1.序列
序列是LINQ的基础。在看到一个查询表达式的时候,应该要想到它所涉及的序列:一开始总是存在至少一个序列,且通常在中间过程会转换为其他序列,也可能和更多的序列连接在一 起。
来看一个简单的例子,我们在人员列表上执行一个查询表达式。附加了一个过滤器,来保证只有成年人出现在结果序列中:
var adultName = from person in people where person.Age > 18 select person.Name;
下图以图表形式把这个查询表达式分解成了独立步骤。
每一个箭头代表一个序列——描述在左边,示例数据在右边。每个框都代表查询表达式的一个步骤。
2.延迟处理和流处理
上图中的查询表达式被创建的时候,不会处理任何数据,也不会访问原始的人员列表。而是在内存中生成了这个查询的表现形式。判断是否为成人的谓词,以及人到人名的转换,都是通过委托实例来表示的。只有在访问结果IEnumerable<string>的第一个元 素的时候,才会处理数据。
LINQ的这个特点称为延迟执行。在终结果的第一个元素被访问的时候,Select转换才会为它的第一个元素调用Where转换。而Where转换会访问列表中的第一个元素,检查这个谓词是否匹配(在这个例子中,是匹配的),并把这个元素返回给Select。后,依次提取出名称作为 结果返回。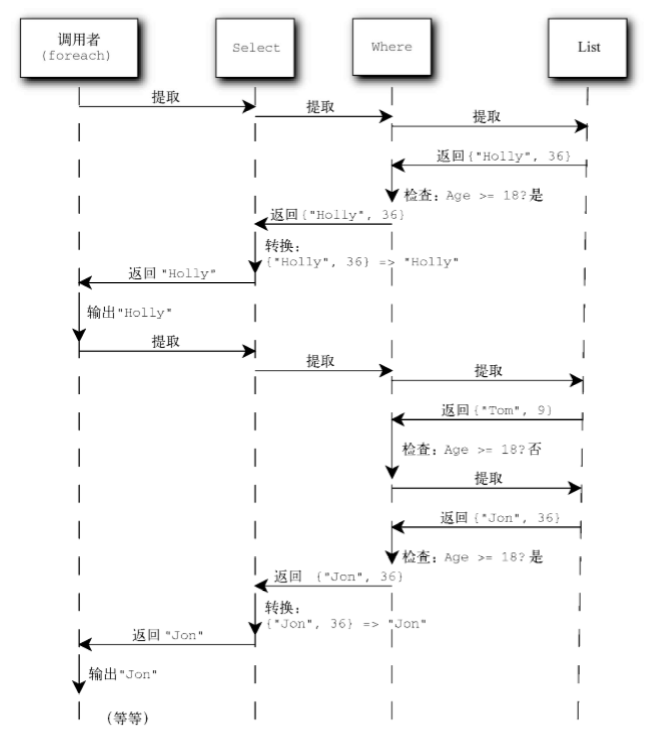
3.LINQ查询语法

using System.Linq; using static System.Console; class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] names = { "Alonso", "Zheng", "Smith", "Jones", "Smythe", "Small", "Ruiz", "Hsieh", "Jorgenson", "Ilyich", "Singh", "Samba", "Fatimah" }; var queryResults = from n in names where n.StartsWith("S") select n; WriteLine("Names beginning with S:"); foreach (var item in queryResults) { WriteLine(item); } Write("Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:"); ReadLine(); } }
输出结果如下:

Names beginning with S: Smith Smythe Small Singh Samba Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:
3.1 var关键字
LINQ查询首先声明一个变量,已包含查询的结果,这通常用var关键字声明来完成:
var queryResult = ... // 查询结果将是实现了IEnumerable<T>接口的类型
3.2 指定数据源:from语句
LINQ查询的下一部分是from语句,它指定了要查询的数据:
from n in names
变量n只是数据源names中的某一元素的代表,类似foreach语句后的变量名,源数据不能是单个值或对象。
3.3 指定条件:where子句
在LINQ查询的下一部分,可以使用where子句指定查询的条件:
where n.StartsWith("S")
3.4 选择元素:select子句
最后,select子句指定结果集中包含哪些元素:
select n;
3.5 完成:使用foreach语句循环
用foreach语句迭代结果:
foreach (var item in queryResults) { WriteLine(item); }
3.6 延迟执行的查询
在访问查询结果(foreach)之前,并没有提取LINQ数据,这称为查询的延迟执行或迟缓执行。生成结果序列(即列表)的查询都要延迟执行。
4.LINQ方法语句
使用Lambda表达式与LINQ方法语句进行查询:

