1、实例代码
在实例搭建文章中,通过 SqlSession 对象查询数据,可乐写了两种方法。
①、常规的需要我们拼接 statement 方式;
②、xxxMapper.interface 接口代理方式;
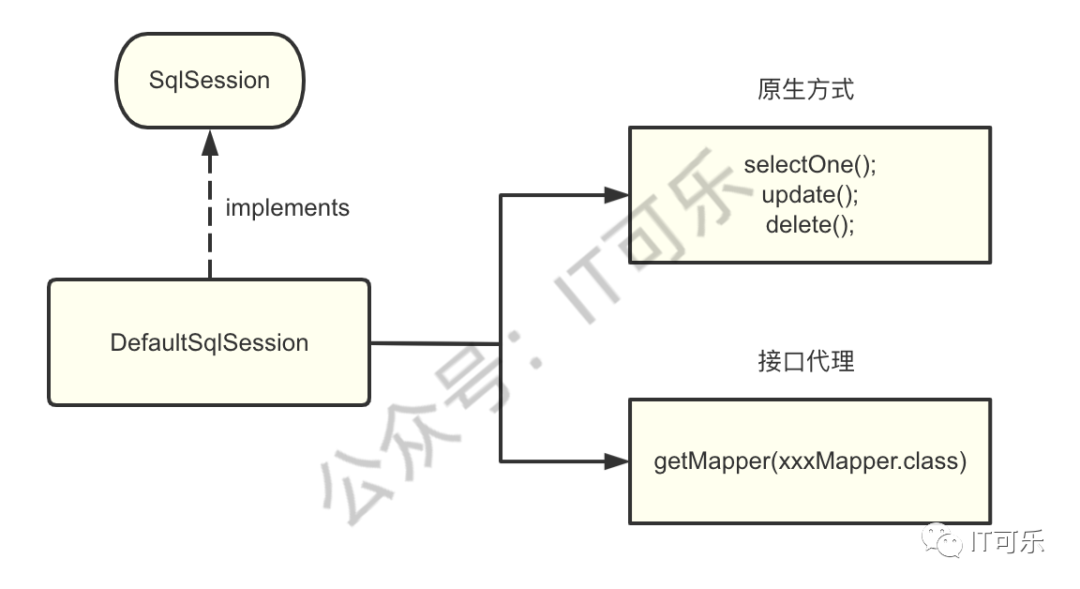
对应下面两种方法:
//根据id查询person表数据 @Test public void testSelectPersonById() { /*这个字符串由 PersonMapper.xml 文件中 两个部分构成 <mapper namespace="com.itcoke.mapper.PersonMapper"> 的 namespace 的值 <select id="selectPersonById" > id 值 */ String namespace = "com.itcoke.mapper.PersonMapper"; String method = "selectPersonById"; //根据 sqlSessionFactory 产生 session SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession(); Person person = sqlSession.selectOne(namespace + "." + method, 1L); System.out.println(person); sqlSession.close(); } //根据id查询person表数据 //通过接口代理的方式 @Test public void testInterfaceSelectPersonById() { //根据 sqlSessionFactory 产生 session SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession(); PersonMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(PersonMapper.class); Person person = mapper.selectPersonById(1L); System.out.println(person); sqlSession.close(); }
2、构建过程图示
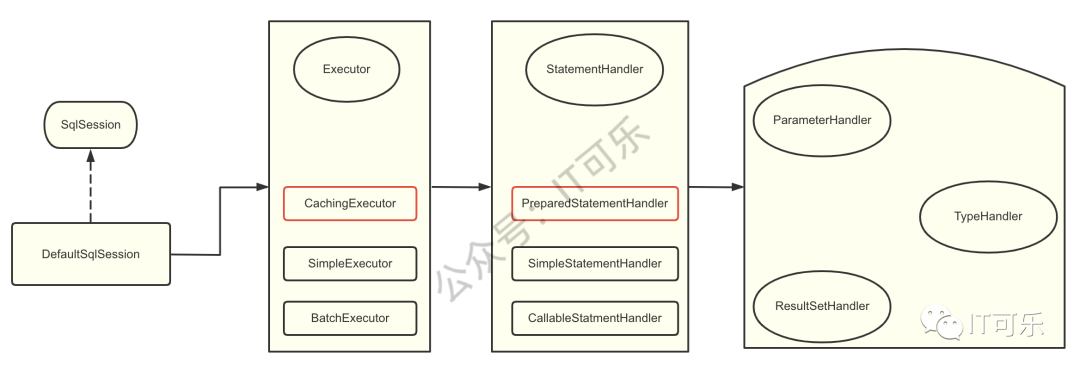
3、代码剖析
3.1 Executor
我们通过 DefaultSessionFactory.openSession() 方法获取 sqlSession
public interface SqlSessionFactory { SqlSession openSession(); SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit); SqlSession openSession(Connection connection); SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection); Configuration getConfiguration(); }
其实是可以通过构造方法指定 Executor 的类型,比如:
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.SIMPLE);
再看生成 Executor 的源代码:在Configuration类中
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
如果不指定执行器类型,直接默认 openSession() 方法,生成的是 CachingExecutor 执行器,这里的 cacheEnabled 其实是默认开启二级缓存的配置,在 mybatis-config.xml 文件中.
并且需要注意的是这里 new CachingExecutor(executor),传进去了一个 SimpleExecutor 对象,后面和数据库交互的实际上是该对象。
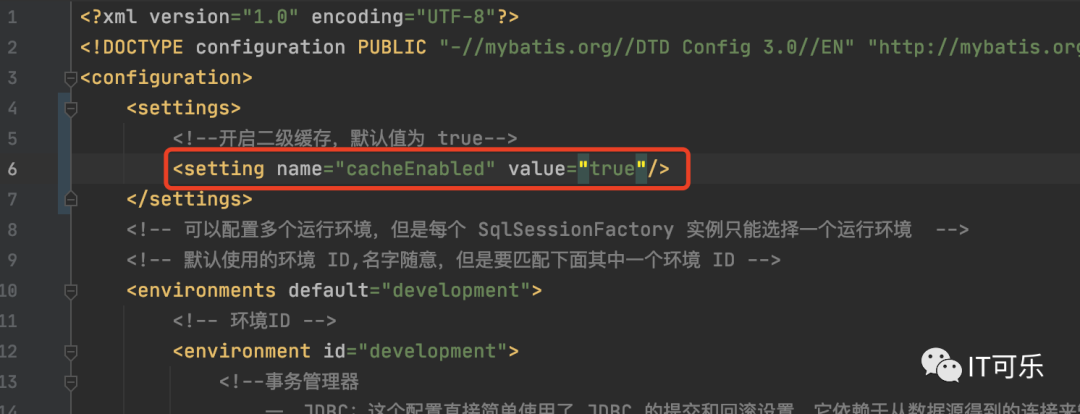
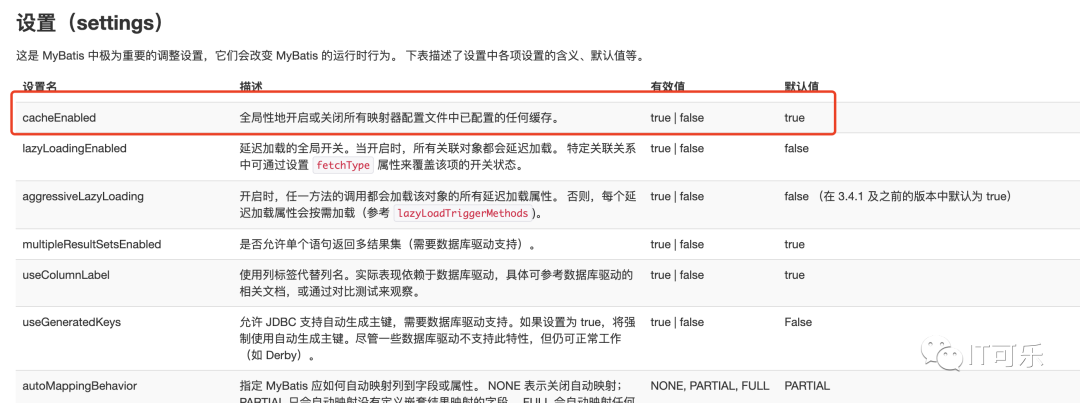
得到了 SqlSession,接下来看这段代码:
Person person = sqlSession.selectOne(namespace + "." + method, 1L);
@Override public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) { // Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many. List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter); if (list.size() == 1) { return list.get(0); } else if (list.size() > 1) { throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size()); } else { return null; } }
直接看上面源码的第 76 行代码:
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
在上一篇文章介绍 SqlSessionFactory 的构建过程时,我们说了 configuration 对象的组成:
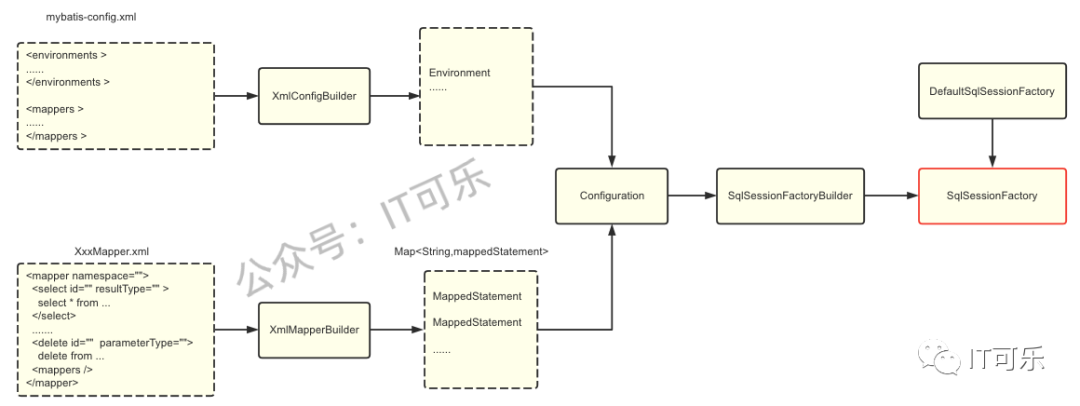
看上面的源码得到 MappedStatement 对象,包含了我们在 mapper.xml 文件中配置的 sql 语句。
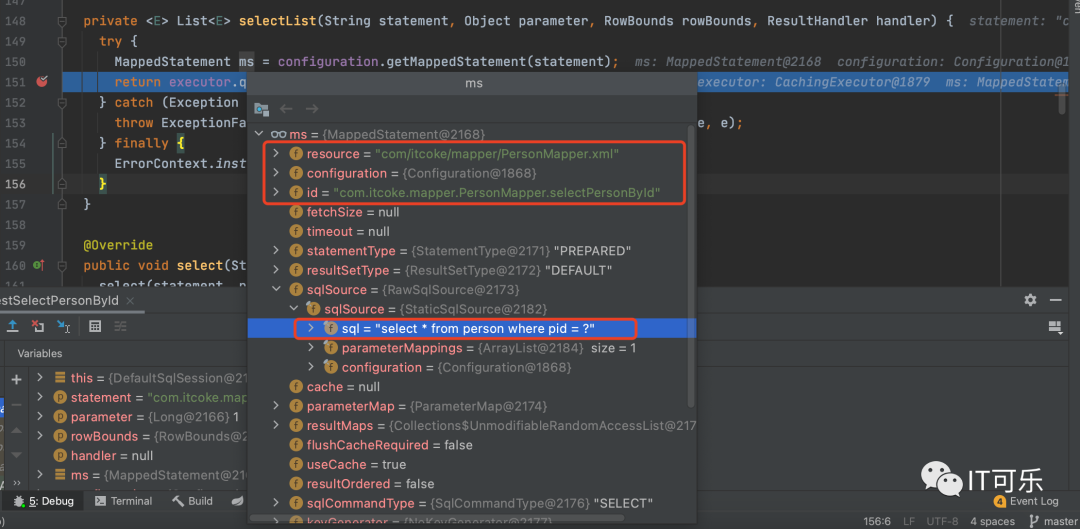
执行 executor.query() 方法,注意,这里的 executor 是 CachingExecutor:
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject); CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
这段源码,我们可以得到两个信息:
①、获取我们指定配置的boundSql 对象,包含我们配置的 sql 语句和参数信息。
②、根据相关信息得到一个缓存 key,通过这个key,连续两次相同的查询,第二次可以不去查数据库,直接获取缓存的数据。
接着我们继续看 query() 方法:
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); if (cache != null) { flushCacheIfRequired(ms); if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); if (list == null) { list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 } return list; } } return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
看源码,也就是说先去查缓存,缓存命中了直接返回数据,没有命中就执行:delegate.query() 方法。
这里的 delegate 是上文我们说的构造 Executor 传进来得 SimpleExecutor 对象。
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { queryStack++; list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; }
关于 mybatis 缓存后面会专门写一篇文章来仔细介绍,这里我们先梳理主线,看上面标红行代码,缓存查不到,从数据库里面查。
继续跟 queryFromDatabase() 方法:
@Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
3.2 StatementHandler
执行到上面第 61 行源码:
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
跟进去:
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }
这里构造的是一个 RoutingStatementHandler 对象,聪明的你一听听名字都知道会路由生成别的对象。
没错,是根据传入的 statementType 生成具体的对象:
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case PREPARED: delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; default: throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } }
在 MappedStatement 对象中,默认 statementType 是 PERPARED:
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, SqlSource sqlSource, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) { mappedStatement.configuration = configuration; mappedStatement.id = id; mappedStatement.sqlSource = sqlSource; mappedStatement.statementType = StatementType.PREPARED; mappedStatement.resultSetType = ResultSetType.DEFAULT; mappedStatement.parameterMap = new ParameterMap.Builder(configuration, "defaultParameterMap", null, new ArrayList<>()).build(); mappedStatement.resultMaps = new ArrayList<>(); mappedStatement.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType; mappedStatement.keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; String logId = id; if (configuration.getLogPrefix() != null) { logId = configuration.getLogPrefix() + id; } mappedStatement.statementLog = LogFactory.getLog(logId); mappedStatement.lang = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance(); }
