1.script标签
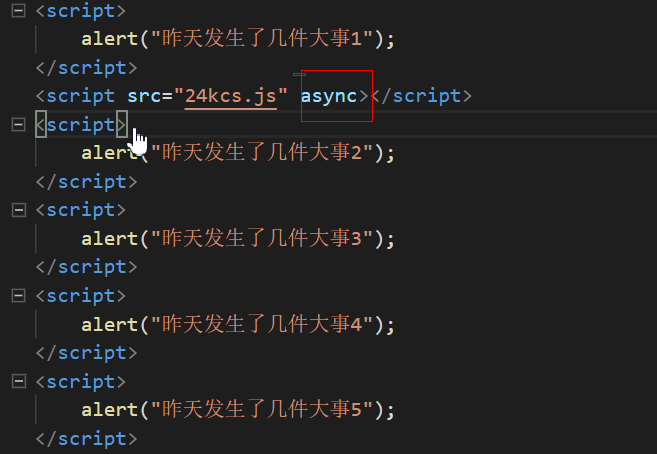
* async是开始就下载,下载完毕就执行。若同时有两个async的script,没有先后顺序
* defer是立即下载,延迟执行。脚本在执行时不会影响页面的构造。HTML5规定,若同时有两个defer的script,要求第一个优先于第二个,但是实际不是,所以最好包含一个defer
执行过程:
如果是async异步----加载完成之后立马执行
如果是defer----页面加载完之后才会执行
2.不引入第三方变量交换两个值(数字/字符串)
一:假如是数字
(1)通过两个值相加
var num1=10;
var num2=20;
num1=num1+num2;//num1=30
num2=num1-num2;//num2=10
num1=num1-num2;//num1=20
console.log(num1);
console.log(num2);
(2)通过位运算符
var num1 = 10;
var num2 = 20;
num1 = num1 ^ num2;//num1=30
num2 = num1 ^ num2;//num2=10
num1 = num1 ^ num2;//num1=20
console.log(num1);
console.log(num2);
二:通用的(无论是字符串、数字、对象)
(1)ES6的解构
let a = 1,
b = 2;
[a, b] = [b, a];
(2) 利用数组特性
var a = 1,
b = 2;
a = [a, b];
b = a[0];
a = a[1];
3.javaScript的数据类型
基本数据类型:Number、String、Boolean、Undfined、Null、Symbol
引用数据类型:Object、Array、Function
typeof() ==== 判断数据类型,常用来判断基本类型。typeof(unll)===》'object'
1)判断是否是undefined
typeof(undefined)====>'undefined' || 某变量 === undefined
2)区分各种类型
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call("jerry"));//[object String]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(12));//[object Number]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(true));//[object Boolean]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined));//[object Undefined]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null));//[object Null]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call({name: "jerry"}));//[object Object]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(function(){}));//[object Function]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([]));//[object Array]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date));//[object Date]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(/d/));//[object RegExp]
function Person(){};
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(new Person));//[object Object]
Object.prototype.toString.call和Object.prototype.toString区别
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call('cLL'));
[object String]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString('CLL'));
[object Object]
call会改变this的指向,指向String
下面的this指向的是Objec.prototype
obj.toString()
console.log("jerry".toString());//jerry
console.log((1).toString());//1
console.log([1,2].toString());//1,2
console.log(new Date().toString());//Wed Dec 21 2016 20:35:48 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
console.log(function(){}.toString());//function (){}
console.log(null.toString());//error
console.log(undefined.toString());//error
toString为Object的原型方法,而Array ,function等类型作为Object的实例,都重写了toString方法。不同的对象类型调用toString方法时,根据原型链的知识,调用的是对应的重写之后的toString方法(function类型返回内容为函数体的字符串,Array类型返回元素组成的字符串.....),而不会去调用Object上原型toString方法(返回对象的具体类型),所以采用obj.toString()不能得到其对象类型,只能将obj转换为字符串类型;因此,在想要得到对象的具体类型时,应该调用Object上原型toString方法
4.数组的方法
1)栈方法:先进后出
var arr = [2]; var length = arr.push(1); // 推入一项 改变原数组,返回长度 var lastItem = arr.pop(); // 取的最后一项 改变原数组,返回取得的最后一项
2)队列方法:先进先出
var arr = [4,5]; var length = arr.unshift(1,2,3); 改变原数组,返回长度 var fistItem = arr.shift(); 改变原数组,返回第一项
3)重排序方法
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6]; arr.reverse(); 改变原数组,进行反转,返回的是处理之后的值 arr.sort((v1,v2)=>v1-v2) 改变原数组,进行排序,返回的是处理之后的值
4)操作方法
concat连接在数组的后面,es6用解构就可以实现
var arr = [1,2,3];
var result = arr.concat('连接',[4,5,6])
不改变原数组,返回操作的数组
