声明:如需引用或者摘抄本博文源码或者其文章的,请在显著处注明,来源于本博文/作者,以示尊重劳动成果,助力开源精神。也欢迎大家一起探讨,交流,以共同进步~ 0.0
多进程代码框架示例
/*
@url:http://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen/p/8022597.html
@author:Johnny Zen
@school:XiHua University
@contact:johnnyztsd@gmail.com or 1125418540@qq.com
@date:2017-12-11 13:08
@description:Linux下多进程代码框架[C编程]
@environment:Linux For Ubuntu 16.04/64
*/
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<signal.h>
int main(){
pid_t sub_a, sub_b, sub_c, sub_d;//4个子进程
while((sub_a = fork()) == -1);//在主进程下,创建子进程a
if(sub_a > 0){//在主进程中,且成功创建子进程a
while((sub_b = fork()) == -1); //在主进程下,创建子进程b
if(sub_b > 0){//在主进程中,且成功创建子进程b
while((sub_c = fork()) == -1); //在主进程下,创建子进程c
if(sub_c > 0){//在主进程中,且成功创建子进程c
while((sub_d = fork()) == -1); //在主进程下,创建子进程d
if(sub_d > 0){//在主进程中,且成功创建子进程d
printf("在主进程中,且已成功创建子进程a/b/c/d:[Current PID:%d; Parent PID:%d;sub_a pid:%d;sub_b pid:%d;sub_c pid:%d;sub_d pid:%d;]
", getpid(), getppid(), sub_a, sub_b, sub_c, sub_d);
} else {//在子进程d中
printf("在子进程d中:[Current PID:%d; Parent PID:%d;sub_d pid:%d]
", getpid(), getppid(), sub_d);
}
} else {//在子进程c中
printf("在子进程c中:[Current PID:%d; Parent PID:%d;sub_c pid:%d]
", getpid(), getppid(), sub_c);
}
} else {//在子进程b中
printf("在子进程b中:[Current PID:%d; Parent PID:%d;sub_b pid:%d]
", getpid(), getppid(), sub_b);
}
} else { //在子进程a中
printf("在子进程a中:[Current PID:%d; Parent PID:%d;sub_a pid:%d]
", getpid(), getppid(), sub_a);
}
return 0;
}
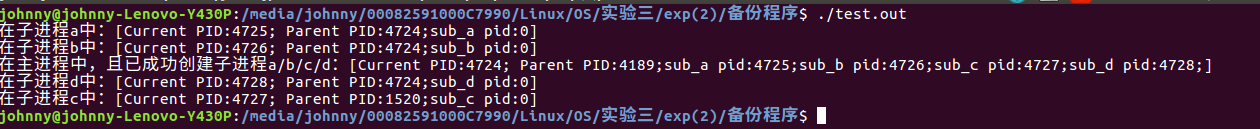
/* 运行结果:
在子进程a中:[Current PID:4605; Parent PID:4604;sub_a pid:0]
在子进程b中:[Current PID:4606; Parent PID:4604;sub_b pid:0]
在主进程中,且已成功创建子进程a/b/c/d:[Current PID:4604; Parent PID:4189;sub_a pid:4605;sub_b pid:4606;sub_c pid:4607;sub_d pid:4608;]
在子进程c中:[Current PID:4607; Parent PID:4604;sub_c pid:0]
在子进程d中:[Current PID:4608; Parent PID:1520;sub_d pid:0]
*/
运行效果
另附一份自己的进程相关实验源码
方便道友们学习之用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void waiting(),stop(),alarming();
int wait_mark;
void main()
{
int p1,p2;//声明两个子进程变量
if(p1=fork())//创建子进程1
{
if(p2=fork())//创建子进程2
{
wait_mark=1;//等待标记
signal(SIGINT,stop);//捕捉中断信号,执行stop
signal(SIGALRM,alarming);//捕捉SIGALRM信号,执行alarming
waiting();//等待软中断信号,5s内按【DEL】发送中断信号SIGINT,否则会向当前进行发送SIGALRM信号。
kill(p1,16);//向子程序p1发送信号16
kill(p2,17);//向子程序p2发送信号17
wait(0);//等待第一个子进程终止
wait(0);//等待第二个子进程终止
printf("parent process is killed!
");//输出父进程终止
exit(0);//正常终止父进程
}
else
{
wait_mark=1;//等待标记
signal(17,stop);//子进程p2接收到信号后执行stop
signal( SIGINT,SIG_IGN);//忽略中断信号SIGINT对本进程的影响
while(wait_mark!=0);
lockf(1,1,0);//锁定屏幕,不让其他进程输出
printf("children process2 is killed by parent
");//输出进程2被父进程终止
lockf(1,0,0);//解锁
exit(0);//正常终止进程2
}
}
else
{
wait_mark=1;//等待标记
signal(16,stop);//子进程p2接收到信号后执行stop
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);//忽略中断信号SIGINT对本进程的影响
while(wait_mark!=0)
lockf(1,1,0);//锁定屏幕,不让其他进程输出
printf("children process1 is killed by parent
");//输出进程1被父进程终止
lockf(1,0,0);//解锁
exit(0);//正常终止进程1
}
}
void waiting()
{
sleep(5);//等待5S
if(wait_mark!=0)
kill(getpid(),SIGALRM);//对当前进程发送SIFALRM信号
}
void alarming()
{
wait_mark=0;
}
void stop()
{
wait_mark=0;
}
参考文献
原创。