一、基本API初探
package java8.stream; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.IntSummaryStatistics; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** * @author jiaqing.xu@hand-china.com * @version 1.0 * @name * @description * @date 2018/7/15 */ public class BasicTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建串行流 List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl"); List<String> filtered = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList()); filtered.forEach(System.out::println); //使用foreach进行数据迭代 limit 方法用于获取指定数量的流 Random random = new Random(); random.ints().limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); //Map用于映射每个元素对应的结果,原值为i 映射到i*i .collect(Collectors.toList()):将stream再转换回list集合 List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5); // 获取对应的平方数 List<Integer> squaresList = numbers.stream().map( i -> i*i).distinct().limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList()); squaresList.forEach(System.out::println); //filter 方法用于通过设置的条件过滤出元素 List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl"); // 获取空字符串的数量 Long count = stringList.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count(); System.out.println("The count of empty string:"+count); //sorted用于对流进行排序,默认是从小到大 List<Integer> array = Arrays.asList(1,3,2,4); List<Integer> sortedList = array.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList()); sortedList.forEach(System.out::println); //流并行处理程序parallelStream List<String> stringList2 = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl",""); // 获取空字符串的数量 Long count2 = stringList2.parallelStream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count(); System.out.println("The count of empty string:"+count2); //collectors 可以返回列表或者字符串 List<String> stringList3 = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl",""); String mergedString = stringList3.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.joining(", ")); System.out.println("合并字符串: " + mergedString); // int[] numberList = {12,3,34,67,100,99}; IntStream intStream = IntStream.of(numberList); IntSummaryStatistics stats = intStream.summaryStatistics(); System.out.println("列表中最大的数 : " + stats.getMax()); System.out.println("列表中最小的数 : " + stats.getMin()); System.out.println("所有数之和 : " + stats.getSum()); System.out.println("平均数 : " + stats.getAverage()); } }
二、分组和合并
1 /** 2 * @author jiaqing.xu@hand-china.com 3 * @version 1.0 4 * @name 5 * @description 分组、合并测试dto 6 * @date 2018/7/15 7 */ 8 public class Foo { 9 10 private int code; 11 12 private int count; 13 14 public Foo(int code, int count) { 15 this.code = code; 16 this.count = count; 17 } 18 19 public int getCode() { 20 return code; 21 } 22 23 public void setCode(int code) { 24 this.code = code; 25 } 26 27 public int getCount() { 28 return count; 29 } 30 31 public void setCount(int count) { 32 this.count = count; 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public String toString() { 37 return "Foo{" + 38 "code=" + code + 39 ", count=" + count + 40 '}'; 41 } 42 }
/** * @author jiaqing.xu@hand-china.com * @version 1.0 * @name * @description 测试分组和合并 groupingBy方法以及reduce方法 * @date 2018/7/15 */ public class TestFoo { public static void main(String[] args) { Foo foo1 = new Foo(1, 2); Foo foo2 = new Foo(2, 23); Foo foo3 = new Foo(2, 6); List<Foo> list = new ArrayList<>(4); list.add(foo1); list.add(foo2); list.add(foo3); Map<Integer, List<Foo>> collect = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Foo::getCode)); //存储最后的汇总结果集合 List<Foo> result = new ArrayList<>(); collect.forEach((k,v)->{ Optional<Foo> sum = v.stream().reduce( (v1, v2) -> { //合并 v1.setCount(v1.getCount()+v2.getCount()); return v1; } ); result.add(sum.orElse(new Foo(0,10))); }); result.forEach(System.out::print); } }
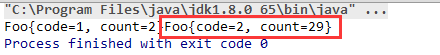
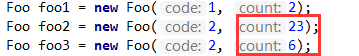
将2号记录的count值进行了合并汇总!23+6=29