In one well-known algorithm of finding the k-th order statistics we should divide all elements into groups of five consecutive elements and find the median of each five. A median is called the middle element of a sorted array (it's the third largest element for a group of five). To increase the algorithm's performance speed on a modern video card, you should be able to find a sum of medians in each five of the array.
A sum of medians of a sorted k-element set S = {a1, a2, ..., ak}, where a1 < a2 < a3 < ... < ak, will be understood by as
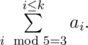
The 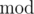 operator stands for taking the remainder, that is
operator stands for taking the remainder, that is 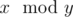 stands for the remainder of dividing x by y.
stands for the remainder of dividing x by y.
To organize exercise testing quickly calculating the sum of medians for a changing set was needed.
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of operations performed.
Then each of n lines contains the description of one of the three operations:
- add x — add the element x to the set;
- del x — delete the element x from the set;
- sum — find the sum of medians of the set.
For any add x operation it is true that the element x is not included in the set directly before the operation.
For any del x operation it is true that the element x is included in the set directly before the operation.
All the numbers in the input are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
For each operation sum print on the single line the sum of medians of the current set. If the set is empty, print 0.
Please, do not use the %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use the cin, cout streams (also you may use the %I64d specificator).
6
add 4
add 5
add 1
add 2
add 3
sum
3
14
add 1
add 7
add 2
add 5
sum
add 6
add 8
add 9
add 3
add 4
add 10
sum
del 1
sum
5
11
13
【分析】有n个操作,1:向集合中加一个数x;2:去掉集合中的数x;3:询问从小到大排序后,所有下标i%5==3的值的和。
刚开始想到线段树了,但是不知道怎么写,然后看了网上的题解。。。好强啊!!!每个节点额外保存此区间i=0~4的和,然后cnt数组保存此区间 元素的个数。
然后求和合并的时候,sum[rt][i]=sum[rt*2][i]+sum[rt*2+1][(i-cnt[rt*2]%5+5)%5];这个公式可以自己推一下。
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <time.h> #include <string> #include <map> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <queue> #define met(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a) #define pb push_back #define lson l,m,rt<<1 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N=2e5+50; const int M=N*N+10; int num,s,m,n,q; int a[N],op[N],b[N]; ll sum[N*2][5]; int cnt[N*2]; inline void PushPlus(int rt) { cnt[rt]=cnt[rt*2]+cnt[rt*2+1]; for(int i=0;i<=4;i++){ sum[rt][i]=sum[rt*2][i]+sum[rt*2+1][(i-cnt[rt*2]%5+5)%5]; } } void Update(int p,int add,int l,int r,int rt,int x) { if(l==r) { sum[rt][0]+=add; cnt[rt]+=x; return; } int m=(r+l)>>1; if(p<=m)Update(p,add,lson,x); else Update(p,add,rson,x); PushPlus(rt); } int main() { int u,vv,w; scanf("%d",&q); char str[10]; n=0; for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){ scanf("%s",str); if(str[0]=='a'){ scanf("%d",&b[i]); op[i]=1; a[++n]=b[i]; } else if(str[0]=='d'){ scanf("%d",&b[i]); op[i]=-1; } else { op[i]=0; } } sort(a+1,a+n+1); n=unique(a+1,a+n+1)-a-1; for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){ if(abs(op[i])==1){ int p=lower_bound(a+1,a+1+n,b[i])-a; Update(p,b[i]*op[i],1,n,1,op[i]); } else { printf("%lld ",sum[1][2]); } } return 0; }