As you know, an undirected connected graph with n nodes and n - 1 edges is called a tree. You are given an integer d and a tree consisting of n nodes. Each node i has a value ai associated with it.
We call a set S of tree nodes valid if following conditions are satisfied:
- S is non-empty.
- S is connected. In other words, if nodes u and v are in S, then all nodes lying on the simple path between u and v should also be presented in S.
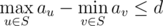 .
.
Your task is to count the number of valid sets. Since the result can be very large, you must print its remainder modulo 1000000007(109 + 7).
The first line contains two space-separated integers d (0 ≤ d ≤ 2000) and n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2000).
The second line contains n space-separated positive integers a1, a2, ..., an(1 ≤ ai ≤ 2000).
Then the next n - 1 line each contain pair of integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n) denoting that there is an edge between u and v. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree.
Print the number of valid sets modulo 1000000007.
1 4
2 1 3 2
1 2
1 3
3 4
8
0 3
1 2 3
1 2
2 3
3
4 8
7 8 7 5 4 6 4 10
1 6
1 2
5 8
1 3
3 5
6 7
3 4
41
In the first sample, there are exactly 8 valid sets: {1}, {2}, {3}, {4}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {3, 4} and {1, 3, 4}. Set {1, 2, 3, 4} is not valid, because the third condition isn't satisfied. Set {1, 4} satisfies the third condition, but conflicts with the second condition.
【题意】给你一棵树,每个节点都有一个 权值a[i],定义一种集合S,不为空,若u,v,属于S,则u->v路径上的所有的点都属于S,且集合中最大权值-最小权值<=d,求 这样的集合个数。
【分析】考虑算每一个节点的贡献。枚举每一个节点,使其成为这个集合的最小值,然后dfs,看他能走多远。dp[u]表示当前节点的子树能形成多少包括u的集合,则dp[u]=dp[u]*(dp[v]+1),v为u的儿子,+1是因为这个儿子形成的集合我可以不取。但是对于权值相同的节点可能形成 一些重复计算的集合,所以要标记一下。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define met(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a) #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N = 2e3+5;; const int M = 160009; const int mod = 1e9+7; const int mo=123; const double pi= acos(-1.0); typedef pair<int,int>pii; int n,d; int a[N],vis[N][N]; ll dp[N],ans; vector<int>edg[N]; void dfs(int u,int fa,int rt){ if(a[u]<a[rt]||a[u]-a[rt]>d)return; if(a[u]==a[rt]){ if(vis[rt][u])return; else vis[u][rt]=vis[rt][u]=1; } dp[u]=1; for(int v : edg[u]){ if(v==fa)continue; dfs(v,u,rt); dp[u]=(dp[u]*(dp[v]+1))%mod; } } int main(){ scanf("%d%d",&d,&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]); for(int i=1,u,v;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); edg[u].pb(v);edg[v].pb(u); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ met(dp,0); dfs(i,0,i); ans=(ans+dp[i])%mod; } printf("%lld ",ans); return 0; }