1.Spring 容器相关的概念理解:
1)Spring的容器为ApplicationContext或BeanFactory(被称为IOC容器)
IOC容器负责实例化、定位、配置应用程序中的对象及建立这些对象间的依赖。应用程序无需直接在代码中new相关的对象,应用程序由IOC容器进行组装。
在Spring中BeanFactory是IOC容器的实际代表者。
2)Spring IOC容器如何知道哪些是它管理的对象呢?
Spring IOC容器通过读取配置文件中的配置元数据,然后对元数据对应用中的各个对象进行实例化及装配。一般使用基于xml配置文件进行配置元数据,而且Spring与配置文件完全解耦的,可以使用其他任何可能的方式进行配置
元数据,比如注解、基于java文件的、基于属性文件的配置都可以。
3)Spring IOC容器管理的对象被称为Bean
Bean就是由Spring容器初始化、装配及管理的对象,除此之外,bean就与应用程序中的其他对象没有什么区别。
疑问:IOC怎样确定如何实例化Bean、管理Bean之间的依赖关系以及管理Bean?简单说:这就需要配置元数据,带着这些疑问开始Spring容器的源码之旅吧.
2.IOC的实现原理就可以分为三个部分
1)通过代码解析xml这些配置文件,因为文件中包含<beans>,<bean>,<property>,<ref>,<value>,<list>等这样的标签内容,而<bean>标签中又有id/class等这样的属性;
2)创建“容器”,因为bean就是类实例化后存放在Spring容器中,所以这个容器需要Spring创建出来;
3)初始化bean
3.基本的初始化容器的代码示列:
public class SpringContainerApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/spring-context.xml");
OrderService orderService= context.getBean(OrderServiceImpl.class);
orderService.getOrderDetail();
//怎么样通过配置文件来启动 Spring 的 ApplicationContext,ApplicationContext 启动过程中,会负责创建实例 Bean,往各个 Bean 中注入依赖等
}
}
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
public String getOrderDetail() {
System.out.println("订单查询执行完成!");
return "";
}
}
public interface OrderService {
String getOrderDetail();
}
4.根据3中容器初始化的代码 并结合如下类图及源码理解Spring容器原理
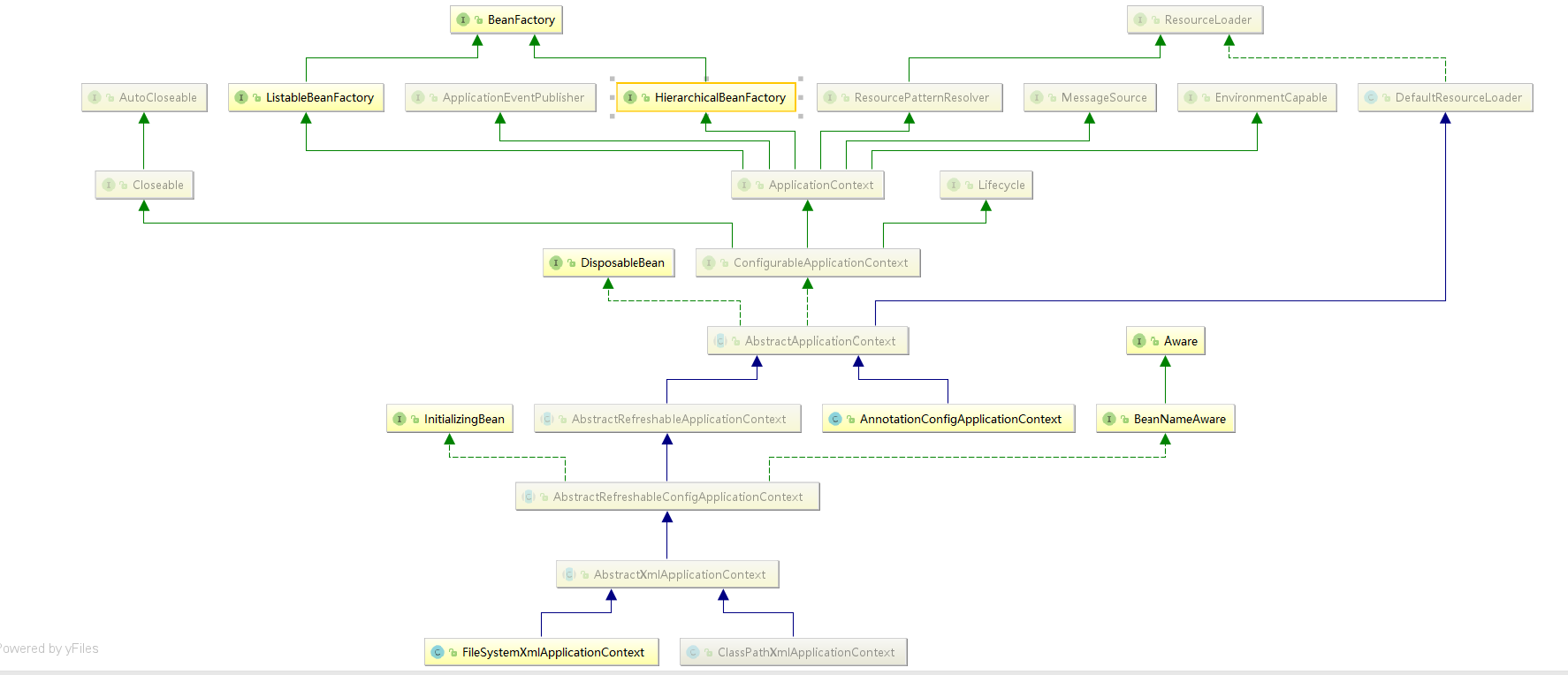
类图简单说明:
1)ApplicationContext(接口)容器继承了 ListableBeanFactory(接口),通过ListableBeanFactory 接口,我们可以获取多个 Bean,最顶层 BeanFactory 接口的方法都是获取单个Bean的。
2)ApplicationContext(接口)容器继承了 HierarchicalBeanFactory(接口),通过HierarchicalBeanFactory接口,我们可以获取父关系的bean、是否包含子bean
3)AutowireCapableBeanFactory(接口) 继承了BeanFactory(接口),它就是用来自动装配 Bean 用的。在 ApplicationContext 中通过方法 getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() 来使用它
这里的 BeanDefinition 就是我们所说的 Spring 的 Bean,我们自己定义的各个 Bean 其实会转换成一个个 BeanDefinition 存在于 Spring 的 BeanFactory 中
步骤1:理解ClassPathXmlApplicationContext

1 public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext { 2 3 private Resource[] configResources; 4 5 //创建一个新的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,从给定的XML文件加载定义信息,并自动刷新上下文。 6 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { 7 this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); 8 } 9 10 11 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 12 throws BeansException { 13 //Create a new AbstractXmlApplicationContext with the given parent context 14 //用已经有的 ApplicationContext 创建一个新的 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 并配置成父子关系 15 super(parent); 16 17 //Set the config locations for this application context. 18 //解析xml配置文件列表,放置到成员变量 configResources 数组中 19 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 20 21 if (refresh) { 22 //在ApplicationContext 建立起来以后,其实我们是可以通过调用 refresh() 这个方法进行重建的,这样会将原来的 ApplicationContext 销毁,然后再重新执行一次初始化操作 23 refresh(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
步骤2:进入org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法

@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { //在销毁ApplicationContext 需要加锁,使用 synchronized 使用同步方法块锁定this.startupShutdownMonitor对象 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // 刷新前准备:记录下容器的启动时间、标记启动状态、处理配置文件(properties文件)中的占位符 prepareRefresh(); /* 这步完成后,配置文件就会解析成一个个BeanDefinition,注册到BeanFactory 中,这里说的 Bean 还没有初始化,只是配置信息都提取出来了, 注册也只是将这些信息都保存到了注册中心(说到底核心是一个beanName->beanDefinition的map) */ // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. //设置BeanFactory的类加载器:在初始化完成之后,修改应用程序上下文的内部bean工厂。所有bean定义都将被加载,但没有加载bean将被实例化。 //这允许注册特殊某些ApplicationContext实现中的BeanPostProcessor等。 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. //调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor各个实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); /* *Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 首先:注册实现PriorityOrdered的beanPostProcessor;其次注册实现Ordered的BeanPostProcessor;最后,重新注册所有内部beanPostProcessor。 */ registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. // 初始化当前 ApplicationContext 的事件广播器 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. //典型的模板方法(钩子方法),具体的子类可以在这里初始化一些特殊的 Bean(在初始化 singleton beans 之前) onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. //注册事件监听器,监听器需要实现 ApplicationListener 接口 registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //初始化所有的 singleton beans finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. // 最后,广播事件,ApplicationContext 初始化完成 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. //销毁已经初始化的 singleton 的 Beans,以免有些 bean 会一直占用资源 destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
步骤2.1 obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法理解:

public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean { protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { /* 子类必须实现此方法才能执行实际的配置加载。在任何其他初始化工作之前,调用该方法。子类要么创建一个新的bean工厂并保存对它的引用,或者返回它持有的单个BeanFactory实例。 在后一种情况下,如果多次刷新上下文,通常会引发IllegalStateException。 关闭旧的 BeanFactory (如果有),创建新的 BeanFactory,加载 Bean 定义、注册 Bean 等等 */ refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; } }

//org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext { @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //如果 ApplicationContext 中已经加载过 BeanFactory 了,销毁所有 Bean,关闭 BeanFactory。 应用中 BeanFactory 本来就是可以多个的,这里可不是说应用全局是否有 BeanFactory,而是当前 ApplicationContext是否有 BeanFactory if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //初始化一个 DefaultListableBeanFactory DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); //用于 BeanFactory 的序列化 beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); //设置 BeanFactory 的两个配置属性:是否允许 Bean 覆盖、是否允许循环引用 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); //加载 BeanDefinition到 BeanFactory 中,但还不是真正的加载BeanDefinition,只是做准备 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } } }
ApplicationContext 继承自 BeanFactory,但是它不应该被理解为 BeanFactory 的实现类,而是说其内部持有一个实例化的 BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory)。
以后所有的 BeanFactory 相关的操作其实是给这个实例来处理的。

//org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#customizeBeanFactory protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) { //是否允许 Bean 定义覆盖 beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) { // 是否允许 Bean 间的循环依赖 beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences); } }

org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory) @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. // 给这个 BeanFactory 实例化一个 XmlBeanDefinitionReader,来加载各个 Bean XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. // 初始化 BeanDefinitionReader,其实这个是提供给子类覆写的 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }

public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement { //默认只提供 sington 和 prototype 大家还知道的:request, session, globalSession, application, websocket 这几种属于基于 web 的扩展 String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton"; String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype"; int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0; int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1; int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2; //获取父 Bean String getParentName(); //设置父 Bean,这里涉及到 bean 继承,不是 java 继承 void setParentName(String var1); //获取 Bean 的类名称 String getBeanClassName(); //设置 Bean 的类名称 void setBeanClassName(String var1); //获取工厂名称 String getFactoryBeanName(); //如果该 Bean 采用工厂方法生成,指定工厂名称。 void setFactoryBeanName(String var1); //获取工厂类中的 工厂方法名称 String getFactoryMethodName(); //指定工厂类中的 工厂方法名称 void setFactoryMethodName(String var1); //获取 bean 的 scope String getScope(); //设置 bean 的 scope void setScope(String var1); boolean isLazyInit(); void setLazyInit(boolean var1); //返回该 Bean 的所有依赖 String[] getDependsOn(); //设置该 Bean 依赖的所有的 Bean,注意,这里的依赖不是指属性依赖(如 @Autowire 标记的),而是 depends-on="" 属性设置的值 void setDependsOn(String... var1); // 该 Bean 是否可以注入到其他 Bean 中 boolean isAutowireCandidate(); //设置该 Bean 是否可以注入到其他 Bean 中,只对根据类型注入有效。如果根据名称注入,即使这边设置了 false,也是可以的 void setAutowireCandidate(boolean var1); boolean isPrimary(); void setPrimary(boolean var1); //获取构造器参数 ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues(); //Bean 中的属性值,后面给 bean 注入属性值的时候会说到 MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues(); boolean isSingleton(); boolean isPrototype(); //如果这个 Bean 原生是抽象类,那么不能实例化 boolean isAbstract(); int getRole(); String getDescription(); String getResourceDescription(); BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); }
未完待续...
参看文章:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/2637e5b2acd1
https://www.cnblogs.com/deng-cc/p/6927447.html idea 查看类的继承关系图
