写在前面:上一篇博客写了spring cache和ehcache的基本介绍,个人建议先把这些最基本的知识了解了才能对今天主题有所感触。不多说了,开干!
注:引入jar
<!-- 引入ehcache缓存 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.8.3</version>
</dependency>
第一步:首先配置ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="true" monitoring="autodetect" dynamicConfig="true"> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000" eternal="false" overflowToDisk="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="30" maxEntriesLocalDisk="10000000" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"> <persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/> </defaultCache> <cache name="myCache" maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000" maxEntriesLocalDisk="1000" eternal="false" diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="30" timeToIdleSeconds="300" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU" transactionalMode="off"> <persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/> </cache> </ehcache>
第二步:在spring.xml的配置文件中引入schema,
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"和http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-3.2.xsd
缓存的配置:
<!-- 启用缓存注解功能,这个是必须的,否则注解不会生效,另外,该注解一定要声明在spring主配置文件中才会生效 -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="ehcacheManager"/>
<!-- cacheManager工厂类,指定ehcache.xml的位置 -->
<bean id="ehcacheManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml" />
</bean>
<!-- 声明cacheManager -->
<bean id="ehcacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="ehcacheManagerFactory" />
</bean>
OK!缓存的相关配置已经完成。下面开始编写测试程序。这里需要连接数据库,我就不写了。这里为了方便就随便找了之前写过的model,这个model就是AOP注解实现日志管理的实体,为了偷懒就直接用了,希望你们不要误解,没有特殊意义的
第三步:编写model,这里需要注意,要实现缓存的实体必须要序列化 private static final long serialVersionUID = -6579533328390250520L; 关于序列化的生成这里就不介绍了,大家可以百度看看。

package org.shop.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; public class SystemLog implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6579533328390250520L; private String id; private String description; private String method; private Long logType; private String requestIp; private String exceptioncode; private String exceptionDetail; private String params; private String createBy; private Date createDate; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id == null ? null : id.trim(); } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description == null ? null : description.trim(); } public String getMethod() { return method; } public void setMethod(String method) { this.method = method == null ? null : method.trim(); } public Long getLogType() { return logType; } public void setLogType(Long logType) { this.logType = logType; } public String getRequestIp() { return requestIp; } public void setRequestIp(String requestIp) { this.requestIp = requestIp == null ? null : requestIp.trim(); } public String getExceptioncode() { return exceptioncode; } public void setExceptioncode(String exceptioncode) { this.exceptioncode = exceptioncode == null ? null : exceptioncode.trim(); } public String getExceptionDetail() { return exceptionDetail; } public void setExceptionDetail(String exceptionDetail) { this.exceptionDetail = exceptionDetail == null ? null : exceptionDetail.trim(); } public String getParams() { return params; } public void setParams(String params) { this.params = params == null ? null : params.trim(); } public String getCreateBy() { return createBy; } public void setCreateBy(String createBy) { this.createBy = createBy == null ? null : createBy.trim(); } public Date getCreateDate() { return createDate; } public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) { this.createDate = createDate; } }
第四步:编写dao,service

package org.shop.dao; import org.shop.entity.SystemLog; public interface SystemLogMapper { int deleteByPrimaryKey(String id); int insert(SystemLog record); int insertSelective(SystemLog record); SystemLog selectByPrimaryKey(String id); int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(SystemLog record); int updateByPrimaryKey(SystemLog record); int count(); }

public interface SystemLogService { int deleteSystemLog(String id); int insert(SystemLog record); int insertTest(SystemLog record); SystemLog findSystemLog(String id); int updateSystemLog(SystemLog record); int count(); }
第五步:编写serviceImpl并添加缓存注解。这里缓存注解的参数不介绍了,不懂得看我上一篇博客,我这里先把需要的注解都写上了,一会一个一个介绍。
@Service("systemLogService")
public class SystemLogServiceImpl implements SystemLogService {
@Resource
private SystemLogMapper systemLogMapper;
@Override
public int deleteSystemLog(String id) {
return systemLogMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);
}
@Override
//@CachePut(value="myCache")
//@CacheEvict(value="myCache",allEntries=true,beforeInvocation=true)
@CacheEvict(value="myCache",key="0",beforeInvocation=true)
public int insert(SystemLog record) {
return systemLogMapper.insertSelective(record);
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value="myCache",key="#id")
public SystemLog findSystemLog(String id) {
return systemLogMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
@Override
public int updateSystemLog(SystemLog record) {
return systemLogMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(record);
}
@Override
public int insertTest(SystemLog record) {
return systemLogMapper.insert(record);
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value="myCache",key="0")
public int count() {
int num = systemLogMapper.count();
return num;
}
}
第六步:编写controller,即我们的测试。
@Controller @RequestMapping("systemLogController") public class SystemLogController { @Resource private SystemLogService systemLogService; @RequestMapping("testLog") public ModelAndView testLog(){ ModelMap modelMap = new ModelMap(); SystemLog systemLog = systemLogService.findSystemLog("c30e2398-079a-406b-a2f7-a85fa15ccac7"); modelMap.addAttribute("data", systemLog); return new ModelAndView("index",modelMap); } @RequestMapping("insert") @ResponseBody public boolean Insert(SystemLog record){ systemLogService.insert(record); return true; } @RequestMapping("test1") public ModelAndView test1(){ ModelMap modelMap = new ModelMap(); int num =systemLogService.count(); modelMap.addAttribute("num", num); return new ModelAndView("pageEhcache",modelMap); } }
我们先测试查询的缓存,即serviceImpl中的 findSystemLog(String id) 方法,我们访问testLog.do,第一次运行如下图,注意控制台中的heap和 disk
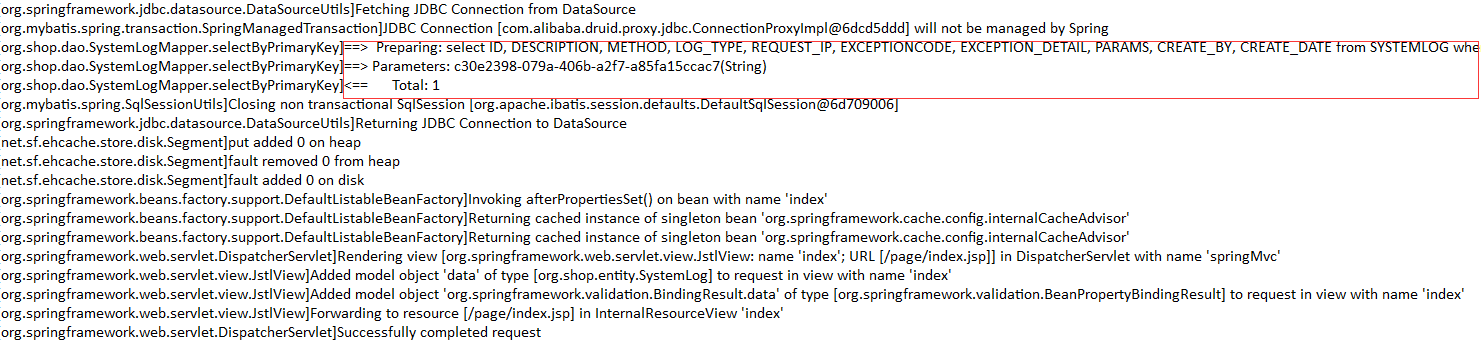
再一次访问testLog.do,运行你会发现没有访问数据库,如图:

到此查询的缓存我们实现了,但是关于缓存的处理我们并没有做完,我们应该在深入思考下,在上面查询的缓存生命周期内,我们对刚才查询的表进行了增删改操作,这时我们再访问该查询方法,你会发现我们的数据并没有改变,还是增删改操作之前的数据(因为缓存的生命还在),这里是不是问题呢?此时我们需要对查询的缓存进行更新或删除。
下面我们看serviceImpl中的insert方法和count()方法,count的方法是统计表中的数据总记录,insert方法是对该表进行新增一条记录,insert的缓存注解用的是@CacheEvict(value="myCache",key="0",beforeInvocation=true),这里清除的是指定缓存,也就是count方法中@Cacheable(value="myCache",key="0")的,(serviceImpl中注释的@CacheEvict(value="myCache",allEntries=true,beforeInvocation=true)是清除所有的缓存,这里我就不演示了,道理是一样的)
这里我提供一个测试pageEhcache.jsp页面,
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <title>测试</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="<%=request.getContextPath()%>/js/jquery-1.11.1.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> function insert(){ var record = $("#formID").serializeArray(); console.info(record); $.ajax({ url : "<%=request.getContextPath()%>/systemLogController/insert.do", type : 'post', async:true, dataType:'json', data : record, success:function(result){ alert("插入成功!"); } }); } </script> </head> <body> <h1><%=new Date()%></h1> <h1>这是一个练习</h1> <form id="formID" action=""> id: <input name="id" type="text"/><br> <input type="button" value="插入" onclick="insert()"/> </form> <br> 总数: <h4>${num}</h4> </body> </html>
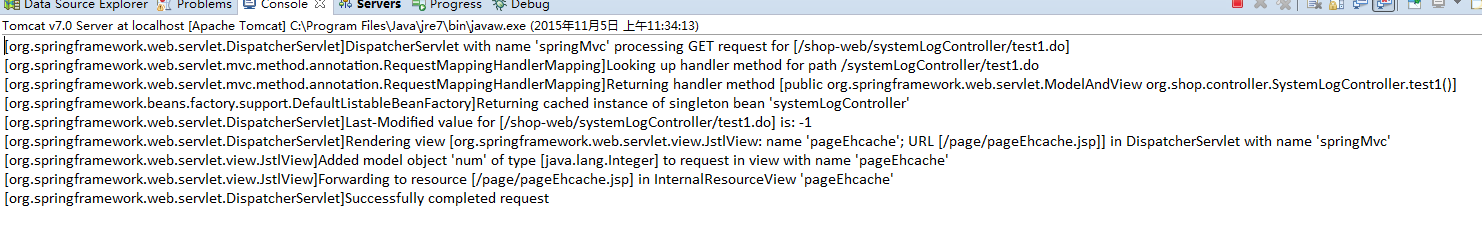
我们先访问test1.do,看下表中的记录数并注意控制台变化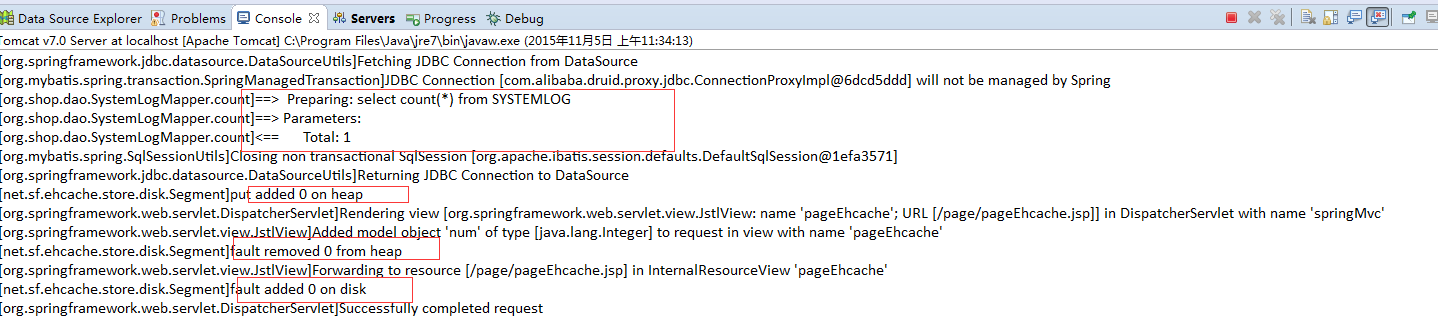
页面显示如下,注意总数是67,

再一次访问test1.do,没有访问数据库,说明count()方法的缓存生效了,
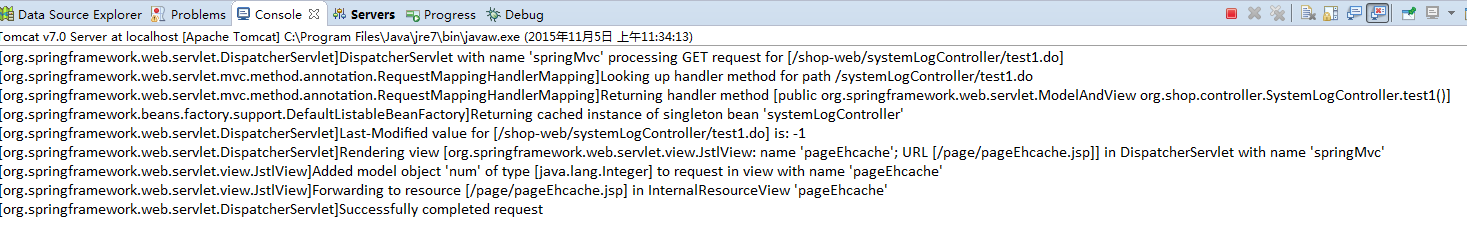
接下来开始新增记录,点击插入按钮

注意控制台显示,这里执行了inserSQL语句,并remove了count()方法上的缓存,
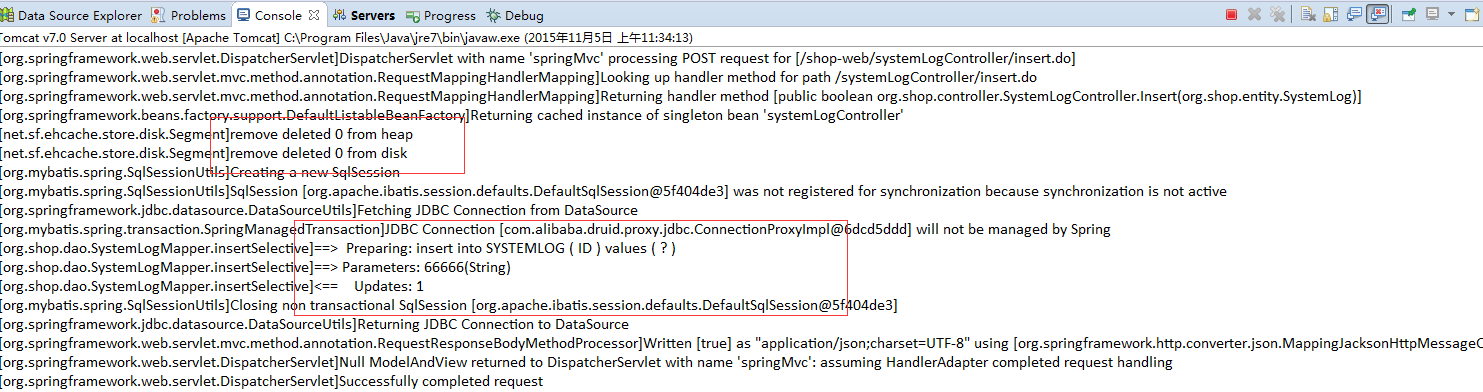
接下来再次访问test1.do,我们看到总数变化了,增加了一条,说明我们把之前count()方法上的缓存删除了,又执行了查询总数的sql

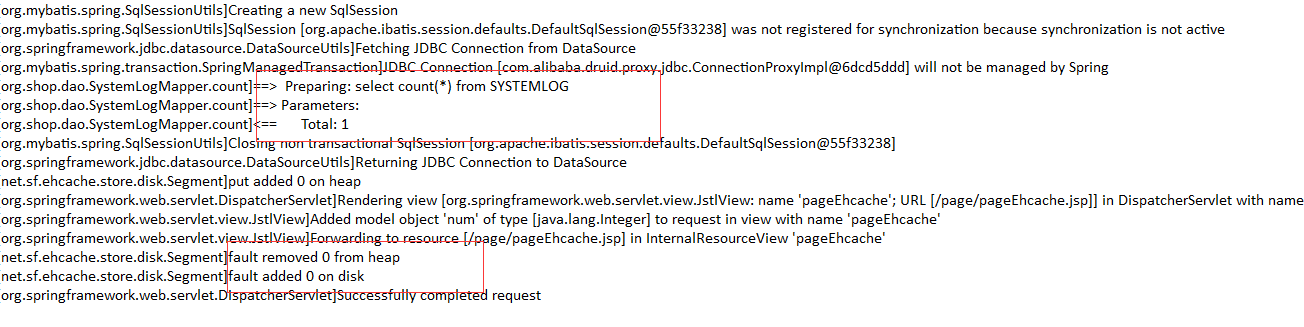
再次访问test1.do,count()方法的缓存生效了,对吧!这个就是@CacheEvict注解的作用。
在insert()方法上还有@CachePut(value="myCache")注解,上面的serviceImpl中注释了,它的作用是:@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
我这里就不做演示了,你们可以自己动手试试。
总结:我个人的理解,对查询方法增加缓存容易,但对于缓存的更新的处理就比较麻烦,我上面的serviceImpl中写了三种处理方式,
1.用@CachePut处理,这中方法需要对指定缓存key保持一致,尽管这样,还是不行,因为它返回的缓存是int(增加或删除或修改的记录数或是该记录的对象,这对我们查询所有或部分记录的缓存还是不可行的)
2.用@CacheEvict(value="myCache",key="0",beforeInvocation=true)处理,清除我们指定key的缓存,这种方式缺点是麻烦,需要我们注意每一个缓存的key
3.用@CacheEvict(value="myCache",allEntries=true,beforeInvocation=true)处理,清除所有缓存,这种方式最省事,但会把其他缓存也一同清除。
随着业务的复杂性的不断增加,这些处理方式,可能会增加代码的复杂性,然后我想到的是对DB层进行缓存,可以利用redis,mamchched的进行处理。当然对于一般的web应用运用ehcache已经刻一解决了,但是对大数据量的运用db级别的缓存效果性能可能会更好。
以上纯粹是个人想法。另外我也想了想缓存到底在哪些场景下应用会比较好,不知道你们是怎么认为的。也请大家给点建议。
