一、Helm引入
K8S 上的应用对象,都是由特定的资源描述组成,包括 deployment、service 等。都保存各自文件中或者集中写到一个配置文件。然后 kubectl apply –f 部署。如果应用只由一个或几个这样的服务组成,上面部署方式足够了。而对于一个复杂的应用,会有很多类似上面的资源描述文件,例如微服务架构应用,组成应用的服务可能多达十个,几十个。如果有更新或回滚应用的需求,可能要修改和维护所涉及的大量资源文件,而这种组织和管理应用的方式就显得力不从心了。且由于缺少对发布过的应用版本管理和控制,使Kubernetes 上的应用维护和更新等面临诸多的挑战,主要面临以下问题:
(1)如何将这些服务作为一个整体管理
(2)这些资源文件如何高效复用
(3)不支持应用级别的版本管理
二、Helm介绍
Helm 是一个 Kubernetes 的包管理工具,就像 Linux 下的包管理器,如 yum/apt 等,可以很方便的将之前打包好的 yaml 文件部署到 kubernetes 上。
Helm 有 3 个重要概念:
1)helm:一个命令行客户端工具,主要用于 Kubernetes 应用 chart 的创建、打包、发布和管理。
2)Chart:应用描述,一系列用于描述 k8s 资源相关文件的集合。
3)Release:基于 Chart 的部署实体,一个 chart 被 Helm 运行后将会生成对应的一个release;将在 k8s 中创建出真实运行的资源对象。
三、Helm作用
#1.使用helm可以这些yaml文件作为一个整体管理
#2.实现yaml高效复用
#3.使用helm应用级别的版本管理
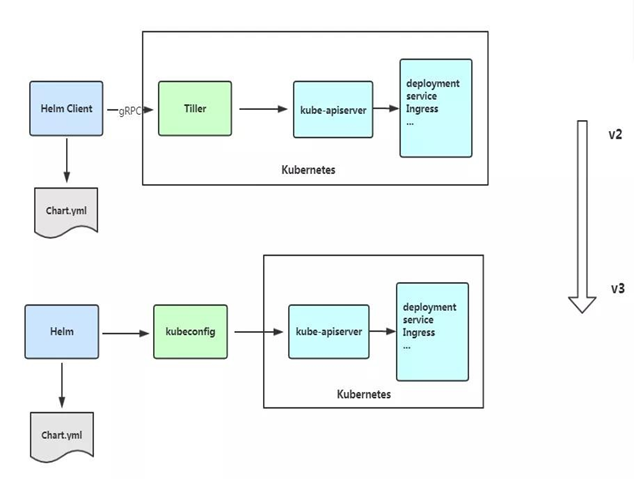
四、Helm v3 变化
2019 年 11 月 13 日, Helm 团队发布 Helm v3 的第一个稳定版本。该版本主要变化如下:
架构变化:
1)最明显的变化是 Tiller 的删除
2)Release 名称可以在不同命名空间重用
3)支持将 Chart 推送至 Docker 镜像仓库中
4)使用 JSONSchema 验证 chart values
5)其他
五、Helm客户端安装
1.下载Helm安装包
Helm 客户端下载地址:https://github.com/helm/helm/releases
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cd /data/software/
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /data/software]# wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
2.解压安装包
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /data/software]# tar xf helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /opt/
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /data/software]# cd /opt/
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 3434 3434 50 Oct 14 04:09 linux-amd64
3.配置环境变量
#1.配置环境变量
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# vim /etc/profile.d/helm.sh
export PATH=/opt/linux-amd64:$PATH
#2.刷新环境变量
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# source /etc/profile.d/helm.sh
4.验证helm
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.7.1", GitCommit:"1d11fcb5d3f3bf00dbe6fe31b8412839a96b3dc4", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.16.9"}
六、Helm常用命令
| 命令 |
描述 |
| create |
创建一个 chart 并指定名字 |
| dependency |
管理 chart 依赖 |
| get |
下载一个 release。可用子命令:all、hooks、manifest、notes、values |
| history |
获取 release 历史 |
| install |
安装一个 chart |
| list |
列出 release |
| package |
将 chart 目录打包到 chart 存档文件中 |
| pull |
从远程仓库中下载 chart 并解压到本地 # helm pull stable/mysql -- untar |
| repo |
添加,列出,移除,更新和索引 chart 仓库。可用子命令:add、index、 list、remove、update |
| rollback |
从之前版本回滚 |
| search |
根据关键字搜索 chart。可用子命令:hub、repo |
| show |
查看 chart 详细信息。可用子命令:all、chart、readme、values |
| status |
显示已命名版本的状态 |
| template |
本地呈现模板 |
| uninstall |
卸载一个 release |
| upgrade |
更新一个 release |
| version |
查看 helm 客户端版本 |
七、配置国内chart仓库
1.常用国内仓库
•微软仓库(http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts/)这个仓库推荐,基本上官网有的 chart 这里都有。
•阿里云仓库(https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts)
•官方仓库(https://hub.kubeapps.com/charts/incubator)官方 chart 仓库,国内有点不好使。
2.添加存储库
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo add stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts
"stable" has been added to your repositories
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo add aliyun https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts
"aliyun" has been added to your repositories
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo update
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "aliyun" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "stable" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈
3.查看配置的存储库
#1.查看配置的存储库
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo list
NAME URL
stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts
aliyun https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts
#2.查看配置存储库的服务清单
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm search repo stable
4.删除存储库
#1.查看存储库
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo list
NAME URL
stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts
aliyun https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts
#2.删除存储库aliyun
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo remove aliyun
"aliyun" has been removed from your repositories
#3.再次查看存储库
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm repo list
NAME URL
stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts
八、Helm基本使用
主要三个命令:
1)chart install
2)chart upgrade
3)chart rollback
1.查找chart
#1.基本命令:
helm search repo 应用名称
#2.查找weave
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm search repo weave
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
stable/weave-cloud 0.3.9 1.4.0 DEPRECATED - Weave Cloud is a add-on to Kuberne...
stable/weave-scope 1.1.12 1.12.0 DEPRECATED - A Helm chart for the Weave Scope c...
2.查看chart信息
#1.基本命令:
helm show chart 应用名称
#2.查看weave信息
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm show chart stable/weave-scope
apiVersion: v1
appVersion: 1.12.0
deprecated: true
description: DEPRECATED - A Helm chart for the Weave Scope cluster visualizer.
home: https://www.weave.works/oss/scope/
icon: https://avatars1.githubusercontent.com/u/9976052?s=64
keywords:
- containers
- dashboard
- monitoring
name: weave-scope
sources:
- https://github.com/weaveworks/scope
version: 1.1.12
3.安装chart包
#1.基本命令:
helm install 安装之后名称 安装应用名称
#2.安装helm的UI界面
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm install ui stable/weave-scope
WARNING: This chart is deprecated
W1122 12:13:50.594830 36094 warnings.go:70] rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 ClusterRole is deprecated in v1.17+, unavailable in v1.22+; use rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 ClusterRole
W1122 12:13:50.621669 36094 warnings.go:70] rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 ClusterRoleBinding is deprecated in v1.17+, unavailable in v1.22+; use rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 ClusterRoleBinding
W1122 12:13:51.944089 36094 warnings.go:70] rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 ClusterRole is deprecated in v1.17+, unavailable in v1.22+; use rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 ClusterRole
W1122 12:13:52.116920 36094 warnings.go:70] rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 ClusterRoleBinding is deprecated in v1.17+, unavailable in v1.22+; use rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 ClusterRoleBinding
NAME: ui
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 22 12:13:50 2021
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
You should now be able to access the Scope frontend in your web browser, by
using kubectl port-forward:
kubectl -n default port-forward $(kubectl -n default get endpoints \
ui-weave-scope -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].targetRef.name}') 8080:4040
then browsing to http://localhost:8080/.
For more details on using Weave Scope, see the Weave Scope documentation:
https://www.weave.works/docs/scope/latest/introducing/
4.查看发布状态
#1.基本命令:
helm status 安装之后名称
#2.查看helm安装之后列表
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm list
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
ui default 1 2021-11-22 12:13:50.403587307 +0800 CST deployed weave-scope-1.1.12 1.12.0
#3.查看应用发布状态
[root@kubernetes-master-001 /opt]# helm status ui
NAME: ui
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 22 12:13:50 2021
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
You should now be able to access the Scope frontend in your web browser, by
using kubectl port-forward:
kubectl -n default port-forward $(kubectl -n default get endpoints \
ui-weave-scope -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].targetRef.name}') 8080:4040
then browsing to http://localhost:8080/.
For more details on using Weave Scope, see the Weave Scope documentation:
https://www.weave.works/docs/scope/latest/introducing/
5.修改服务对外访问状态
#1.查看Pod
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
weave-scope-agent-ui-ldk4w 1/1 Running 0 9m27s
weave-scope-agent-ui-qmnjj 1/1 Running 0 9m26s
weave-scope-agent-ui-rqb4j 1/1 Running 0 9m26s
weave-scope-cluster-agent-ui-5cbc84db49-mqq6n 1/1 Running 0 9m26s
weave-scope-frontend-ui-6698fd5545-dcjfj 1/1 Running 0 9m26s
web-96d5df5c8-prps4 1/1 Running 0 3d21h
#2.查看Service
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 3d21h
ui-weave-scope ClusterIP 10.99.33.100 <none> 80/TCP 9m35s
web NodePort 10.106.214.3 <none> 80:30645/TCP 3d21h
#3.修改Service
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl edit svc ui-weave-scope #搜索type,将Type:ClusterIP改成 Type:NodePort
service/ui-weave-scope edited
#4.再次查看Service
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 3d21h
ui-weave-scope NodePort 10.99.33.100 <none> 80:30779/TCP 12m
web NodePort 10.106.214.3 <none> 80:30645/TCP 3d21h
#5.web访问验证
九、安装前自定义 chart 配置选项
自定义选项是因为并不是所有的 chart 都能按照默认配置运行成功,可能会需要一些环境依赖,例如 PV。
所以我们需要自定义 chart 配置选项,安装过程中有两种方法可以传递配置数据:
• --values(或-f):指定带有覆盖的 YAML 文件。这可以多次指定,最右边的文件优先
• --set:在命令行上指定替代。如果两者都用,--set 优先级高
1.--values 使用,先将修改的变量写到一个文件中
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm show values stable/mysql
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# vim config.yaml
persistence:
enabled: true
storageClass: "managed-nfs-storage"
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 8Gi
mysqlUser: "k8s"
mysqlPassword: "123456"
mysqlDatabase: "k8s"
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm install db -f config.yaml stable/mysql
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
db-mysql-57485b68dc-4xjhv 1/1 Running 0 8m51s
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl run -it db-client --rm --restart=Never --image=mysql:5.7 -- bash
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.
root@db-client:/# mysql -hdb-mysql -uk8s -p123456
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 36
Server version: 5.7.30 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h'for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| k8s |
+--------------------+
以上将创建具有名称的默认 MySQL 用户 k8s,并授予此用户访问新创建的 k8s 数据库的权限,但将接受该图表的所有其余默认值。
2.命令行替代变量
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm install db --set persistence.storageClass="managed-nfs-storage" stable/mysql
也可以把 chart 包下载下来查看详情:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm pull stable/mysql --untar
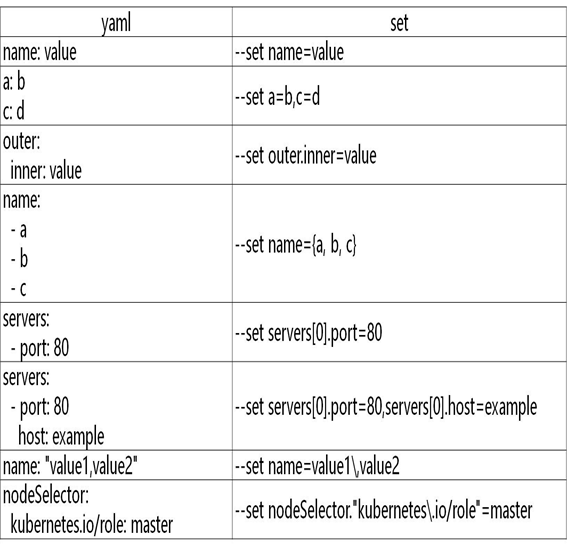
values yaml 与 set 使用:
该 helm install 命令可以从多个来源安装:
1)chart 存储库
2)本地 chart 存档(helm install foo-0.1.1.tgz)
3)chart 目录(helm install path/to/foo)
4)完整的 URL(helm install https://example.com/charts/foo-1.2.3.tgz)
十、构建一个 Helm Chart
1. Helm Chart目录结构
#1.创建chart
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm create mychart
Creating mychart
#2.查看chart
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# tree mychart/
mychart/
├── charts
├── Chart.yaml
├── templates
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── _helpers.tpl
│ ├── hpa.yaml
│ ├── ingress.yaml
│ ├── NOTES.txt
│ ├── serviceaccount.yaml
│ ├── service.yaml
│ └── tests
│ └── test-connection.yaml
└── values.yaml
3 directories, 10 files
• Chart.yaml:用于描述这个 Chart 的基本信息,包括名字、描述信息以及版本等。
• values.yaml :用于存储 templates 目录中模板文件中用到变量的值。
• Templates: 目录里面存放所有 yaml 模板文件。
• charts:目录里存放这个 chart 依赖的所有子 chart。
• NOTES.txt :用于介绍 Chart 帮助信息, helm install 部署后展示给用户。例如: 如何使用这个 Chart、列出缺省的设置等。
• _helpers.tpl:放置模板助手的地方,可以在整个 chart 中重复使用
#3.创建 Chart 后,接下来就是将其部署
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm install web mychart/
也可以打包推送的 charts 仓库共享别人使用。
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm package mychart/ mychart-0.1.0.tgz
2.定义chart 模板
Helm 最核心的就是模板,即模板化的 K8S manifests 文件。它本质上就是一个 Go 的 template 模板。Helm 在 Go template 模板的基础上,还会增加很多东西。如一些自定义的元数据信息、扩展的库以及一些类似于编程形式的工作流,例如条件语句、管道等等。这些东西都会使得我们的模板变得更加丰富。有了模板,我们怎么把我们的配置融入进去呢?用的就是这个 values 文件。这两部分内容其实就是 chart 的核心功能。接下来,部署 nginx 应用,熟悉模板使用
#1.在values.yaml中定义变量和值
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm create nginx
Creating nginx
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cd nginx/templates/
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~/nginx/templates]# vim ../values.yaml
replicas: 1
image: nginx
tag: 1.16
label: nginx
port: 80
#2.在templates的yaml文件使用values。yaml定义变量
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# rm -rf ./*
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl create deployment web1 --image=nginx --dry-run -o yaml > deployment.yaml
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl expose deployment web1 --port=80 --target-port=80 --dry-run -o yaml > service.yaml
#3.修改yaml文件
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~/nginx/templates]# vim deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: web1
name: {{ .Release.Name}}-deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: {{ .Values.label}}
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: {{ .Values.label}}
spec:
containers:
- image: {{ .Values.image}}
name: nginx
resources: {}
status: {}
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~/nginx/templates]# vim service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: web1
name: {{ .Release.Name}}-svc
spec:
ports:
- port: {{ .Values.port}}
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: {{ .Values.label}}
status:
loadBalancer: {}
3.调试
Helm 也提供了--dry-run --debug 调试参数,帮助你验证模板正确性。在执行 helm install 时候带上这两个参数就可以把对应的 values 值和渲染的资源清单打印出来,而不会真正的去部署一个 release。
比如我们来调试上面创建的 chart 包:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm install --dry-run web1 nginx/
NAME: web1
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 22 15:53:01 2021
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: pending-install
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
HOOKS:
MANIFEST:
---
# Source: nginx/templates/service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: web1
name: web1-svc
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
status:
loadBalancer: {}
---
# Source: nginx/templates/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: web1
name: web1-deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
resources: {}
status: {}
4.内置对象
刚刚我们使用 {{.Release.Name}}将 release 的名称插入到模板中。这里的 Release 就是 Helm 的内置对象,下面是一些常用的内置对象:
| Release.Name |
release 名称 |
| Release.Name |
release 名字 |
| Release.Namespace |
release 命名空间 |
| Release.Service |
release 服务的名称 |
| Release.Revision |
release 修订版本号,从 1 开始累加 |
5.Values
Values 对象是为 Chart 模板提供值,这个对象的值有 4 个来源:
• chart 包中的 values.yaml 文件
• 父 chart 包的 values.yaml 文件
• 通过 helm install 或者 helm upgrade 的 -f 或者 --values 参数传入的自定义的 yaml 文件
• 通过 --set 参数传入的值
chart 的 values.yaml 提供的值可以被用户提供的 values 文件覆盖,而该文件同样可以被 --set 提供的参数所覆盖。
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm upgrade web --set replicas=5 nginx/
Release "web" has been upgraded. Happy Helming! NAME: web
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri May 2916:34:172020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None NOTES:
hello
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm history web
REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
1 Fri May 2916:33:562020 superseded nginx-0.1.01.15 Install complete
2 Fri May 2916:34:172020 deployed nginx-0.1.01.15 Upgrade complete
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web-5675686b8-7n7bg 1/1 Running 0 54s
web-5675686b8-9vf28 1/1 Running 0 33s
web-5675686b8-9wkgz 1/1 Running 0 54s
web-5675686b8-jdrhr 1/1 Running 0 54s
web-5675686b8-rrrxc 1/1 Running 0 33s
6.升级、回滚和删除
#1.发布新版本的 chart 时,或者当您要更改发布的配置时,可以使用该 helm upgrade 命令。
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm upgrade --set imageTag=1.17 web nginx
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm upgrade -f values.yaml web nginx
#2.如果在发布后没有达到预期的效果,则可以使用 helm rollback 回滚到之前的版本。例如将应用回滚到第一个版本:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm rollback web 1
#3.卸载发行版,请使用以下 helm uninstall 命令:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm uninstall web
#4.查看历史版本配置信息
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm get all --revision 1 web
7.管道与函数
前面讲的模块,其实就是将值传给模板引擎进行渲染,模板引擎还支持对拿到数据进行二次处理。
例如从.Values 中读取的值变成字符串,可以使用 quote 函数实现:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# vi templates/deployment.yaml
app: {{ quote .Values.label.app }}
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm install --dry-run web ../mychart/ project: ms
app: "nginx"
quote .Values.label.app 将后面的值作为参数传递给 quote 函数。模板函数调用语法为:functionName arg1 arg2...
另外还会经常使用一个 default 函数,该函数允许在模板中指定默认值,以防止该值被忽略掉。例如忘记定义,执行 helm install 会因为缺少字段无法创建资源,这时就可以定义一个默认值。
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# catvalues.yaml
replicas: 2
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat templates/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-deployment
- name: {{ .Values.name | default "nginx" }}
其他函数:
缩进:{{ .Values.resources | indent 12 }} 大写:{{ upper .Values.resources }}
首字母大写:{{ title .Values.resources }}
十一、Helm流程控制
流程控制是为模板提供了一种能力,满足更复杂的数据逻辑处理。
Helm 模板语言提供以下流程控制语句:
• if/else 条件块
• with 指定范围
• range 循环块
1.if
#1.if/else 块是用于在模板中有条件地包含文本块的方法,条件块的基本结构如下:
{{ if PIPELINE }}
# Do something
{{ elseif OTHER PIPELINE }}
# Do something else
{{ else }}
# Default case
{{ end }}
#2.示例
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat values.yaml
devops: k8
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat templates/deployment.yaml
...
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
{{ if eq .Values.devops "k8s" }}
devops: 123
{{ else }}
devops: 456
{{ end }}
在上面条件语句使用了 eq 运算符判断是否相等,除此之外,还支持ne、 lt、 gt、 and、 or 等运算符。注意数据类型。通过模板引擎来渲染一下,会得到如下结果:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# helm install --dry-run web ../mychart/
...
labels:
app: nginx
devops: 456
可以看到渲染出来会有多余的空行,这是因为当模板引擎运行时,会将控制指令删除,所有之前占的位置也就空白了,需要使用{{- if ...}} 的方式消除此空行:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# vim templates/deploymemt.yaml
...
env:
{{- ifeq .Values.env.hello "world" }}
- name: hello
value: 123
{{- end }}
现在是不是没有多余的空格了,如果使用-}}需谨慎,比如上面模板文件中:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# vim templates/deploymemt.yaml
...
env:
{{- ifeq .Values.env.hello "world" -}}
- hello: true
{{- end }}
这会渲染成:
env:- hello: true
因为-}}它删除了双方的换行符。
条件判断就是判断条件是否为真,如果值为以下几种情况则为 false:
• 一个布尔类型的 false
• 一个数字 零
• 一个 空的字符串
• 一个空的集合( map、 slice、 tuple、 dict、 array) 除了上面的这些情况外,其他所有条件都为 真。
例如,判断一个空的数组
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat values.yaml
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi # requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# vim templates/deploymemt.yaml
...
