MapReduce计算框架
既然MR是一种计算框架,那么也存在其他的计算框架。
From: [Distributed ML] Yi WANG's talk
- Message Passing(消息传递)范式的一个框架叫做MPI,其实现叫作:MPICH2
- MapReduce范式的框架也叫MapReduce,其实现叫作:Apache Hadoop
- BSP范式,其实现叫作:Google Pregel (类似Spark)
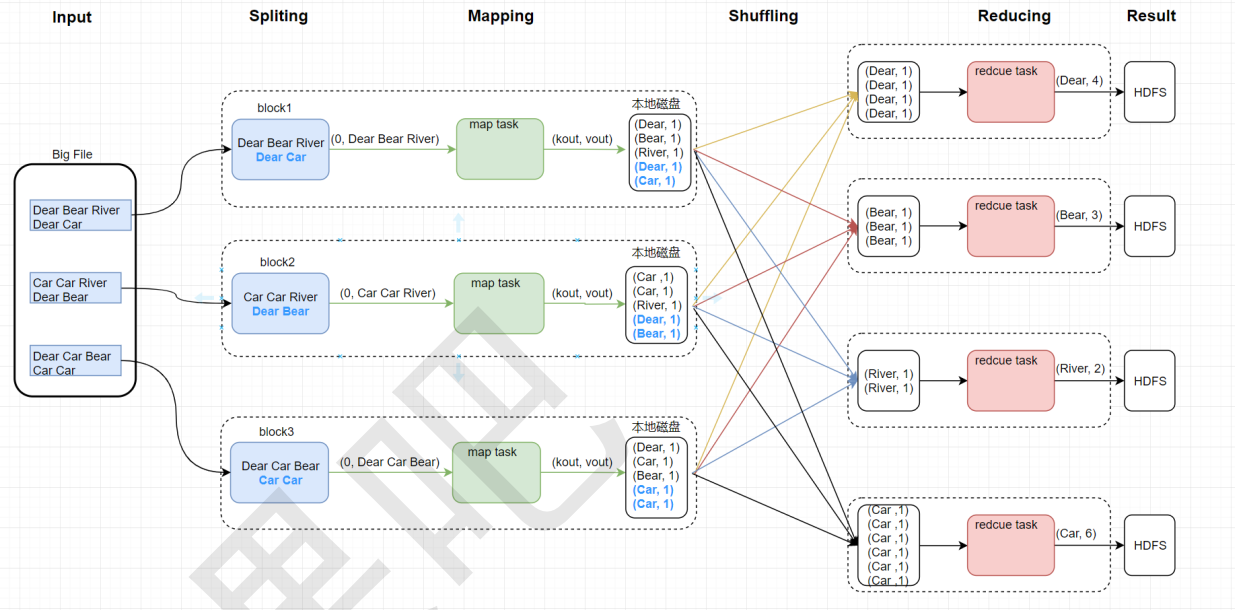
一、逻辑流程
Mapping与Shuffling之间可以插入”Combine“过程,但不一定都适合,比如”求平均值“。
Ref: Java总结篇系列:Java泛型
Ref: Word Count MapReduce Program in Hadoop
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
// Map function public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>{ private Text word = new Text(); public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // Splitting the line on spaces String[] stringArr = value.toString().split("\\s+"); for (String str : stringArr) { word.set(str);
// 每个单词出现1次,作为中间结果输出 context.write(word, new IntWritable(1)); } } } // Reduce function public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{ private IntWritable result = new IntWritable(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0; for (IntWritable val : values) { sum += val.get(); } result.set(sum);
// 输出最终结果 context.write(key, result); } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "WC");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 设置输入输出路径 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
// 提交作业 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); } }
二、执行流程
其实就是 对 Yarn 的学习和理解。
Yarn不光能运行MapReduce程序,还能运行Spark程序等。
更多参考:MapReduce执行过程
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36951116/article/details/92435687
1、启动 RunJar
2、启动 MRAppMaster
3、启动 mapper的yarnChild(运行map or reduce)
4、销毁 mapper的yarnChild
5、启动 reduce的yarnChild(运行map or reduce)
6、销毁 reduce的yarnChild
7、销毁 RunJar
8、销毁 MRAppMaster
Ref: 实战案例玩转Hadoop系列11--运行Map Reduce程序
在真实的生产环境中,MAP REDUCE程序应该提交到Yarn集群上分布式运行,这样才能发挥出MAP REDUCE分布式并行计算的效果。
MAP REDUCE程序提交给Yarn执行的过程如下:
1、客户端代码中设置好MAP REDUCE程序运行时所要使用的Mapper类、Reducer类、程序Jar包所在路径、Job名称、Job输入数据的切片信息、Configuration所配置的参数等资源,统一提交给Yarn所指定的位于HDFS上的Job资源提交路径;
2、客户端向Yarn中的Resource Manager请求运行Jar包中MRAppMaster进程的资源容器Container;
3、Yarn将提供Container的任务指派给某个拥有空闲资源的 Node Manager节点,Node Manager接受任务后创建资源容器(即所谓的Container);
4、客户端向创建好容器的Node Manager发送启动MRAppMaster进程的shell脚本命令,启动MRAppMaster;
5、MRAppMaster启动后,读取 job相关配置及程序资源,向Resource Manager请求N个资源容器来启动若干个Map Task进程和若干个Reduce Task进程,并监控这些Map Task进程和Reduce Task进程的运行状态;
6、当整个Job的所有Map Task进程和Reduce Task进程任务处理完成后,整个Job的所有进程全部注销,Yarn则销毁Container,回收运算资源。
运行过程示意图如下:

三、自定义分区
Ref: Hadoop详解(四)——Shuffle原理,Partitioner分区原理,Combiner编程,常见的MR算法
Partitioner是shuffle的一部分。
默认规则:Hadoop有一个默认的分区规则。
手动规则:Partitioner是partitioner的基类,如果需要定制partitioner也需要继承该类。HashPartitioner是mapreduce的默认partitioner。通过如下计算方法得到当前的 "目的reducer"。
which reducer=(key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks,
日志数据
1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200
1363157995052 13826544101 5C-0E-8B-C7-F1-E0:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 264 0 200
1363157991076 13926435656 20-10-7A-28-CC-0A:CMCC 120.196.100.99 2 4 132 1512 200
1363154400022 13926251106 5C-0E-8B-8B-B1-50:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 240 0 200
代码演示

package liuxun.hadoop.mr.dc; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable; public class DataBean implements Writable { private String tel; private long upPayLoad; private long downPayLoad; private long totalPayLoad; public DataBean() { } public DataBean(String tel, long upPayLoad, long downPayLoad) { this.tel = tel; this.upPayLoad = upPayLoad; this.downPayLoad = downPayLoad; this.totalPayLoad = upPayLoad + downPayLoad; } @Override public String toString() { return this.upPayLoad + "\t" + this.downPayLoad + "\t" + this.totalPayLoad; } public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { this.tel = in.readUTF(); this.upPayLoad = in.readLong(); this.downPayLoad = in.readLong(); this.totalPayLoad = in.readLong(); } // 注意两点:写入的顺序和写入的类型 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeUTF(tel); out.writeLong(upPayLoad); out.writeLong(downPayLoad); out.writeLong(totalPayLoad); } public String getTel() { return tel; } public void setTel(String tel) { this.tel = tel; } public long getUpPayLoad() { return upPayLoad; } public void setUpPayLoad(long upPayLoad) { this.upPayLoad = upPayLoad; } public long getDownPayLoad() { return downPayLoad; } public void setDownPayLoad(long downPayLoad) { this.downPayLoad = downPayLoad; } public long getTotalPayLoad() { return totalPayLoad; } public void setTotalPayLoad(long totalPayLoad) { this.totalPayLoad = totalPayLoad; } }
package liuxun.hadoop.mr.dc; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class DataCountPartition { public static class DCMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, DataBean> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // accept String line = value.toString();
// split String[] fields = line.split("\t");
String tel= fields[1];
long up = Long.parseLong(fields[8]); long down = Long.parseLong(fields[9]); DataBean bean = new DataBean(tel, up, down);
// send context.write(new Text(tel), bean); } }
public static class DCReducer extends Reducer<Text, DataBean, Text, DataBean> { @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<DataBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long up_sum = 0; long down_sum = 0;
for (DataBean bean : values) { up_sum += bean.getUpPayLoad(); down_sum += bean.getDownPayLoad(); } DataBean bean = new DataBean("", up_sum, down_sum); context.write(key, bean); } }
