第五章:Linux内核链表的遍历
/** * list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each(pos, head) for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
这是遍历链表的一个方法,其实就是一个for循环的宏啦!写得很清楚。但是这些操作的还是struct list_head,跟我要的结构体没有半毛钱关系,怎么办?继续看:
/** * list_entry - get the struct for this entry * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr, type, member)
这个就是由我们自定义的结构体中包含的struct list_head获得结构体的方式,其实就是上一篇博客的container_of的第二个名字啦!container_of到了这山沟里就换了一个很土的名字啦!
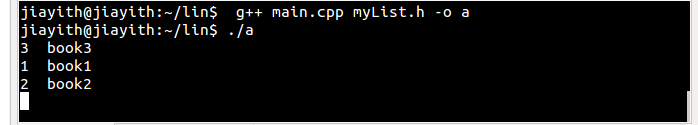
好了,下面看代码就一清二楚了:
struct list_head *p; //pointer to each struct list_head struct Book *pb; //pointer to struct Book list_for_each(p,&MyBkList) { pb = list_entry(p, struct Book,list); cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; }
输出:

#include <string> using std::string; /*ÁŽ±íœÚµã*/ struct list_head { struct list_head *next, *prev; }; /*±íÊŸÊéµÄœá¹¹Ìå*/ struct Book { int bkId; string bkName; struct list_head list; //ËùÓеÄBookœá¹¹ÌåÐγÉÁŽ±í }; /*³õÊŒ»¯ÁŽ±í*/ static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) { list->next = list; list->prev = list; } /* * Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries. * * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know * the prev/next entries already! */ static inline void __list_add(struct list_head * new1,struct list_head * prev,struct list_head * next) { next->prev = new1; new1->next = next; new1->prev = prev; prev->next = new1; } /** * list_add_tail - add a new entry * @new: new entry to be added * @head: list head to add it before * * Insert a new entry before the specified head. * This is useful for implementing queues. */ static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new1, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new1, head->prev, head); } /** * list_add - add a new entry * @new: new entry to be added * @head: list head to add it after * * Insert a new entry after the specified head. * This is good for implementing stacks. */ static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new1, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new1, head, head->next); } /** * container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure * @ptr: the pointer to the member. * @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the member within the struct. * */ #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ const typeof(((type *)0)->member) *__mptr = (ptr); (type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); }) /** * list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each(pos, head) for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) /** * list_entry - get the struct for this entry * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr, type, member) /** * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. */ #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member) /** * list_next_entry - get the next element in list * @pos: the type * to cursor * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_next_entry(pos, member) list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member) /** * list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); &pos->member != (head); pos = list_next_entry(pos, member)) #undef offsetof #ifdef __compiler_offsetof #define offsetof(TYPE,MEMBER) __compiler_offsetof(TYPE,MEMBER) #else #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER) #endif

#include <iostream> #include "myList.h" using namespace std; int main(void) { struct list_head MyBkList; //ŽŽœšÎÒµÄÁŽ±íÍ· INIT_LIST_HEAD(&MyBkList); //³õÊŒ»¯ÕâžöÁŽ±í /*ŽŽœšÐÂÊéœá¹¹Ìå*/ struct Book bk1; bk1.bkId = 1; bk1.bkName = "book1"; list_add_tail(&bk1.list, &MyBkList); //°ÑÐÂÊé1ŒÓµœÍ·œáµãMyBkListºóÃæ struct Book bk2; bk2.bkId = 2; bk2.bkName = "book2"; list_add_tail(&bk2.list,&MyBkList); //°ÑÊé2ŒÓµœbk1ÓëMyBkListÖ®Œä£¬°ÑMyBkList¿Ž×öÍ·£¬ÔòΪMyBkList->bk1->bk2(°ŽÕ՜ڵãnextÖžÕ룬MyBkListµÄnextÖžÕëÊÇûÓбäµÄ£¬MyBkListµÄprevÖžÕë±äÁË) struct Book bk3 = { 3, "book3" }; list_add(&bk3.list, &MyBkList); //°ÑÊé3ŒÓµœheadÖ®ºó£¬ŒŽheadµÄnextÖžÕë struct list_head *p; //pointer to each struct list_head struct Book *pb; //pointer to struct Book list_for_each(p,&MyBkList) { pb = list_entry(p, struct Book,list); cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; } /* list_for_each_entry(pb, &MyBkList, list) { cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; }*/ cin.get(); }
还有一个人更漂亮的遍历函数list_for_each_entry:
/** * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. */ #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member) /** * list_next_entry - get the next element in list * @pos: the type * to cursor * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_next_entry(pos, member) list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member) /** * list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); &pos->member != (head); pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))
使用起来更好看:
struct Book *pb; //pointer to struct Book list_for_each_entry(pb, &MyBkList, list) { cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; }
当然还有反向遍历等,就不多赘述了。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
第六章:Linux内核链表删除
先来看看这个基本的删除节点的函数,这是其他删除函数的基础。其实这个删除函数和添加节点到链表的函数是对应的,添加的基本函数不也是以前后指针为参数并把节点添加到中间吗?Linux内核就是帅!
/* * Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries * point to each other. * * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know * the prev/next entries already! */ static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next) { next->prev = prev; prev->next = next; }
下面看调用上面函数的函数,其实list_del()是最常用的函数了,其他函数也只是铺垫:
/** * list_del - deletes entry from list. * @entry: the element to delete from the list. * Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is * in an undefined state. */ #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); } static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); entry->next = LIST_POISON1; entry->prev = LIST_POISON2; } #else extern void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry); extern void list_del(struct list_head *entry); #endif
其中,LIST_POISON1、LIST_POISON2 在我的M:linux-3.14.5includelinux下poison.h文件中:
/* * These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults * under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses * non-initialized list entries. */ #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA) #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
/* * Architectures might want to move the poison pointer offset * into some well-recognized area such as 0xdead000000000000, * that is also not mappable by user-space exploits: */ #ifdef CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA _AC(CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE, UL) #else # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0 #endif
上面的一些宏定义作用是:调用 __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)删除一个给定节点,这个函数会调用__list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next),这样使得待删除的节点的前后节点因为正确连到链表里面而没有了问题了,但是待删除节点还是的结构体还是在的,其实并没有删除它,只是把它从链表里面踢出去了。为了防止意外访问到这个节点的前后节点(因为它已经不在链表中了)而出错,就给它的前后指针赋了一个非空但访问会引起页面错误的指针,表明小心中毒哦!
目前为止代码如下:

#include <iostream> #include "myList.h" using namespace std; int main(void) { struct list_head MyBkList; //ŽŽœšÎÒµÄÁŽ±íÍ· INIT_LIST_HEAD(&MyBkList); //³õÊŒ»¯ÕâžöÁŽ±í /*ŽŽœšÐÂÊéœá¹¹Ìå*/ struct Book bk1; bk1.bkId = 1; bk1.bkName = "book1"; list_add_tail(&bk1.list, &MyBkList); //°ÑÐÂÊé1ŒÓµœÍ·œáµãMyBkListºóÃæ struct Book bk2; bk2.bkId = 2; bk2.bkName = "book2"; list_add_tail(&bk2.list,&MyBkList); //°ÑÊé2ŒÓµœbk1ÓëMyBkListÖ®Œä£¬°ÑMyBkList¿Ž×öÍ·£¬ÔòΪMyBkList->bk1->bk2(°ŽÕ՜ڵãnextÖžÕ룬MyBkListµÄnextÖžÕëÊÇûÓбäµÄ£¬MyBkListµÄprevÖžÕë±äÁË) struct Book bk3 = { 3, "book3" }; list_add(&bk3.list, &MyBkList); //°ÑÊé3ŒÓµœheadÖ®ºó£¬ŒŽheadµÄnextÖžÕë struct list_head *p; //pointer to each struct list_head /* list_for_each(p,&MyBkList) { pb = list_entry(p, struct Book,list); cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; }*/ struct Book *pb; //pointer to struct Book list_for_each_entry(pb, &MyBkList, list) { cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; } cout<<"------------------------------------"<<endl; struct Book bk4={4,"book4"}; list_add_tail(&bk4.list,&MyBkList); list_del(&bk3.list); list_for_each_entry(pb, &MyBkList, list) { cout << pb->bkId << " " << pb->bkName << endl; } cin.get(); }

#include <string> /* * Architectures might want to move the poison pointer offset * into some well-recognized area such as 0xdead000000000000, * that is also not mappable by user-space exploits: */ #ifdef CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA _AC(CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE, UL) #else # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0 #endif /* * These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults * under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses * non-initialized list entries. */ #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA) #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA) using std::string; /*ÁŽ±íœÚµã*/ struct list_head { struct list_head *next, *prev; }; /*±íÊŸÊéµÄœá¹¹Ìå*/ struct Book { int bkId; string bkName; struct list_head list; //ËùÓеÄBookœá¹¹ÌåÐγÉÁŽ±í }; /*³õÊŒ»¯ÁŽ±í*/ static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) { list->next = list; list->prev = list; } /* * Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries. * * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know * the prev/next entries already! */ static inline void __list_add(struct list_head * new1,struct list_head * prev,struct list_head * next) { next->prev = new1; new1->next = next; new1->prev = prev; prev->next = new1; } /** * list_add_tail - add a new entry * @new: new entry to be added * @head: list head to add it before * * Insert a new entry before the specified head. * This is useful for implementing queues. */ static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new1, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new1, head->prev, head); } /** * list_add - add a new entry * @new: new entry to be added * @head: list head to add it after * * Insert a new entry after the specified head. * This is good for implementing stacks. */ static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new1, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new1, head, head->next); } /** * container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure * @ptr: the pointer to the member. * @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the member within the struct. * */ #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ const typeof(((type *)0)->member) *__mptr = (ptr); (type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); }) /** * list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each(pos, head) for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) /** * list_entry - get the struct for this entry * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr, type, member) /** * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. */ #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member) /** * list_next_entry - get the next element in list * @pos: the type * to cursor * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_next_entry(pos, member) list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member) /** * list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); &pos->member != (head); pos = list_next_entry(pos, member)) /* * Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries * point to each other. * * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know * the prev/next entries already! */ static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next) { next->prev = prev; prev->next = next; } /** * list_del - deletes entry from list. * @entry: the element to delete from the list. * Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is * in an undefined state. */ static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); } static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); entry->next = (struct list_head *)LIST_POISON1; //Linux kernel source does not have (struct list_head *) entry->prev = (struct list_head *)LIST_POISON2; } #undef offsetof #ifdef __compiler_offsetof #define offsetof(TYPE,MEMBER) __compiler_offsetof(TYPE,MEMBER) #else #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER) #endif
到这里已经简单模拟实现了Linux内核链表最最基本的功能,还有其他功能,有兴趣的直接上源代码!
