多线程 运行速度不变,程序运行效率提高,CPU的使用率更高
分时调度 :多个线程切换时 平均分配CPU的占用时间。
抢占式调度:多个线程切换时 优先级高的先使用 CPU 相同:随机
1.定义Thread子类 重写run()方法
public class Demo01 { //运行main方法 系统 开启一条执行路径(主线程)
public static void main(String[] args) {//进栈执行
MyThread td = new MyThread(); //创建线程子类对象
//MyThread td1=new MyThread("ccc");//构造方法 线程重命名
//Thread td2=Thread.currentThread(); //当前运行的线程对象
//td.run();//调用子线程run()方法 不是多线程
td.setName("子线程"); //修改线程名字
td.start();//开启子线程(新的栈) 调用run()方法(进新栈)只调一次
String str = td.getName()); //获取线程名称
//String str2 = Thread.currentThread().getName() //→ main
method01();//运行主线程 method01()方法
}
public static void method01(){
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println("main..."+i);
}
}
}
public classMyThread extends Thread{
public ThreadZi(){}
public ThreadZi(String name){//构造方法 线程名
super(name); //调用父类构造方法
}
public void run() { //重写run()方法
//setName("bbb");//运行中修改线程名称
//System.out.println(super.getName());
System.out.println(getName()); //获取当前线程名称 继承
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
sleep(1000);//暂停1秒 父类run()无异常 只能try
System.out.println(getName()+"..."+i);
}
}
}
//创建线程对象时,直接重写Thread类中的run方法
new Thread() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("重写的run方法");
}
}.start();
多线程2(常用) 线程对象、任务解耦
//2.实现Runnable接口 实现run()方法
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{//解决多继承问题
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"..."+i);
}
}
}
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable mr=new MyRunnable(); //任务对象
Thread t1=new Thread(mr); //线程对象 传入任务Runnable
//Thread t1=new Thread(mr,"ccc"); //构造方法 线程重命名
t1.start(); //开启线程 执行任务对象的run方法
Thread t2=new Thread(mr); //再开一个线程
t2.start();
method(); //整个线程
}
//匿名内部类的方式实现Runnable接口,重新Runnable接口中的run方法
new Thread(
new Runnable(){
public void run(){
System.out.println("重写的run方法");
}
}
).start();
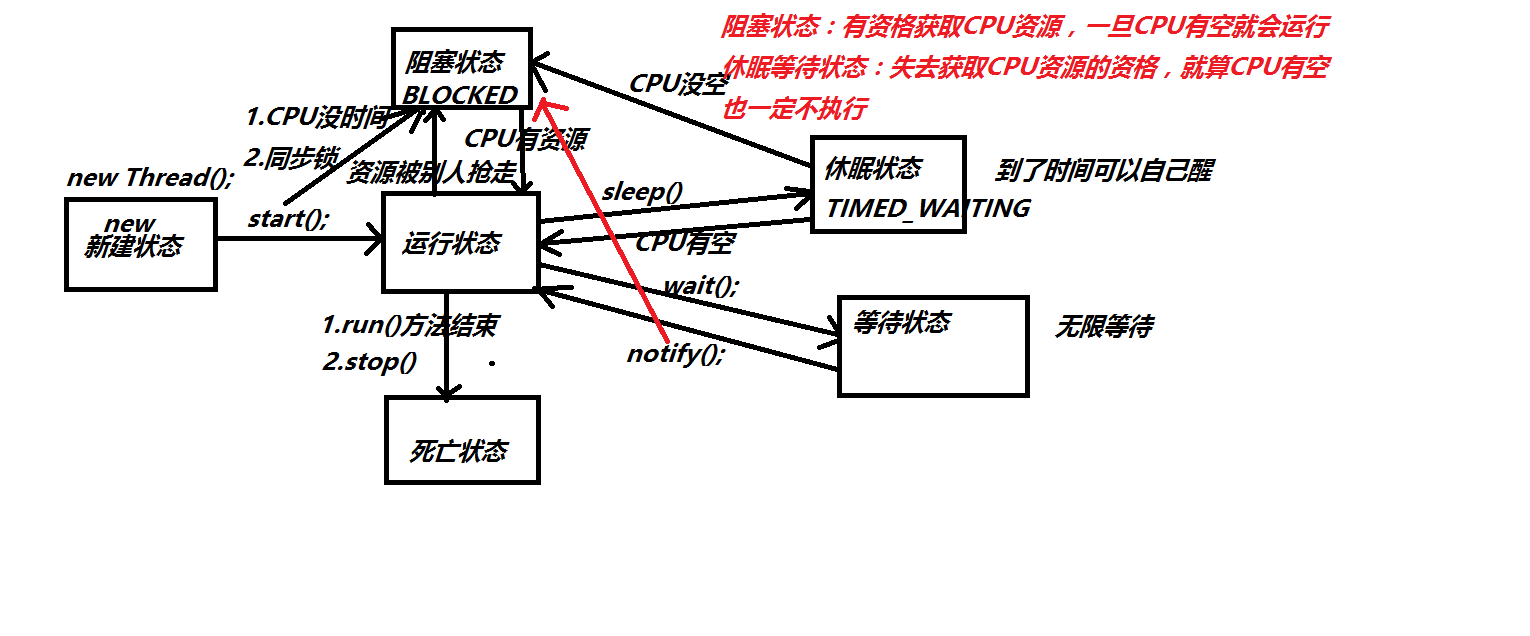
//Thread.State 线程状态 枚举
//New :创建 new Thread()
//Blocked :阻塞 CPU没时间/同步锁
//Runnable :运行 td.start()
//Timed_waiting:休眠 到时间自己进入运行/阻塞状态
//Waiting :无限等待 wait(); notify()唤醒
//Terminated :死亡 run()方法结束 /td.stop()结束线程
线程池原理
