参考:
1、《Python机器学习:预测分析核心算法》 P258-P266
1 import numpy 2 3 #from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split 4 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 5 6 #这里是可以用来构建GradientBoostingRegressor模型 7 from sklearn import ensemble 8 from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error 9 import pylab as plot
1 # 从本机读取数据 2 target_file = open('winequality-red.csv','r') 3 data = target_file.readlines() 4 target_file.close()
1 #整理原始数据,将原始数据分为属性列表(xList),标签列表(labels) 2 #将各个属性的名称存入names列表 3 xList = [] 4 labels = [] 5 names = [] 6 firstLine = True 7 for line in data: 8 if firstLine: 9 names = line.strip().split(";") 10 firstLine = False 11 else: 12 #split on semi-colon 13 row = line.strip().split(";") 14 #put labels in separate array 15 labels.append(float(row[-1])) 16 #remove label from row 17 row.pop() 18 #convert row to floats 19 floatRow = [float(num) for num in row] 20 xList.append(floatRow) 21 22 #计算属性列表的行数和列数 23 nrows = len(xList) 24 ncols = len(xList[0])
1 #将各列表转为numpy数组形式,此形式是RandomForestRegressor的要求 2 #并且这些对象可以使用sklearn的train_test_split构建训练和测试集 3 X = numpy.array(xList) 4 y = numpy.array(labels) 5 wineNames = numpy.array(names)
1 #构建test集为30%规模的训练集和测试集 2 #random_state设置为一个特殊整数,而不是让随机数生成器自己选择一个不可重复的内部值 3 #这样重复代码可以获得同样的结果,便于开发阶段的调整,否则随机性会掩盖所做的改变 4 #固定random_state就固定了测试集,会对测试数据集过度训练 5 #take fixed holdout set 30% of data rows 6 xTrain, xTest, yTrain, yTest = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.30, random_state=531)
1 # Train gradient boosting model to minimize mean squared error 2 3 #对梯度提升法参数设置和调整的建议: 4 #1、除了设置subsample为0.5的情况,其他情况都以缺省值开始训练。 5 #2、模型训练完成后,观察模型在测试数据(out_of_sample, oos)下的预测性能与决策树数目的关系及变化。 6 #3、如果测试数据性能在图的右侧迅速提高,增加n_estimators或者learning_rate 7 #4、如果测试数据性能在图的右侧迅速恶化,则减少learning_rate 8 #5、一旦测试数据的性能曲线在整体都有改善,并且图的右侧基本持平,则尝试改变max_depth和max_features 9 10 nEst = 2000 11 depth = 7 12 learnRate = 0.01 13 subSamp = 0.5 14 15 wineGBMModel = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=nEst, 16 max_depth=depth, 17 learning_rate=learnRate, 18 subsample = subSamp, 19 loss='ls') 20 21 wineGBMModel.fit(xTrain, yTrain)
运行后显示:
GradientBoostingRegressor(alpha=0.9, ccp_alpha=0.0, criterion='friedman_mse',
init=None, learning_rate=0.01, loss='ls', max_depth=7,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=2000,
n_iter_no_change=None, presort='deprecated',
random_state=None, subsample=0.5, tol=0.0001,
validation_fraction=0.1, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
1 # compute mse on test set 2 msError = [] 3 #利用迭代器staged_predict观察测试数据误差与决策树数目的关系 4 predictions = wineGBMModel.staged_predict(xTest) 5 for p in predictions: 6 msError.append(mean_squared_error(yTest, p)) 7 8 print("MSE" ) 9 print(min(msError)) 10 print(msError.index(min(msError)))
运行后显示:
MSE 0.3155227031463733 826
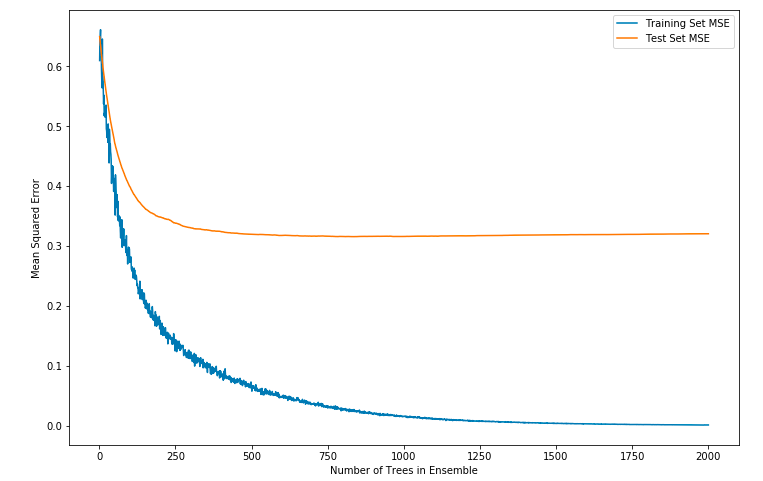
1 #plot training and test errors vs number of trees in ensemble 2 plot.figure(figsize=(12,8)) 3 plot.plot(range(1, nEst + 1), wineGBMModel.train_score_, label='Training Set MSE') 4 plot.plot(range(1, nEst + 1), msError, label='Test Set MSE') 5 plot.legend(loc='upper right') 6 plot.xlabel('Number of Trees in Ensemble') 7 plot.ylabel('Mean Squared Error') 8 plot.show()
运行后显示:
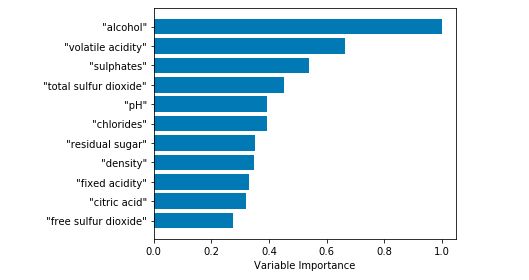
1 # Plot feature importance 2 featureImportance = wineGBMModel.feature_importances_ 3 4 # normalize by max importance 5 featureImportance = featureImportance / featureImportance.max() 6 idxSorted = numpy.argsort(featureImportance) 7 barPos = numpy.arange(idxSorted.shape[0]) + .5 8 plot.barh(barPos, featureImportance[idxSorted], align='center') 9 plot.yticks(barPos, wineNames[idxSorted]) 10 plot.xlabel('Variable Importance') 11 plot.subplots_adjust(left=0.2, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.1) 12 plot.show()
运行后显示: