index PRIMARY of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43850 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 1: len 6; hex 00000000ab2b; asc +;; 2: len 7; hex 82000000a7012a; asc *;; 3: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; 4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 5: len 4; hex 80000009; asc ;;
在 T2 中将 c2 = 4 插入间隙中,该事务在等待获取独占锁时使用插入意向锁:
-- T2 mysql> insert into t(c1,c2,c3) values (4,4,4);
使用 SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS命令可以显示插入意向锁事务数据:
---TRANSACTION 43854, ACTIVE 5 sec inserting mysql tables in use 1, locked 1 LOCK WAIT 2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 1 row lock(s), undo log entries 1 MySQL thread id 106, OS thread handle 140437512111872, query id 23957 localhost root update insert into t(c1,c2,c3) values (4,4,4) ------- TRX HAS BEEN WAITING 5 SEC FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED: RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 6 n bits 72 index idx_t_c2 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43854 lock_mode X locks gap before rec insert intention waiting Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;; ------------------ TABLE LOCK table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43854 lock mode IX RECORD LOCKS space id 102 page no 6 n bits 72 index idx_t_c2 of table `hrdb`.`t` trx id 43854 lock_mode X locks gap before rec insert intention waiting Record lock, heap no 4 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 2; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;; 1: len 4; hex 80000003; asc ;;
其中,locks gap before rec insert intention 表示插入意向锁。由于 T1 锁定了 3 和 6 之间的范围,T2 需要等待;如果 T1 插入数据 4,T2 插入数据 5,互相之间不需要等待。
插入意向锁的作用是为了提高并发插入的性能。间隙锁不允许多个事务同时插入同一个索引间隙,但是插入意向锁允许多个事务同时插入同一个索引间隙内的不同数据值。