红黑树操作
实验目的
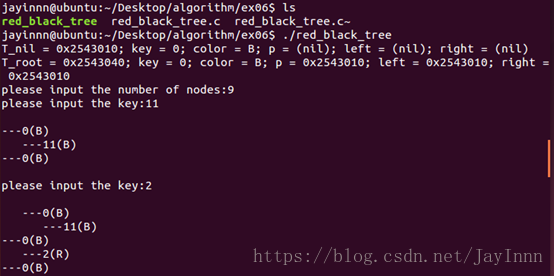
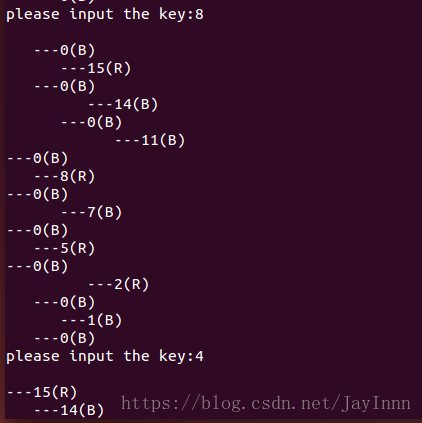
通过插入操作建立一个红黑树,输入为1…n的数,同时将每次插入后的树信息打印出来。
实验原理
红黑树是一棵二叉搜索树,它在每个结点上增加了一个存储位来表示结点的颜色,可以是RED或BLACK。通过对任何一条从根到叶子的简单路径上各个结点的颜色约束,红黑树确保没有一条路径比其他路径长出2倍,因而是近似于平衡的。
树中每个结点有五个属性:color,key,left,right和p;通过添加哨兵(T_nil)对红黑树的边界进行限定。
一棵红黑树是满足下面红黑性质的二叉搜索树:
(1)每个结点或是红色,或是黑色的;
(2)根节点是黑色的;
(3)每个叶节点(NIL)是黑色的;
(4)如果一个结点是红色的,则它的两个子节点都是黑色的;
(5)对每个结点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色结点;
实验过程
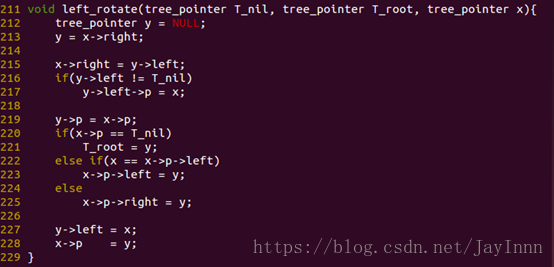
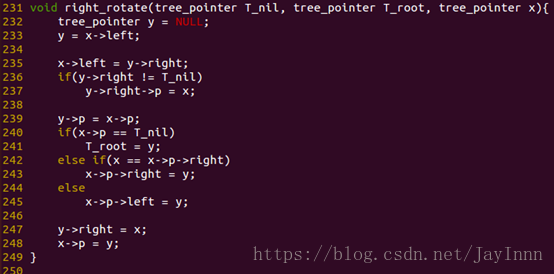
旋转操作:左旋和右旋
LEFT-ROTATE(T, x)
1 y = x.right
2 x.right = y.left
3 if y.left !=T.nil
4 y.left.p = x
5 y.p = x.p
6 if x.p == T.nil
7 T.root = y
8 elseif x ==x.p.left
9 x.p.left = y
10 else x.p.right= y
11 y.left = x
12 x.p = y
RIGHT-ROTATE(T, x)
1 y = x.left
2 x.left = y.right
3 if y.right !=T.nil
4 y.right.p = x
5 y.p = x.p
6 if x.p == T.nil
7 T.root = y
8 elseif x ==x.p.right
9 x.p.right = y
10 else x.p.left =y
11 y.right = x
12 x.p = y
插入操作:插入一个新节点就像在二叉树中插入一个结点一样,但是由于红黑树多了一个颜色属性,因此初始插入的结点的颜色属性为RED。选择将插入结点的颜色属性初始为RED的原因:在红黑树中插入一个结点时,如果初始插入结点的颜色为BLACK时,那么将会破坏性质(5),而且在修改性质(5)的过程中,需要去遍历每条路径,显然这是低效率的;如果将颜色初始为RED时,那么将会破坏性质(2)和性质(4),性质(2)修改很简单,性质(4)的修改过程只需要考虑叔叔结点的颜色,就可以逐步实现;显然在通过将插入结点初始为RED是更高效的操作。
RB-INSERT(T, z)
1 y = T.nil
2 x = T.root
3 while x != T.nil
4 y = x
5 if z.key < x.key
6 x = x.left
7 else x = x.right
8 z.p = y
9 if y == T.nil
10 T.root = z
11 elseif z.key< y.key
12 y.left = z
13 else y.right =z
14 z.left = T.nil
15 z.right = T.nil
16 z.color = RED
17RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T, z)
RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T,z)
1 while z.p.color== RED
2 if z.p == z.p.p.left
3 y = z.p.p.right
4 if y.color == RED
5 z.p.color = BLACK
6 y.color = BLACK
7 z.p.p.color = RED
8 z = z.p.p
9 else if z == z.p.right
10 z = z.p
11 LEFT-ROTATE(T, z)
12 else
13 z.p.color = BLACK
14 z.p.p.color = RED
15 RIGHT-ROTATE(T, z.p.p)
16 else(same as then clause with “right” and“left” exchanged)
17 T.root.color = BLACK
实验总结
(一)在实验过程中,输入是通过调用一个struct node * creat_node(tree_pointerT, int key)来实现的,但是这种方法存在一个问题:使用malloc分配内存时,在最后没有进行free处理,容易造成内存泄漏;
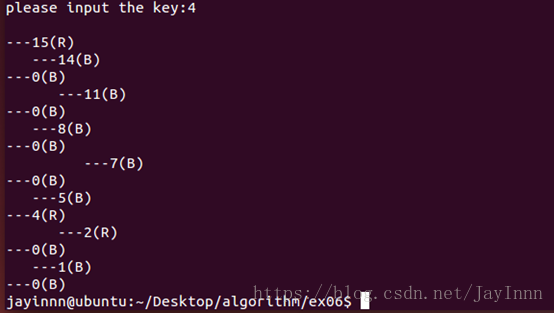
(二)关于树的打印,实验主要关注的是红黑树算法代码的实现,所以没有过于的去关注数的可视性。说明一下如何理解打印下来的树,右端最突出的是根节点,下端是左子树,上端是右子树;,
(三)在整个实验过程中,由于自己基础较差,可能附录的代码中有多处注释,想了想还是没有删掉,也是一种实现算法的过程,以及如何去调试程序吧。
附录(代码)

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 6 7 typedef structnode *tree_pointer; 8 9 typedef struct node { 10 11 int key; 12 13 char color; //R represents red; B represents black 14 15 tree_pointerp; 16 17 tree_pointerleft; 18 19 tree_pointerright; 20 21 } *tree_pointer; 22 23 24 25 void RB_insert(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer z); 26 27 void left_rotate(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer x); 28 29 void right_rotate(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer x); 30 31 void RB_insert_fixup(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer z); 32 33 void print_tree(tree_pointer T_root, int n); 34 35 36 37 38 39 int get_tree_height(tree_pointer T_root); 40 41 42 43 struct node * creat_node(tree_pointer T, int key); 44 45 46 47 48 49 int main(){ 50 51 inti,num,key,tree_height; 52 53 54 55 tree_pointernew_node = NULL; 56 57 tree_pointerT_root = NULL; 58 59 tree_pointerT_nil = NULL; 60 61 T_nil =(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); 62 63 T_nil->color= 'B'; 64 65 66 67 T_root =(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); 68 69 // T_root->key = 11; 70 71 T_root->color= 'B'; 72 73 T_root->p = T_nil; 74 75 T_root->left = T_nil; 76 77 T_root->right= T_nil; 78 79 80 81 printf("T_nil= %p; key = %d; color = %c; p = %p; left = %p; right = %p ",T_nil,T_nil->key, T_nil->color, T_nil->p, T_nil->left, T_nil->right); 82 83 printf("T_root= %p; key = %d; color = %c; p = %p; left = %p; right = %p ",T_root,T_root->key, T_root->color, T_root->p, T_root->left,T_root->right); 84 85 86 87 printf("pleaseinput the number of nodes:"); 88 89 scanf("%d",&num); 90 91 printf("pleaseinput the key:"); 92 93 scanf("%d",&key); 94 95 T_root->key= key; 96 97 printf(" "); 98 99 tree_height =get_tree_height(T_root); 100 101 print_tree(T_root,tree_height); 102 103 104 105 printf(" "); 106 107 for(i = 0; i< num-1; i++){ 108 109 printf("pleaseinput the key:"); 110 111 scanf("%d",&key); 112 113 printf(" "); 114 115 new_node =creat_node(T_nil, key); 116 117 RB_insert(T_nil,T_root, new_node); 118 119 // tree_height= get_tree_height(T_root); 120 121 // print_tree(T_root,tree_height); 122 123 // printf(" 666666666666666666666666 "); 124 125 } 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 /* 134 135 tree_pointernew1 = NULL; 136 137 tree_pointernew2 = NULL; 138 139 tree_pointernew3 = NULL; 140 141 tree_pointernew4 = NULL; 142 143 tree_pointernew5 = NULL; 144 145 // T_root =creat_node(T_nil, 11); 146 147 new1 =creat_node(T_nil, 2); 148 149 new2 =creat_node(T_nil, 14); 150 151 new3 =creat_node(T_nil, 1); 152 153 new4 =creat_node(T_nil, 7); 154 155 new5 =creat_node(T_nil, 15); 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 RB_insert(T_nil,T_root, new1); 164 165 RB_insert(T_nil,T_root, new2); 166 167 RB_insert(T_nil,T_root, new3); 168 169 RB_insert(T_nil,T_root, new4); 170 171 RB_insert(T_nil,T_root, new5); 172 173 174 175 printf("%p, %p %p",new1->p,new1->left,new1->right); 176 177 new1 = new2; 178 179 180 181 printf(" 1111111111111111111111111 "); 182 183 printf("new1= %p; key = %d; color = %c;",new1,new1->key,new1->color); 184 185 printf("p=%p; left = %p; right = %p ",new1->p,new1->left,new1->right); 186 187 188 189 printf("new2= %p; key = %d; color = %c; p = %p; left = %p; right = %p ",new2,new2->key, new2->color, new2->p, new2->left, new2->right); 190 191 */ 192 193 // tree_height =get_tree_height(T_root); 194 195 // print_tree(T_root,tree_height); 196 197 198 199 } 200 201 202 203 struct node * creat_node(tree_pointer T, int key){ 204 205 tree_pointernew = NULL; 206 207 new = (structnode *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); 208 209 new->key = key; 210 211 new->color= 'R'; 212 213 new->p = T; 214 215 new->left = T; 216 217 new->right= T; 218 219 return new; 220 221 } 222 223 224 225 void RB_insert(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer z){ 226 227 tree_pointerx = NULL; 228 229 tree_pointery = NULL; 230 231 y = T_nil; 232 233 x = T_root; 234 235 236 237 // printf(" nowRB_insert is running! "); 238 239 240 241 while(x !=T_nil){ 242 243 y = x; 244 245 if(z->key< x->key) 246 247 x =x->left; 248 249 else 250 251 x =x->right; 252 253 } 254 255 256 257 z->p = y; 258 259 if(y ==T_nil) 260 261 T_root = z; 262 263 elseif(z->key < y->key) 264 265 y->left = z; 266 267 else 268 269 y->right= z; 270 271 272 273 z->left = T_nil; 274 275 z->right =T_nil; 276 277 z->color ='R'; 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 RB_insert_fixup(T_nil,T_root, z); 286 287 288 289 // printf(" nowRB_insert is over! "); 290 291 } 292 293 294 295 void RB_insert_fixup(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer z){ 296 297 tree_pointery = NULL; 298 299 300 301 // printf(" nowRB_insert_fixup is running! "); 302 303 304 305 while(z->p->color== 'R'){ 306 307 if(z->p== z->p->p->left){ 308 309 y =z->p->p->right; 310 311 312 313 if(y->color== 'R'){ 314 315 z->p->color = 'B'; 316 317 y->color = 'B'; 318 319 z->p->p->color= 'R'; 320 321 z =z->p->p; 322 323 } 324 325 elseif(z == z->p->right){ 326 327 z =z->p; 328 329 left_rotate(T_nil,T_root, z); 330 331 } 332 333 else{ 334 335 z->p->color = 'B'; 336 337 z->p->p->color= 'R'; 338 339 right_rotate(T_nil,T_root, z->p->p); 340 341 342 343 } 344 345 } 346 347 ////////////////////////////////// 348 349 elseif(z->p = z->p->p->right){ 350 351 y =z->p->p->left; 352 353 354 355 if(y->color== 'R'){ 356 357 z->p->color = 'B'; 358 359 y->color = 'B'; 360 361 z->p->p->color= 'R'; 362 363 z =z->p->p; 364 365 } 366 367 elseif(z == z->p->left){ 368 369 z =z->p; 370 371 right_rotate(T_nil,T_root, z); 372 373 } 374 375 else{ 376 377 z->p->color = 'B'; 378 379 z->p->p->color= 'R'; 380 381 left_rotate(T_nil,T_root, z->p->p); 382 383 } 384 385 } 386 387 T_root->color= 'B'; 388 389 } 390 391 392 393 // printf(" nowRB_insert_fixup is over! "); 394 395 inttree_height; 396 397 if(T_root->p== T_nil){ 398 399 tree_height= get_tree_height(T_root); 400 401 print_tree(T_root,tree_height); 402 403 } 404 405 else{ 406 407 tree_height= get_tree_height(T_root); 408 409 print_tree(T_root->p,tree_height); 410 411 } 412 413 } 414 415 416 417 418 419 void left_rotate(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer x){ 420 421 tree_pointery = NULL; 422 423 y =x->right; 424 425 426 427 x->right =y->left; 428 429 if(y->left!= T_nil) 430 431 y->left->p= x; 432 433 434 435 y->p =x->p; 436 437 if(x->p ==T_nil) 438 439 T_root =y; 440 441 else if(x ==x->p->left) 442 443 x->p->left= y; 444 445 else 446 447 x->p->right= y; 448 449 450 451 y->left =x; 452 453 x->p = y; 454 455 } 456 457 458 459 void right_rotate(tree_pointer T_nil, tree_pointerT_root, tree_pointer x){ 460 461 tree_pointery = NULL; 462 463 y =x->left; 464 465 466 467 x->left =y->right; 468 469 if(y->right!= T_nil) 470 471 y->right->p= x; 472 473 474 475 y->p =x->p; 476 477 if(x->p ==T_nil) 478 479 T_root =y; 480 481 else if(x ==x->p->right) 482 483 x->p->right= y; 484 485 else 486 487 x->p->left= y; 488 489 490 491 y->right =x; 492 493 x->p = y; 494 495 } 496 497 498 499 int get_tree_height(tree_pointer T_root){ 500 501 if(!T_root) 502 503 return 0; 504 505 intleft_height,right_height; 506 507 left_height = get_tree_height(T_root->left); 508 509 right_height= get_tree_height(T_root->right); 510 511 return(left_height < right_height)?(right_height+1):(left_height+1); 512 513 } 514 515 516 517 void print_tree(tree_pointer T_root, int n){ 518 519 int i; 520 521 if(T_root ==NULL) 522 523 return; 524 525 print_tree(T_root->right, n-1); 526 527 528 529 for(i = 0; i< n-1; i++) 530 531 printf(" "); 532 533 if(n > 0){ 534 535 printf("---"); 536 537 printf("%d(%c) ",T_root->key,T_root->color); 538 539 } 540 541 542 543 print_tree(T_root->left,n-1); 544 545 }