public static class ProviderPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, DataBean> { private static Map<String, Integer> prividerMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); static { // 实际开发时是从数据库加载这种映射关系的 // 1:中国移动 2:中国联通 3:中国电信 prividerMap.put("135", 1); prividerMap.put("136", 1); prividerMap.put("137", 1); prividerMap.put("150", 2); prividerMap.put("159", 2); prividerMap.put("182", 3); prividerMap.put("183", 3); } // 此方法的返回值是分区号 // key: mapper一次输出的key 这里是手机号 // key: mapper一次输出的Value 这里是DataBean // numPartitions:分区数量,由Reducer的数量决定,启动几个Reducer就会有几个partition @Override public int getPartition(Text key, DataBean value, int numPartitions) { // 根据手机号得到运营商 此处根据key进行分区,实际开发中也可以根据value进行分区 String account = key.toString(); String sub_acc = account.substring(0, 3); Integer code = prividerMap.get(sub_acc); if (code == null) { code = 0; } return code; } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(DataCountPartition.class); job.setMapperClass(DCMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(DataBean.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); job.setReducerClass(DCReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(DataBean.class); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); job.setPartitionerClass(ProviderPartitioner.class); // 设置启动Reducer的数量 job.setNumReduceTasks(Integer.parseInt(args[2])); job.waitForCompletion(true); } }
设置Partitioner之前后对比
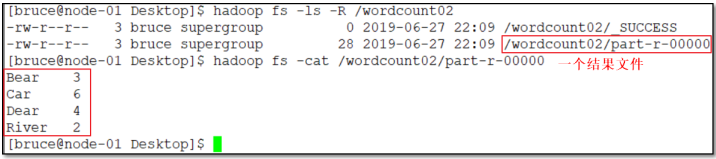
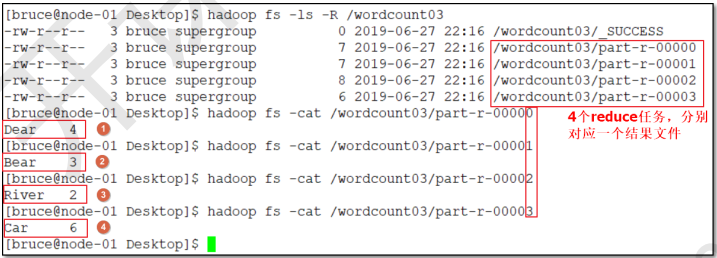
<k,v>中v可以是一个类(如上),k可以么?当然也可以。
四、二次排序
key使用了类,可以支持更为复杂的操作,比如这里的 "二次排序"。
所以,需要自定义BeanInfo类并实现WritableComparable接口,并重写compareTo方法和toString方法。
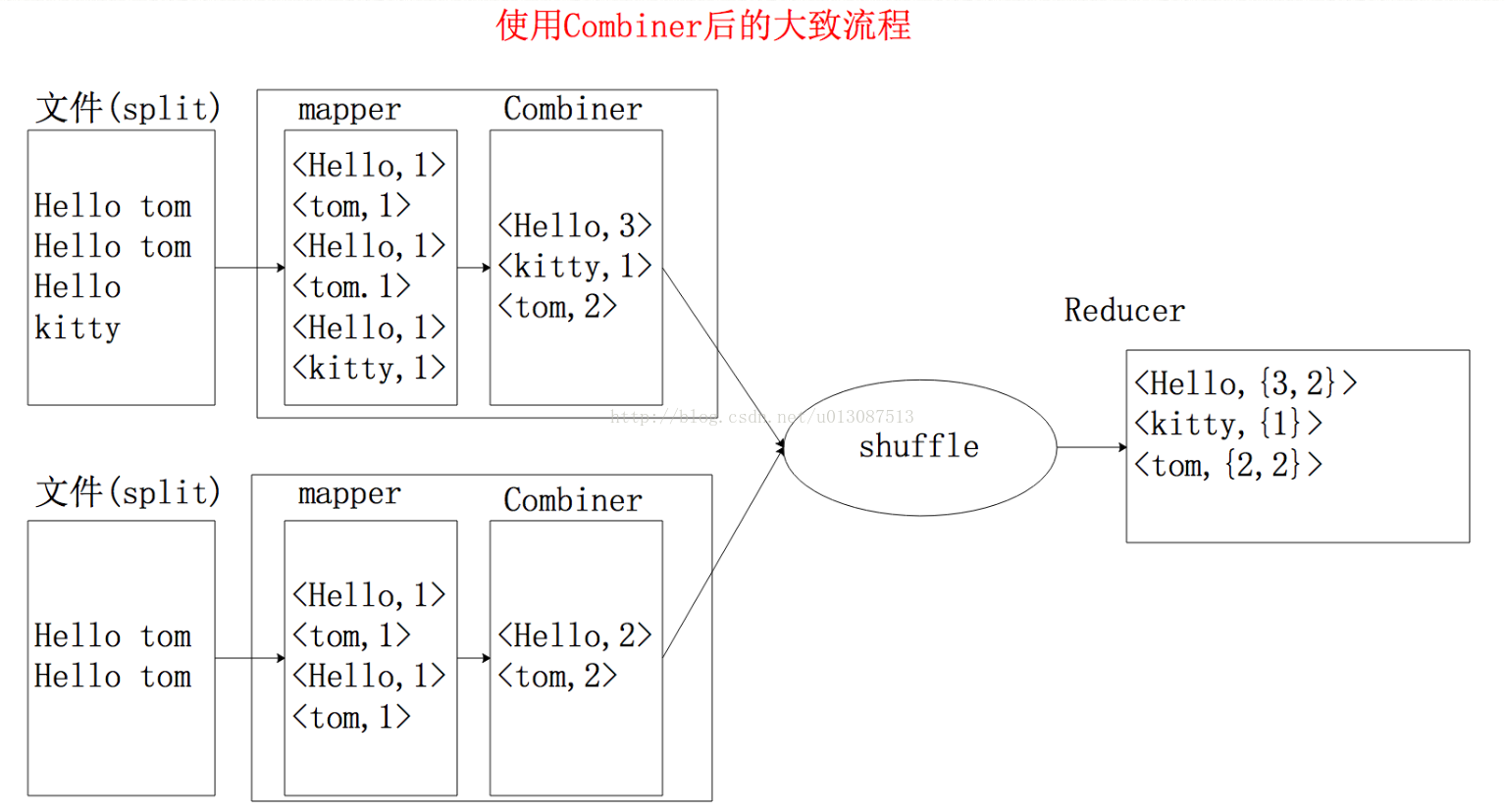
五、Combiners编程
每一个map可能会产生大量的输出,combiner的作用就是在map端对输出先做一次合并,以减少传输到reducer的数据量。
六、MR实现倒排序索引
参见链接中最后的例子:https://blog.csdn.net/u013087513/article/details/77799686
七、数据倾斜诊断和优化
此部分可以放在 yarn的章节一并讲解。
交互命令与编程
mrjob
一、相关资源
Github: mrjob: the Python MapReduce library
文档版本:mrjob Documentation Release 0.7.0.dev0
网页版本:mrjob v0.7.0.dev0 documentation
二、Hello world 程序
/* implement */

