NN,Nearest Neighbor,最近邻
KNN,K-Nearest Neighbor,K最近邻
KNN分类的思路:
- 分类的过程其实是直接将测试集的每一个图片和训练集中的所有图片进行比较,计算距离(这里使用L2距离)。
- 距离越远,代表图片之间的相似度越低;距离越近,代表图片之间越相似。
- 找到和测试图片距离最近的K个图,统计它们的分类,数量最多的分类就作为测试图片的分类。
Python实现:
1、加载CIFAR-10数据,参考前一篇 CIFAR-10和python读取
- X_train,训练集 (50000,32,32,3)
- y_train, 训练分类集 (50000,)
- X_test, 测试集 (5000,32,32,3)
- y_test,测试分类集 (5000,)
# Load the raw CIFAR-10 data. cifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py' # Cleaning up variables to prevent loading data multiple times (which may cause memory issue) try: del X_train, y_train #del 只删除变量,不删变量引用的数据 del X_test, y_test print('Clear previously loaded data.') except: pass X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir)
为了提高执行效率,只从中取出5000和500个训练和测试数据,并变形为(5000,3072)和(500,3072)。
其中,3072=32*32*3,代表一个图片。
2、创建KNN分类器
from cs231n.classifiers import KNearestNeighbor classifier = KNearestNeighbor() classifier.train(X_train, y_train)
KNN分类并不对训练集做处理,只是单纯的保存下来。
class KNearestNeighbor(object): def __init__(self): pass def train(self, X, y): self.X_train = X self.y_train = y
3、计算距离
下面给出了三种计算距离的方式,最后可以看出向量计算的效率是最高的,
- 双层循环
- 单层循环
- 无循环
双层循环:效率低
def compute_distances_two_loops(self, X): num_test = X.shape[0] num_train = self.X_train.shape[0] dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train)) for i in range(num_test): for j in range(num_train): # numpy中的array可以直接逐元素相减 # square可以对整个array中的某一行中的每个元素做平方 dists[i, j] = np.sqrt( np.sum( np.square( self.X_train[ j, : ] - X[ i, : ]) ) )
return dists
单层循环:
和双层循环的区别在于,直接用整个数组减去另一个数组的一行,实现的就是每行相减的效果。
def compute_distances_one_loop(self, X): num_test = X.shape[0] num_train = self.X_train.shape[0] dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train)) for i in range(num_test): # self.X_train - X[ i, : ], 前者的每行减去后者 # np.sum中的axis =1, 表示每行中的所有列相加 dists[i, :] = np.sqrt( np.sum( np.square( self.X_train - X[ i, : ]), axis=1 ) ) return dists
无循环:
利用
- L2距离平方和的展开
- numpy的广播机制(broadcast)https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/user/basics.broadcasting.html
def compute_distances_no_loops(self, X): num_test = X.shape[0] num_train = self.X_train.shape[0] dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train)) # 思路:L2距离展开,x-y的平方等于 x的平方 + y的平方 - 2xy, 2xy中的y需要从行转为列,再和x做点积。 # 最后生成的矩阵的每个元素,就是x-y的平方 # 2xy d1 = np.dot(X, self.X_train.T) #x的平方,keepdims=True,是保持矩阵的维度;500*1 # False,结果是一维的, 1*500 d2 = np.sum( np.square(X), axis=1, keepdims=True) #y的平方 d3 = np.sum( np.square(self.X_train), axis=1, keepdims=True)
# 广播 # 500*1 和5000* 1是不能相加的 # 500*1 和5000*1的转置(1*5000)相加,会得到500 * 5000矩阵 dists = np.sqrt(d2 + d3.T - 2*d1) return dists
可以计算三个方式获取的dists之间的差别,没有问题的话,difference应该是0
# np.linalg.norm, 计算范数 # fro,F-范数,矩阵范数,矩阵中各项元素的绝对值平方的总和 difference = np.linalg.norm(dists - dists_one, ord='fro')
4、分类
def predict_labels(self, dists, k=1): num_test = dists.shape[0] y_pred = np.zeros(num_test) for i in range(num_test): closest_y = [] # np.argsort,排序后的索引list,对应原array_like labels = self.y_train[np.argsort(dists[i, :])].flatten() # [0:k] 取0到k-1 closest_y = labels[0:k] # Counter, 统计每个元素出现的次数 c = Counter(closest_y) # most_common(n) 取数量最多的前n种 # most_common(1) = [(2, 3)], list, 2是种类,3是次数 # c.most_common(1)[0] = (2, 3), tuple # c.most_common(1)[0][0] = 2 y_pred[i] = c.most_common(1)[0][0] return y_pred
5、交叉验证
- 交叉验证就是将训练集分为N等分,
- 取其中一份作为验证集,其他作为训练集。
- 每个等分分别做一次验证集,实现交叉验证。
- 交叉验证可以减少过拟合。
num_folds = 5 k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100] X_train_folds = [] y_train_folds = [] # array_split,将数组等分 # 和split的区别是,在不能等分的情况下,也能做到尽量等分。 X_train_folds = np.array_split(X_train, num_folds) y_train_folds = np.array_split(y_train, num_folds) k_to_accuracies = {} for k in k_choices: k_to_accuracies[k] = [] for i in range(num_folds): y_pred = classifier.predict_labels(X_train_folds[i], k=k) # ==比较两个数组,可以得到相等元素的个数 num_correct = np.sum(y_pred == y_train_folds[i]) accuracy = float(num_correct) / len(X_train_folds[i]) k_to_accuracies[k].append(accuracy)
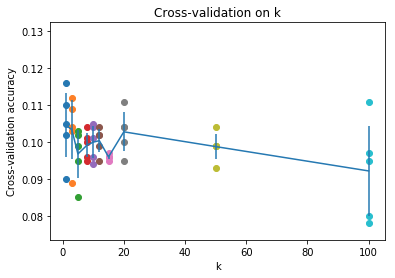
准确率统计图
# plot the raw observations for k in k_choices: accuracies = k_to_accuracies[k] plt.scatter([k] * len(accuracies), accuracies) # plot the trend line with error bars that correspond to standard deviation # 平均值 accuracies_mean = np.array([np.mean(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())]) # 标准差 accuracies_std = np.array([np.std(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())]) plt.errorbar(k_choices, accuracies_mean, yerr=accuracies_std) # 误差图 plt.title('Cross-validation on k') plt.xlabel('k') plt.ylabel('Cross-validation accuracy') plt.show()
每个k对应5个交叉验证数据集,得到5个准确率,再取均值。最后的连线就是均值的连线。
python相关:
1、ndarray之间可以直接算术运算,相同维度的可以,不同维度的,通过广播也可以做到。
2、一些函数也可以直接对整个ndarray操作,实际上是对其中的每个元素操作。np.square
用到的一些方法:
- np.sqrt, np.sum
- np.argsort,排序后得到的对应原数组的索引数组。
- flattern,转为1维数组
- Counter,from collections import Counter, 统计list中每个元素出现的次数
- most_common(n),取数量最多的前n种
- np.array_split,等分ndarray
- ==,可以取得数组中对应的元素个数
- np.linalg.norm, 计算范数
- np.random.choice, 随机选择
- np.flatnonzero, 返回不等于0 的索引集合
- np.mean, 计算平均值
- np.std, 计算标准差
- %load_ext autoreload,# 引用的其他模块更改了,可以自动重新加载
Reference: