There is an n × m rectangular grid, each cell of the grid contains a single integer: zero or one. Let's call the cell on the i-th row and the j-th column as (i, j).
Let's define a "rectangle" as four integers a, b, c, d (1 ≤ a ≤ c ≤ n; 1 ≤ b ≤ d ≤ m). Rectangle denotes a set of cells of the grid {(x, y) : a ≤ x ≤ c, b ≤ y ≤ d}. Let's define a "good rectangle" as a rectangle that includes only the cells with zeros.
You should answer the following q queries: calculate the number of good rectangles all of which cells are in the given rectangle.
There are three integers in the first line: n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 40, 1 ≤ q ≤ 3·105). Each of the next n lines contains m characters — the grid. Consider grid rows are numbered from top to bottom, and grid columns are numbered from left to right. Both columns and rows are numbered starting from 1.
Each of the next q lines contains a query — four integers that describe the current rectangle, a, b, c, d (1 ≤ a ≤ c ≤ n; 1 ≤ b ≤ d ≤ m).
For each query output an answer — a single integer in a separate line.
5 5 5
00101
00000
00001
01000
00001
1 2 2 4
4 5 4 5
1 2 5 2
2 2 4 5
4 2 5 3
10
1
7
34
5
4 7 5
0000100
0000010
0011000
0000000
1 7 2 7
3 1 3 1
2 3 4 5
1 2 2 7
2 2 4 7
3
1
16
27
52
For the first example, there is a 5 × 5 rectangular grid, and the first, the second, and the third queries are represented in the following image.
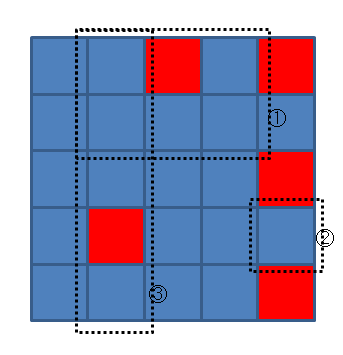
- For the first query, there are 10 good rectangles, five 1 × 1, two 2 × 1, two 1 × 2, and one 1 × 3.
- For the second query, there is only one 1 × 1 good rectangle.
- For the third query, there are 7 good rectangles, four 1 × 1, two 2 × 1, and one 3 × 1.
题意:给你一个n*m的矩形,q个询问,求左上角的(a,b)位置到(c, d)位置所有全0的矩形的个数
思路:四维前缀和;利用容斥,写写方程,或者dp的思想也行;
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #include<stack> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<list> #include<set> #include<map> #include<stdlib.h> #include<time.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) #define eps 1e-14 #define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<x<<endl; const int N=50+10,M=1e6+10,inf=1e9+10; const ll INF=5e17+10,mod=1e9+7; ///数组大小 int a[N][N],cnt[N][N][N][N]; int s[N][N],sum[N][N][N][N]; /// a表示初始数组 /// cnt表示以i.j为固定起点的总0个数 /// s表示1,1的1的数目,也就是前缀和 /// sum表示答案 int main() { int n,m,q; scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { scanf("%1d",&a[i][j]); s[i][j]=a[i][j]+s[i-1][j]+s[i][j-1]-s[i-1][j-1]; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { for(int k=i;k<=n;k++) { for(int l=j;l<=m;l++) { int x=s[k][l]-s[i-1][l]-s[k][j-1]+s[i-1][j-1]; cnt[i][j][k][l]=cnt[i][j][k][l-1]+cnt[i][j][k-1][l]-cnt[i][j][k-1][l-1]+!x; //cout<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<k<<" "<<l<<" "<<cnt[i][j][k][l]<<endl; } } } } for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) { for(int j=m;j>=1;j--) { for(int k=i;k<=n;k++) { for(int l=j;l<=m;l++) { sum[i][j][k][l]=sum[i+1][j][k][l]+sum[i][j+1][k][l]-sum[i+1][j+1][k][l]+cnt[i][j][k][l]; } } } } while(q--) { int a,b,c,d; scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d); printf("%d ",sum[a][b][c][d]); } return 0; }