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.16 name: nginx
{{- if .Values.resources }} resources:
{{ toYaml .Values.resources | indent 10 }}
{{- end }}
例如,判断一个布尔值
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat values.yaml
service:
type: ClusterIP
port: 80
ingress:
enabled: true
host: example.ctnrs.com
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# vim templates/ingress.yaml
{{- if .Values.ingress.enabled -}}
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: {{ .Values.ingress.host }}
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: {{ .Release.Name }}
servicePort: {{ .Values.service.port }}
{{ end }}
2.range
在 Helm 模板语言中,使用 range 关键字来进行循环操作。我们在values.yaml 文件中添加上一个变量列表:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat values.yaml
test:
- 1
- 2
- 3
循环打印该列表:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}
data:
test: |
{{- range .Values.test }}
{{ . }}
{{- end }}
循环内部我们使用的是一个 .,这是因为当前的作用域就在当前循环内,这个 .引用的当前读取的元素。
3.with
with :控制变量作用域。
还记得之前我们的{{.Release.xxx}}或者 {{.Values.xxx}}吗?其中的 .就是表示对当前范围的引用, .Values 就是告诉模板在当前范围中查找 Values 对象的值。而 with 语句就可以来控制变量的作用域范围,其语法和一个简单的 if 语句比较类似:
{{ with PIPELINE }}
# restricted scope
{{ end }}
with 语句可以允许将当前范围 .设置为特定的对象,比如我们前面一直使用的 .Values.label,我们可以使用 with 来将 .范围指向 .Values.label:
在 Helm 模板语言中,使用 range 关键字来进行循环操作。我们在values.yaml 文件中添加上一个变量列表:
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat values.yaml
...
nodeSelector:
team: a
gpu: yes
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat templates/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-deployment spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
{{- with .Values.nodeSelector }}
nodeSelector:
team: {{ .team }}
gpu: {{ .gpu }}
{{- end }}
containers:
- image: nginx:1.16
name: nginx
优化后:
{{- with .Values.nodeSelector }}
nodeSelector:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
上面增加了一个{{- with .Values.nodeSelector}} xxx {{- end }}的一个块,这样的话就可以在当前的块里面直接引用 .team 和 .gpu 了。with 是一个循环构造。使用.Values.nodeSelector 中的值:将其转换为 Yaml。toYaml 之后的点是循环中.Values.nodeSelector 的当前值
4.变量
变量,在模板中,使用变量的场合不多,但我们将看到如何使用它来简化代码,并更好地利用 with 和 range。
问题 1:获取数组键值
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat ../values.yaml
env:
NAME: "gateway"
JAVA_OPTS: "-Xmx1G"
[root@kubernetes-master-001 ~]# cat deployment.yaml
...
env:
{{- range $k, $v := .Values.env }}
- name: {{ $k }}
value: {{ $v | quote }}
{{- end }}
结果如下
env:
- name: JAVA_OPTS
value: "-Xmx1G"
- name: NAME
value: "gateway"
上面在 range 循环中使用 $key 和 $value 两个变量来接收后面列表循环的键和值。
问题 2:with 中不能使用内置对象
with 语句块内不能再 .Release.Name 对象,否则报错。我们可以将该对象赋值给一个变量可以来解决这个问题:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-deployment
spec:
replicas: {{ .Values.replicas }}
template:
metadata:
labels:
project: {{ .Values.label.project }}
app: {{ quote .Values.label.app }}
{{- with .Values.label }}
project: {{ .project }}
app: {{ .app }}
release: {{ .Release.Name }}
{{- end }}
上面会出错
{{- $releaseName := .Release.Name -}}
{{- with .Values.label }}
project: {{ .project }}
app: {{ .app }}
release: {{ $releaseName }}
# 或者可以使用$符号,引入全局命名空间
release:{{ $.Release.Name }}
{{- end }}
可
以看到在 with 语句上面增加了一句 {{-$releaseName:=.Release.Name-}},其中$releaseName 就是后面的对象的一个引用变量,它的形式就是 $name,赋值操作使用:=,这样with 语句块内部的$releaseName 变量仍然指向的是.Release.Name
5.命名模板
需要复用代码的地方用。
命名模板:使用 define 定义,template 引入,在 templates 目录中默认下划线开头的文 件为公共模板(helpers.tpl)
# cat _helpers.tpl
{{- define "demo.fullname" -}}
{{- .Chart.Name -}}-{{ .Release.Name }}
{{- end -}}
# catd eployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ template"demo.fullname" . }}
...
template 指令是将一个模板包含在另一个模板中的方法。但是,template 函数不能用于
Go 模板管道。为了解决该问题,增加 include 功能。
# cat _helpers.tpl
{{- define "demo.labels" -}}
app: {{ template"demo.fullname" . }}
chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
release: "{{ .Release.Name }}"
{{- end -}}
# cat deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ include"demo.fullname" . }}
labels:
{{- include "demo.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
...
上面包含一个名为 demo.labels 的模板,然后将值 . 传递给模板,最后将该模板的输出传递给 nindent 函数。
6.开发自己的 chart
1、先创建模板
2、修 改Chart.yaml,Values.yaml, 添 加 常 用 的 变 量
3、在 templates 目录下创建部署镜像所需要的 yaml 文件,并变量引用 yaml 里经常变动的字段