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] names = { "Alonso", "Zheng", "Smith", "Jones", "Smythe", "Small", "Rodriguez", "Hsieh", "Jorgenson", "Ilyich", "Singh", "Samba", "Fatimah" }; var queryResults = names.Where(n => n.StartsWith("S")); // Where()方法的调用 WriteLine("Names beginning with S:"); foreach (var item in queryResults) { WriteLine(item); } Write("Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:"); ReadLine(); } }
5.orderby子句
orderby子句如下所示:

// orderby n class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] names = { "Alonso", "Zheng", "Smith", "Jones", "Smythe", "Small", "Ruiz", "Hsieh", "Jorgenson", "Ilyich", "Singh", "Samba", "Fatimah" }; var queryResults = from n in names where n.StartsWith("S") orderby n select n; WriteLine("Names beginning with S:"); foreach (var item in queryResults) { WriteLine(item); } Write("Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:"); ReadLine(); } }
通过LINQ方法语句查询:
var queryResults = names.Where(n => n.StartsWith("S")).Orderby(n => n);
多级排序:
orderby c.Region, c.Country descending, c.City // descending反转该字段排序(即逆序)
groupby,orderby结合使用(按日期分类,ID排序)
var query = tests.GroupBy(s => s.apptDate) .Select(testgroup => new { Date = testgroup.Key, ID = testgroup.OrderBy(x => x.calOId) }) .OrderBy(testgroup => testgroup.Date); foreach (var testgroup in query) { Console.WriteLine($"ApptDate {testgroup.Date.ToString("MMM dd")}"); foreach (var id in testgroup.ID) { Console.WriteLine($"calOId = {id.calOId}"); } }
分组求和:
list.Add(new NetContents("Product_A", "Test001", 1)); list.Add(new NetContents("Product_B", "Test002", 2)); list.Add(new NetContents("Product_A", "Test001", 4)); list.Add(new NetContents("Product_A", "Test001", 3)); var newList = list.GroupBy(x => new { x.Name, x.Number }) .Select(x => new YourClass(x.Key.Name, x.Key.Number, x.Sum(a => a.Quantity))) .ToList();
6.单值选择查询
LINQ提供了Distinct()方法查找获得唯一的不重复项(去除重复项)。

var queryResults = customers.Select(c => c.Region).Distinct(); class Customer { public string ID { get; set; } public string City { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public string Region { get; set; } public decimal Sales { get; set; } public override string ToString() { return "ID: " + ID + " City: " + City + " Country: " + Country + " Region: " + Region + " Sales: " + Sales; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<Customer> customers = new List<Customer> { new Customer { ID="A", City="New York", Country="USA", Region="North America", Sales=9999}, new Customer { ID="B", City="Mumbai", Country="India", Region="Asia", Sales=8888}, new Customer { ID="C", City="Karachi", Country="Pakistan", Region="Asia", Sales=7777}, new Customer { ID="D", City="Delhi", Country="India", Region="Asia", Sales=6666}, new Customer { ID="E", City="São Paulo", Country="Brazil", Region="South America", Sales=5555 }, new Customer { ID="F", City="Moscow", Country="Russia", Region="Europe", Sales=4444 }, new Customer { ID="G", City="Seoul", Country="Korea", Region="Asia", Sales=3333 }, new Customer { ID="H", City="Istanbul", Country="Turkey", Region="Asia", Sales=2222 }, new Customer { ID="I", City="Shanghai", Country="China", Region="Asia", Sales=1111 }, new Customer { ID="J", City="Lagos", Country="Nigeria", Region="Africa", Sales=1000 }, new Customer { ID="K", City="Mexico City", Country="Mexico", Region="North America", Sales=2000 }, new Customer { ID="L", City="Jakarta", Country="Indonesia", Region="Asia", Sales=3000 }, new Customer { ID="M", City="Tokyo", Country="Japan", Region="Asia", Sales=4000 }, new Customer { ID="N", City="Los Angeles", Country="USA", Region="North America", Sales=5000 }, new Customer { ID="O", City="Cairo", Country="Egypt", Region="Africa", Sales=6000 }, new Customer { ID="P", City="Tehran", Country="Iran", Region="Asia", Sales=7000 }, new Customer { ID="Q", City="London", Country="UK", Region="Europe", Sales=8000 }, new Customer { ID="R", City="Beijing", Country="China", Region="Asia", Sales=9000 }, new Customer { ID="S", City="Bogotá", Country="Colombia", Region="South America", Sales=1001 }, new Customer { ID="T", City="Lima", Country="Peru", Region="South America", Sales=2002 } }; //method syntax var queryResults = customers.Select(c => c.Region).Distinct(); //query syntax: var queryResults = (from c in customers select c.Region).Distinct(); foreach (var item in queryResults) { WriteLine(item); } Write("Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:"); ReadLine(); } }
输出结果如下:

North America Asia South America Europe Africa Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:
7.使用聚合运算符
数字结果的聚合运算符:
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Count() | 结果的个数 |
| Min() | 结果中的最小值 |
| Max() | 结果中的最大值 |
| Average() | 数字结果的品均值 |
| Sum() | 所有数字结果的总和 |
WriteLine(queryResults.Count());
8.组合查询
组合查询中的数据通过键(key)字段来组合,每个组的所以成员都共享这个字段,下例中的键字段为Region:
group c by c.Region
要和计算每个组的总和,应生成一个新的结果集cg:

group c by c.Region into cg var queryResults = from c in customers group c by c.Region into cg select new { TotalSales = cg.Sum(c => c.Sales), Region = cg.Key } ; var orderedResults = from cg in queryResults orderby cg.TotalSales descending select cg ; WriteLine("Total : By Sales : Region ----- ------"); foreach (var item in orderedResults) { WriteLine($"{item.TotalSales} : {item.Region}"); }
9.Join查询
使用join,即可用一个查询搜索两个列表中的相关数据,用键字段把结果连接起来
9.1 内部联接