也就是这里最终生成的 StatementHandler 实际上是 PreparedStatementHandler 对象。
通常情况下:
①、不带参数的 SQL语句执行,会生成 SimpleStatementHandler 对象。
②、带参数的 SQL 语句执行,会生成 PreparedStatementHandler 对象。
③、存储过程执行,会生成 CallableStatementHandler 对象。
3.3 ParameterHandler
再回到 SimpleExecutor 的 doQuery() 方法:
@Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
看第 62 行代码:
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
跟进去:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
这里第 86 行获取数据库连接。
第 88 行,进行参数处理,说直接点,就是将 SQL 语句中的 “?” 替换成我们传入的具体值。
但是我们知道 Java对象参数和数据库参数是不一样的,那么肯定还会做参数类型转换,没错,就是通过下面将要介绍 TypeHandler 来完成。
3.4 TypeHandler
也就是将 Java 类型和 数据库类型进行互相转换。
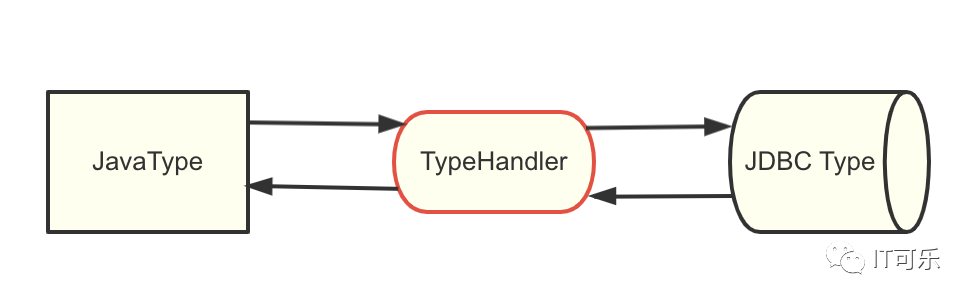
Mybatis 提供给了很多内置的参数转换,基本上不需要我们自己去定义。
当然,聪明的你可能会问了,假如这些都不满足呢?假如我要自定义一些类型呢?
不用担心,Mybatis 给我们预留了自定义类型的接口,如果你想自定义类型,通常分为两步:
①、实现 org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler 接口, 或继承类 org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler
②、在配置文件中配置自定义的 TypeHnadler。
https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#typeHandlers
3.4 ResultSetHandler
还是回到 SimpleExecutor 的 doQuery() 方法:
@Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
上一步我们得到了 PrepraedStatementHandler 对象,接着看 handler.query() 方法:
@Override public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute(); return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps); }
通过执行 ps.execute() 方法,得到结果集,然后通过 resultSetHandler 去处理结果集。
4、总结
本文讲解了如何通过 SqlSession 进行一次数据库查询操作,但是正如文章开头所言给大家介绍了两种查询方式,一种是需要自己拼接 namespace+method 语句,另一种是通过 接口的形式。其实这两种方式是一样的,namespace 就是接口的包名(对应xxxMapper.xml 的namespace名称),method 就是接口的方法名(对应到xxxMapper.xml 的每个SQL语句的 id 属性),通过两者拼接,我们能去 xxxMapper.xml 文件中定位到具体的 SQL 语句。很明显,通过接口的形式避免了我们写字符串错误的可能,实际开发中,我们基本上都是这种方式。