在前两篇《Spring Cloud Ribbon的原理》,《Spring Cloud Ribbon的原理-负载均衡器》中,整理了Ribbon如何通过负载均衡拦截器植入RestTemplate,以及调用负载均衡器获取服务列表,如何过滤,如何更新等的处理过程。
因为,负载均衡器最终是调用负载均衡策略的choose方法来选择一个服务,所以这一篇,整理Ribbon的负载均衡策略。
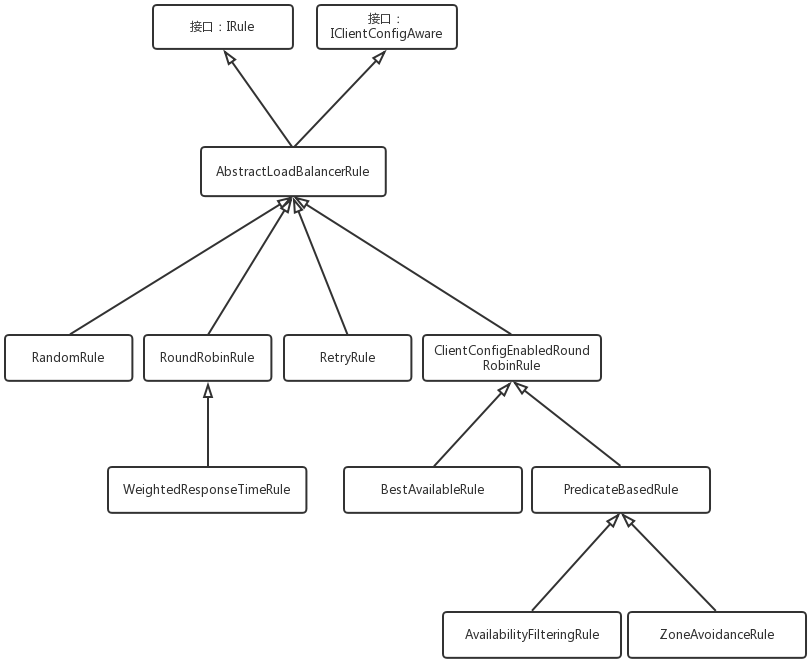
策略类
- RandomRule
- RoundRobinRule
- RetryRule
- WeightedResponseTimeRule
- ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule
- BestAvailableRule
- PredicateBasedRule
- AvailabilityFilteringRule
- ZoneAvoidanceRule
类继承关系
RandomRule
随机选取负载均衡策略。
choose方法中,通过随机Random对象,在所有服务实例数量中随机找一个服务的索引号,然后从上线的服务中获取对应的服务。
这时候,很可能会有不在线的服务,就有可能从上线的服务中获取不到,那么休息会儿再获取知道随机获取到一个上线的服务为止。
1 public class RandomRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule { 2 3 /** 4 * Randomly choose from all living servers 5 */ 6 @edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.SuppressWarnings(value = "RCN_REDUNDANT_NULLCHECK_OF_NULL_VALUE") 7 public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { 8 if (lb == null) { 9 return null; 10 } 11 Server server = null; 12 13 while (server == null) { 14 if (Thread.interrupted()) { 15 return null; 16 } 17 List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers(); 18 List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers(); 19 20 int serverCount = allList.size(); 21 if (serverCount == 0) { 22 /* 23 * No servers. End regardless of pass, because subsequent passes 24 * only get more restrictive. 25 */ 26 return null; 27 } 28 29 int index = chooseRandomInt(serverCount); 30 server = upList.get(index); 31 32 if (server == null) { 33 /* 34 * The only time this should happen is if the server list were 35 * somehow trimmed. This is a transient condition. Retry after 36 * yielding. 37 */ 38 Thread.yield(); 39 continue; 40 } 41 42 if (server.isAlive()) { 43 return (server); 44 } 45 46 // Shouldn't actually happen.. but must be transient or a bug. 47 server = null; 48 Thread.yield(); 49 } 50 51 return server; 52 53 } 54 55 protected int chooseRandomInt(int serverCount) { 56 return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(serverCount); 57 } 58 59 @Override 60 public Server choose(Object key) { 61 return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key); 62 } 63 64 @Override 65 public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) { 66 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 67 68 }
RoundRobinRule
线性轮询负载均衡策略。
choose方法中,通过incrementAndGetModulo方法以线性轮询方式获取服务。
在incrementAndGetModulo中,实际上在类中维护了一个原子性的nextServerCyclicCounter成员变量作为当前服务的索引号,每次在所有服务数量的限制下,就是将服务的索引号加1,到达服务数量限制时再从头开始。
1 public class RoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule { 2 3 private AtomicInteger nextServerCyclicCounter; 4 private static final boolean AVAILABLE_ONLY_SERVERS = true; 5 private static final boolean ALL_SERVERS = false; 6 7 private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RoundRobinRule.class); 8 9 public RoundRobinRule() { 10 nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0); 11 } 12 13 public RoundRobinRule(ILoadBalancer lb) { 14 this(); 15 setLoadBalancer(lb); 16 } 17 18 public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { 19 if (lb == null) { 20 log.warn("no load balancer"); 21 return null; 22 } 23 24 Server server = null; 25 int count = 0; 26 while (server == null && count++ < 10) { 27 List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers(); 28 List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers(); 29 int upCount = reachableServers.size(); 30 int serverCount = allServers.size(); 31 32 if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) { 33 log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb); 34 return null; 35 } 36 37 int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount); 38 server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex); 39 40 if (server == null) { 41 /* Transient. */ 42 Thread.yield(); 43 continue; 44 } 45 46 if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) { 47 return (server); 48 } 49 50 // Next. 51 server = null; 52 } 53 54 if (count >= 10) { 55 log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " 56 + lb); 57 } 58 return server; 59 } 60 61 /** 62 * Inspired by the implementation of {@link AtomicInteger#incrementAndGet()}. 63 * 64 * @param modulo The modulo to bound the value of the counter. 65 * @return The next value. 66 */ 67 private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) { 68 for (;;) { 69 int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get(); 70 int next = (current + 1) % modulo; 71 if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) 72 return next; 73 } 74 } 75 76 @Override 77 public Server choose(Object key) { 78 return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key); 79 } 80 81 @Override 82 public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) { 83 } 84 }
WeightedResponseTimeRule
响应时间作为选取权重的负载均衡策略。其含义就是,响应时间越短的服务被选中的可能性大。继承自RoundRobinRule类。
1 public class WeightedResponseTimeRule extends RoundRobinRule { 2 3 public static final IClientConfigKey<Integer> WEIGHT_TASK_TIMER_INTERVAL_CONFIG_KEY = new IClientConfigKey<Integer>() { 4 @Override 5 public String key() { 6 return "ServerWeightTaskTimerInterval"; 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public String toString() { 11 return key(); 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public Class<Integer> type() { 16 return Integer.class; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 public static final int DEFAULT_TIMER_INTERVAL = 30 * 1000; 21 22 private int serverWeightTaskTimerInterval = DEFAULT_TIMER_INTERVAL; 23 24 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WeightedResponseTimeRule.class); 25 26 // holds the accumulated weight from index 0 to current index 27 // for example, element at index 2 holds the sum of weight of servers from 0 to 2 28 private volatile List<Double> accumulatedWeights = new ArrayList<Double>(); 29 30 31 private final Random random = new Random(); 32 33 protected Timer serverWeightTimer = null; 34 35 protected AtomicBoolean serverWeightAssignmentInProgress = new AtomicBoolean(false); 36 37 String name = "unknown"; 38 39 public WeightedResponseTimeRule() { 40 super(); 41 } 42 43 public WeightedResponseTimeRule(ILoadBalancer lb) { 44 super(lb); 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb) { 49 super.setLoadBalancer(lb); 50 if (lb instanceof BaseLoadBalancer) { 51 name = ((BaseLoadBalancer) lb).getName(); 52 } 53 initialize(lb); 54 } 55 56 void initialize(ILoadBalancer lb) { 57 if (serverWeightTimer != null) { 58 serverWeightTimer.cancel(); 59 } 60 serverWeightTimer = new Timer("NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-" 61 + name, true); 62 serverWeightTimer.schedule(new DynamicServerWeightTask(), 0, 63 serverWeightTaskTimerInterval); 64 // do a initial run 65 ServerWeight sw = new ServerWeight(); 66 sw.maintainWeights(); 67 68 Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(new Runnable() { 69 public void run() { 70 logger 71 .info("Stopping NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-" 72 + name); 73 serverWeightTimer.cancel(); 74 } 75 })); 76 } 77 78 public void shutdown() { 79 if (serverWeightTimer != null) { 80 logger.info("Stopping NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-" + name); 81 serverWeightTimer.cancel(); 82 } 83 } 84 85 List<Double> getAccumulatedWeights() { 86 return Collections.unmodifiableList(accumulatedWeights); 87 } 88 89 @edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.SuppressWarnings(value = "RCN_REDUNDANT_NULLCHECK_OF_NULL_VALUE") 90 @Override 91 public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { 92 if (lb == null) { 93 return null; 94 } 95 Server server = null; 96 97 while (server == null) { 98 // get hold of the current reference in case it is changed from the other thread 99 List<Double> currentWeights = accumulatedWeights; 100 if (Thread.interrupted()) { 101 return null; 102 } 103 List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers(); 104 105 int serverCount = allList.size(); 106 107 if (serverCount == 0) { 108 return null; 109 } 110 111 int serverIndex = 0; 112 113 // last one in the list is the sum of all weights 114 double maxTotalWeight = currentWeights.size() == 0 ? 0 : currentWeights.get(currentWeights.size() - 1); 115 // No server has been hit yet and total weight is not initialized 116 // fallback to use round robin 117 if (maxTotalWeight < 0.001d || serverCount != currentWeights.size()) { 118 server = super.choose(getLoadBalancer(), key); 119 if(server == null) { 120 return server; 121 } 122 } else { 123 // generate a random weight between 0 (inclusive) to maxTotalWeight (exclusive) 124 double randomWeight = random.nextDouble() * maxTotalWeight; 125 // pick the server index based on the randomIndex 126 int n = 0; 127 for (Double d : currentWeights) { 128 if (d >= randomWeight) { 129 serverIndex = n; 130 break; 131 } else { 132 n++; 133 } 134 } 135 136 server = allList.get(serverIndex); 137 } 138 139 if (server == null) { 140 /* Transient. */ 141 Thread.yield(); 142 continue; 143 } 144 145 if (server.isAlive()) { 146 return (server); 147 } 148 149 // Next. 150 server = null; 151 } 152 return server; 153 } 154 155 class DynamicServerWeightTask extends TimerTask { 156 public void run() { 157 ServerWeight serverWeight = new ServerWeight(); 158 try { 159 serverWeight.maintainWeights(); 160 } catch (Exception e) { 161 logger.error("Error running DynamicServerWeightTask for {}", name, e); 162 } 163 } 164 } 165 166 class ServerWeight { 167 168 public void maintainWeights() { 169 ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer(); 170 if (lb == null) { 171 return; 172 } 173 174 if (!serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) { 175 return; 176 } 177 178 try { 179 logger.info("Weight adjusting job started"); 180 AbstractLoadBalancer nlb = (AbstractLoadBalancer) lb; 181 LoadBalancerStats stats = nlb.getLoadBalancerStats(); 182 if (stats == null) { 183 // no statistics, nothing to do 184 return; 185 } 186 double totalResponseTime = 0; 187 // find maximal 95% response time 188 for (Server server : nlb.getAllServers()) { 189 // this will automatically load the stats if not in cache 190 ServerStats ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server); 191 totalResponseTime += ss.getResponseTimeAvg(); 192 } 193 // weight for each server is (sum of responseTime of all servers - responseTime) 194 // so that the longer the response time, the less the weight and the less likely to be chosen 195 Double weightSoFar = 0.0; 196 197 // create new list and hot swap the reference 198 List<Double> finalWeights = new ArrayList<Double>(); 199 for (Server server : nlb.getAllServers()) { 200 ServerStats ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server); 201 double weight = totalResponseTime - ss.getResponseTimeAvg(); 202 weightSoFar += weight; 203 finalWeights.add(weightSoFar); 204 } 205 setWeights(finalWeights); 206 } catch (Exception e) { 207 logger.error("Error calculating server weights", e); 208 } finally { 209 serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.set(false); 210 } 211 212 } 213 } 214 215 void setWeights(List<Double> weights) { 216 this.accumulatedWeights = weights; 217 } 218 219 @Override 220 public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) { 221 super.initWithNiwsConfig(clientConfig); 222 serverWeightTaskTimerInterval = clientConfig.get(WEIGHT_TASK_TIMER_INTERVAL_CONFIG_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMER_INTERVAL); 223 } 224 225 }
既然是按照响应时间权重来选择服务,那么先整理一下权重算法是怎么做的。
观察initialize方法,启动了定时器定时执行DynamicServerWeightTask的run来调用计算服务权重,计算权重是通过内部类ServerWeight的maintainWeights方法来进行。
整理一下maintainWeights方法的逻辑,里面有两个for循环,第一个for循环拿到所有服务的总响应时间,第二个for循环计算每个服务的权重以及总权重。
第一个for循环。
假设有4个服务,每个服务的响应时间(ms):
A: 200
B: 500
C: 30
D: 1200
总响应时间:
200+500+30+1200=1930ms
接下来第二个for循环,计算每个服务的权重。
服务的权重=总响应时间-服务自身的响应时间:
A: 1930-200=1730
B: 1930-500=1430
C: 1930-30=1900
D: 1930-1200=730
总权重:
1730+1430+1900+730=5790
结果就是响应时间越短的服务,它的权重就越大。
再看一下choose方法。重点在while循环的第3个if这里。首先如果判定没有服务或者权重还没计算出来时,会采用父类RoundRobinRule以线性轮询的方式选择服务器。
有服务,有权重计算结果后,就是以总权重值为限制,拿到一个随机数,然后看随机数落到哪个区间,就选择对应的服务。
所以选取服务的结论就是:响应时间越短的服务,它的权重就越大,被选中的可能性就越大。
还有其他的负载均衡选择策略,下面就不一一列举了。