class Customer { public string ID { get; set; } public string City { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public string Region { get; set; } public decimal Sales { get; set; } } class Order { public string ID { get; set; } public decimal Amount { get; set; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<Order> orders = new List<Order> { new Order { ID="P", Amount=100 }, new Order { ID="Q", Amount=200 }, new Order { ID="R", Amount=300 }, new Order { ID="S", Amount=400 }, new Order { ID="T", Amount=500 }, new Order { ID="U", Amount=600 }, new Order { ID="V", Amount=700 }, new Order { ID="W", Amount=800 }, new Order { ID="X", Amount=900 }, new Order { ID="Y", Amount=1000 }, new Order { ID="Z", Amount=1100 } }; List<Customer> customers = new List<Customer> { new Customer { ID="A", City="New York", Country="USA", Region="North America", Sales=9999}, new Customer { ID="B", City="Mumbai", Country="India", Region="Asia", Sales=8888}, new Customer { ID="C", City="Karachi", Country="Pakistan", Region="Asia", Sales=7777}, new Customer { ID="D", City="Delhi", Country="India", Region="Asia", Sales=6666}, new Customer { ID="E", City="São Paulo", Country="Brazil", Region="South America", Sales=5555 }, new Customer { ID="F", City="Moscow", Country="Russia", Region="Europe", Sales=4444 }, new Customer { ID="G", City="Seoul", Country="Korea", Region="Asia", Sales=3333 }, new Customer { ID="H", City="Istanbul", Country="Turkey", Region="Asia", Sales=2222 }, new Customer { ID="I", City="Shanghai", Country="China", Region="Asia", Sales=1111 }, new Customer { ID="J", City="Lagos", Country="Nigeria", Region="Africa", Sales=1000 }, new Customer { ID="K", City="Mexico City", Country="Mexico", Region="North America", Sales=2000 }, new Customer { ID="L", City="Jakarta", Country="Indonesia", Region="Asia", Sales=3000 }, new Customer { ID="M", City="Tokyo", Country="Japan", Region="Asia", Sales=4000 }, new Customer { ID="N", City="Los Angeles", Country="USA", Region="North America", Sales=5000 }, new Customer { ID="O", City="Cairo", Country="Egypt", Region="Africa", Sales=6000 }, new Customer { ID="P", City="Tehran", Country="Iran", Region="Asia", Sales=7000 }, new Customer { ID="Q", City="London", Country="UK", Region="Europe", Sales=8000 }, new Customer { ID="R", City="Beijing", Country="China", Region="Asia", Sales=9000 }, new Customer { ID="S", City="Bogotá", Country="Colombia", Region="South America", Sales=1001 }, new Customer { ID="T", City="Lima", Country="Peru", Region="South America", Sales=2002 } }; var queryResults = from c in customers join o in orders on c.ID equals o.ID select new { c.ID, c.City, SalesBefore = c.Sales, NewOrder = o.Amount, SalesAfter = c.Sales + o.Amount }; foreach (var item in queryResults) { WriteLine(item); } Write("Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:"); ReadLine(); } }
输出结果如下:

{ ID = P, City = Tehran, SalesBefore = 7000, NewOrder = 100, SalesAfter = 7100 }
{ ID = Q, City = London, SalesBefore = 8000, NewOrder = 200, SalesAfter = 8200 }
{ ID = R, City = Beijing, SalesBefore = 9000, NewOrder = 300, SalesAfter = 9300 }
{ ID = S, City = Bogotá, SalesBefore = 1001, NewOrder = 400, SalesAfter = 1401 }
{ ID = T, City = Lima, SalesBefore = 2002, NewOrder = 500, SalesAfter = 2502 }
Program finished, press Enter/Return to continue:
9.2 分组联接
使用join...into...实现分组连接

class Person { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } } class Pet { public string Name { get; set; } public Person Owner { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// This example performs a grouped join. /// </summary> public static void GroupJoinExample() { Person magnus = new Person { FirstName = "Magnus", LastName = "Hedlund" }; Person terry = new Person { FirstName = "Terry", LastName = "Adams" }; Person charlotte = new Person { FirstName = "Charlotte", LastName = "Weiss" }; Person arlene = new Person { FirstName = "Arlene", LastName = "Huff" }; Pet barley = new Pet { Name = "Barley", Owner = terry }; Pet boots = new Pet { Name = "Boots", Owner = terry }; Pet whiskers = new Pet { Name = "Whiskers", Owner = charlotte }; Pet bluemoon = new Pet { Name = "Blue Moon", Owner = terry }; Pet daisy = new Pet { Name = "Daisy", Owner = magnus }; // Create two lists. List<Person> people = new List<Person> { magnus, terry, charlotte, arlene }; List<Pet> pets = new List<Pet> { barley, boots, whiskers, bluemoon, daisy }; // Create a list where each element is an anonymous type // that contains the person's first name and a collection of // pets that are owned by them. var query = from person in people join pet in pets on person equals pet.Owner into gj // join...into...语句 select new { OwnerName = person.FirstName, Pets = gj }; foreach (var v in query) { // Output the owner's name. Console.WriteLine($"{v.OwnerName}:"); // Output each of the owner's pet's names. foreach (Pet pet in v.Pets) Console.WriteLine($" {pet.Name}"); } }
输出结果如下:

This code produces the following output:
Magnus:
Daisy
Terry:
Barley
Boots
Blue Moon
Charlotte:
Whiskers
Arlene:
9.3 左外部联接
左外部联接是这样定义的:返回第一个集合的每个元素,无论该元素在第二个集合中是否有任何相关元素。 可以使用 LINQ 通过对分组联接的结果调用 DefaultIfEmpty 方法来执行左外部联接。

class Person { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } } class Pet { public string Name { get; set; } public Person Owner { get; set; } } public static void LeftOuterJoinExample() { Person magnus = new Person { FirstName = "Magnus", LastName = "Hedlund" }; Person terry = new Person { FirstName = "Terry", LastName = "Adams" }; Person charlotte = new Person { FirstName = "Charlotte", LastName = "Weiss" }; Person arlene = new Person { FirstName = "Arlene", LastName = "Huff" }; Pet barley = new Pet { Name = "Barley", Owner = terry }; Pet boots = new Pet { Name = "Boots", Owner = terry }; Pet whiskers = new Pet { Name = "Whiskers", Owner = charlotte }; Pet bluemoon = new Pet { Name = "Blue Moon", Owner = terry }; Pet daisy = new Pet { Name = "Daisy", Owner = magnus }; // Create two lists. List<Person> people = new List<Person> { magnus, terry, charlotte, arlene }; List<Pet> pets = new List<Pet> { barley, boots, whiskers, bluemoon, daisy }; var query = from person in people join pet in pets on person equals pet.Owner into gj from subpet in gj.DefaultIfEmpty() // 调用 DefaultIfEmpty 方法 select new { person.FirstName, PetName = subpet?.Name ?? String.Empty }; foreach (var v in query) { Console.WriteLine($"{v.FirstName+":",-15}{v.PetName}"); } }
输出结果如下:

This code produces the following output:
Magnus: Daisy
Terry: Barley
Terry: Boots
Terry: Blue Moon
Charlotte: Whiskers
Arlene:
10.LINQ to XML
10.1 LINQ to XML函数构造方式
引入命名空间System.Xml.Linq

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { XDocument xdoc = new XDocument( // XML文档 new XElement("BookStore", // 元素列表 new XElement("Book", new XElement("Name", "C#", new XAttribute("BookName", "C#")), // 元素特性 new XElement("Author", "Martin", new XAttribute("Name", "Martin")), new XElement("Adress", "ShangHai"), new XElement("Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd")) ), new XElement("Book", new XElement("Name", "WCF", new XAttribute("BookName", "WCF")), new XElement("Author", "Mary", new XAttribute("Name", "Mary")), new XElement("Adress", "BeiJing"), new XElement("Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd")) ) ) ) ); WriteLine(xdoc); ReadLine(); } }
输出结果如下:

<BookStore> <Book> <Name BookName="C#">C#</Name> <Author Name="Martin">Martin</Author> <Adress>ShangHai</Adress> <Date>2018-09-19</Date> </Book> <Book> <Name BookName="WCF">WCF</Name> <Author Name="Mary">Mary</Author> <Adress>BeiJing</Adress> <Date>2018-09-19</Date> </Book> </BookStore>
10.2 将XML写入文件

class Program
{
public static void CreatXmlTree(string xmlPath)
{
XElement xElement = new XElement(
new XElement("BookStore",
new XElement("Book",
new XElement("Name", "C#", new XAttribute("BookName", "C#")),
new XElement("Author", "Martin", new XAttribute("Name", "Martin")),
new XElement("Adress", "ShangHai"),
new XElement("Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd"))
),
new XElement("Book",
new XElement("Name", "WCF", new XAttribute("BookName", "WCF")),
new XElement("Author", "Mary", new XAttribute("Name", "Mary")),
new XElement("Adress", "BeiJing"),
new XElement("Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd"))
)
)
);
XmlWriterSettings settings = new XmlWriterSettings
{
Encoding = new UTF8Encoding(false),
Indent = true
};
XmlWriter xw = XmlWriter.Create(xmlPath, settings);
xElement.Save(xw);
//写入文件
xw.Flush();
xw.Close();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string path = @"D:BookStore.xml";
CreatXmlTree(path);
}
}