slice 截取数组中的某几项 var arr = ['red','yellow','green','pink','white']; var arr1 = arr.slice(1); ["yellow", "green", "pink", "white"] var arr2 = arr.slice(1,3); ["yellow", "green"] arr.slice(-2,-1) === arr.slice(3,4) 不改变原数组,返回的是操作之后的数组 接受的参数:1:截取到最后 2:按照索引值进行截取 负值返回空
splice 删除 插入 替换 var colors = ["red", "green", "blue"]; var removed = colors.splice(0,1); // 删除第一项 alert(colors); // green,blue alert(removed); // red,返回的数组中只包含一项 removed = colors.splice(1, 0, "yellow", "orange"); // 从位置 1 开始插入两项 alert(colors); // green,yellow,orange,blue alert(removed); // 返回的是一个空数组 removed = colors.splice(1, 1, "red", "purple"); // 插入两项,删除一项 alert(colors); // green,red,purple,orange,blue alert(removed); // yellow,返回的数组中只包含一项 删除:2 要删除的第一项的位置和要删除的项数 插入:3 起始位置、0(要删除的项数)和要插入的项 替换:3 起始位置、要删除的项数和要插入的任意数量的项 改变原数组
5)位置方法
indexOf()和 lastIndexOf()
indexOf()方法从数组的开头(位置 0)开始向后查找,lastIndexOf()方法则从数组的末尾开始向前查找。
在比较第一个参数与数组中的每一项时,会使用全等操作符
var numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1];
alert(numbers.indexOf(4)); //3
alert(numbers.lastIndexOf(4)); //5
alert(numbers.indexOf(4, 4)); //5
alert(numbers.lastIndexOf(4, 4)); //3
var person = { name: "Nicholas" };
var people = [{ name: "Nicholas" }];
var morePeople = [person];
alert(people.indexOf(person)); //-1
alert(morePeople.indexOf(person)); //0
6)迭代方法
every():对数组中的每一项运行给定函数,如果该函数对每一项都返回 true,则返回 true。 filter():对数组中的每一项运行给定函数,返回该函数会返回 true 的项组成的数组。 forEach():对数组中的每一项运行给定函数。这个方法没有返回值。 map():对数组中的每一项运行给定函数,返回每次函数调用的结果组成的数组。 some():对数组中的每一项运行给定函数,如果该函数对任一项返回 true,则返回 true。 以上方法都不会修改数组中的包含的值。
every和some
var numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1]; var everyResult = numbers.every(function(item, index, array){ return (item > 2); }); alert(everyResult); //false 每一项 var someResult = numbers.some(function(item, index, array){ return (item > 2); }); alert(someResult); //true 有一项
filter 过滤
var numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1];
var filterResult = numbers.filter(function(item, index, array){
return (item > 2);
});
alert(filterResult); //[3,4,5,4,3]
map:地图,映射
var numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1];
var mapResult = numbers.map(function(item, index, array){
return item * 2; //有返回值,每一项做一些操作
});
alert(mapResult); //[2,4,6,8,10,8,6,4,2]
forEach 每一次
var numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1];
numbers.forEach(function(item, index, array){
//执行某些操作 无返回值
});
7)归并
reduce()和 reduceRight()
reduce()方法可以执行求数组中所有值之和的操作,比如:
var values = [1,2,3,4,5];
var sum = values.reduce(function(prev, cur, index, array){
return prev + cur;
});
alert(sum); //15
var values = [1,2,3,4,5];
var sum = values.reduceRight(function(prev, cur, index, array){
return prev + cur;
});
alert(sum); //15
5.字符串的方法
split: 将字符串分割为数组,不改变原字符串 const str = '1,2,3,4,5'; const result = str.split(); join:
查找字符串中的字符串
indexOf() 方法返回字符串中指定文本首次出现的索引(位置):
var str = "The full name of China is the People's Republic of China.";
var pos = str.indexOf("China");
lastIndexOf() 方法返回指定文本在字符串中最后一次出现的索引:
var str = "The full name of China is the People's Republic of China.";
var pos = str.lastIndexOf("China");
提取部分字符串 有三种提取部分字符串的方法: slice(start, end) substring(start, end) substr(start, length) substring() 类似于 slice()。 不同之处在于 substring() 无法接受负的索引。 substr() 类似于 slice()。 不同之处在于第二个参数规定被提取部分的长度。
String.trim() trim() 方法删除字符串两端的空白符: