来源:blog.csdn.net/qq_42105629/article/details/102589319
一、Jedis,Redisson,Lettuce三者的区别
共同点:都提供了基于Redis操作的Java API,只是封装程度,具体实现稍有不同。
不同点:
1.1、Jedis
是Redis的Java实现的客户端。支持基本的数据类型如:String、Hash、List、Set、Sorted Set。
特点:使用阻塞的I/O,方法调用同步,程序流需要等到socket处理完I/O才能执行,不支持异步操作。Jedis客户端实例不是线程安全的,需要通过连接池来使用Jedis。
1.2、Redisson
优点点:分布式锁,分布式集合,可通过Redis支持延迟队列。
1.3、 Lettuce
用于线程安全同步,异步和响应使用,支持集群,Sentinel,管道和编码器。
基于Netty框架的事件驱动的通信层,其方法调用是异步的。Lettuce的API是线程安全的,所以可以操作单个Lettuce连接来完成各种操作。
二、RedisTemplate
2.1、使用配置
maven配置引入,(要加上版本号,我这里是因为Parent已声明)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
application-dev.yml
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.1.140
port: 6379
password:
database: 15 # 指定redis的分库(共16个0到15)
Spring Boot 基础就不介绍了,推荐下这个实战教程:
https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
2.2、使用示例
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Override
public CustomersEntity findById(Integer id) {
// 需要缓存
// 所有涉及的缓存都需要删除,或者更新
try {
String toString = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().get(REDIS_CUSTOMERS_ONE, id + "").toString();
if (toString != null) {
return JSONUtil.toBean(toString, CustomersEntity.class);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 缓存为空的时候,先查,然后缓存redis
Optional<CustomersEntity> byId = customerRepo.findById(id);
if (byId.isPresent()) {
CustomersEntity customersEntity = byId.get();
try {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put(REDIS_CUSTOMERS_ONE, id + "", JSONUtil.toJsonStr(customersEntity));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return customersEntity;
}
return null;
}
2.3、扩展
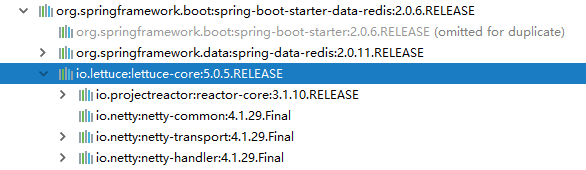
2.3.1、spring-boot-starter-data-redis的依赖包
3.3.2、stringRedisTemplate API(部分展示)
- opsForHash --> hash操作
- opsForList --> list操作
- opsForSet --> set操作
- opsForValue --> string操作
- opsForZSet --> Zset操作

3.3.3 StringRedisTemplate默认序列化机制
public class StringRedisTemplate extends RedisTemplate<String, String> {
/**
* Constructs a new <code>StringRedisTemplate</code> instance. {@link #setConnectionFactory(RedisConnectionFactory)}
* and {@link #afterPropertiesSet()} still need to be called.
*/
public StringRedisTemplate() {
RedisSerializer<String> stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
setValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
}
}
三、RedissonClient 操作示例
3.1 基本配置
3.1.1、Maven pom 引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.8.2</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>LATEST</version>
</dependency>
3.1.2、添加配置文件Yaml或者json格式
redisson-config.yml
# Redisson 配置
singleServerConfig:
address: "redis://192.168.1.140:6379"
password: null
clientName: null
database: 15 #选择使用哪个数据库0~15
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
pingTimeout: 1000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
reconnectionTimeout: 3000
failedAttempts: 3
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
connectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
connectionPoolSize: 64
dnsMonitoringInterval: 5000
#dnsMonitoring: false
threads: 0
nettyThreads: 0
codec:
class: "org.redisson.codec.JsonJacksonCodec"
transportMode: "NIO"
或者,配置 redisson-config.json
{
"singleServerConfig": {
"idleConnectionTimeout": 10000,
"pingTimeout": 1000,
"connectTimeout": 10000,
"timeout": 3000,
"retryAttempts": 3,
"retryInterval": 1500,
"reconnectionTimeout": 3000,
"failedAttempts": 3,
"password": null,
"subscriptionsPerConnection": 5,
"clientName": null,
"address": "redis://192.168.1.140:6379",
"subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize": 1,
"subscriptionConnectionPoolSize": 50,
"connectionMinimumIdleSize": 10,
"connectionPoolSize": 64,
"database": 0,
"dnsMonitoring": false,
"dnsMonitoringInterval": 5000
},
"threads": 0,
"nettyThreads": 0,
"codec": null,
"useLinuxNativeEpoll": false
}
3.1.3、读取配置
新建读取配置类
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redisson() throws IOException {
// 两种读取方式,Config.fromYAML 和 Config.fromJSON
// Config config = Config.fromJSON(RedissonConfig.class.getClassLoader().getResource("redisson-config.json"));
Config config = Config.fromYAML(RedissonConfig.class.getClassLoader().getResource("redisson-config.yml"));
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
或者,在 application.yml中配置如下
spring:
redis:
redisson:
config: classpath:redisson-config.yaml
3.2 使用示例
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class TeController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
static long i = 20;
static long sum = 300;
// ========================== String =======================
@GetMapping("/set/{key}")
public String s1(@PathVariable String key) {
// 设置字符串
RBucket<String> keyObj = redissonClient.getBucket(key);
keyObj.set(key + "1-v1");
return key;
}
@GetMapping("/get/{key}")
public String g1(@PathVariable String key) {
// 设置字符串
RBucket<String> keyObj = redissonClient.getBucket(key);
String s = keyObj.get();
return s;
}
// ========================== hash =======================-=
@GetMapping("/hset/{key}")
public String h1(@PathVariable String key) {
Ur ur = new Ur();
ur.setId(MathUtil.randomLong(1,20));
ur.setName(key);
// 存放 Hash
RMap<String, Ur> ss = redissonClient.getMap("UR");
ss.put(ur.getId().toString(), ur);
return ur.toString();
}
@GetMapping("/hget/{id}")
public String h2(@PathVariable String id) {
// hash 查询
RMap<String, Ur> ss = redissonClient.getMap("UR");
Ur ur = ss.get(id);
return ur.toString();
}
// 查询所有的 keys
@GetMapping("/all")
public String all(){
RKeys keys = redissonClient.getKeys();
Iterable<String> keys1 = keys.getKeys();
keys1.forEach(System.out::println);
return keys.toString();
}
// ================== ==============读写锁测试 =============================
@GetMapping("/rw/set/{key}")
public void rw_set(){
// RedissonLock.
RBucket<String> ls_count = redissonClient.getBucket("LS_COUNT");
ls_count.set("300",360000000l, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
// 减法运算
@GetMapping("/jf")
public void jf(){
String key = "S_COUNT";
// RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(key);
// atomicLong.set(sum);
// long l = atomicLong.decrementAndGet();
// System.out.println(l);
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(key);
if (!atomicLong.isExists()) {
atomicLong.set(300l);
}
while (i == 0) {
if (atomicLong.get() > 0) {
long l = atomicLong.getAndDecrement();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" + i + "->" + l);
}
}
}
@GetMapping("/rw/get")
public String rw_get(){
String key = "S_COUNT";
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(key);
if (!atomicLong.isExists()) {
atomicLong.set(300l);
}
if (atomicLong.get() > 0) {
long l = atomicLong.getAndDecrement();
i --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" + i + "->" + l);
}
}
};
while (i != 0) {
new Thread(r).start();
// new Thread(r).run();
// new Thread(r).run();
// new Thread(r).run();
// new Thread(r).run();
}
RBucket<String> bucket = redissonClient.getBucket(key);
String s = bucket.get();
System.out.println("================线程已结束================================" + s);
return s;
}
}
4.3 扩展
4.3.1 丰富的jar支持,尤其是对 Netty NIO框架
4.3.2 丰富的配置机制选择,这里是详细的配置说明
关于序列化机制中,就有很多


4.3.3 API支持(部分展示),具体的 Redis --> RedissonClient ,可查看这里
https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/11.-Redis-commands-mapping

4.3.4 轻便的丰富的锁机制的实现
- Lock
- Fair Lock
- MultiLock
- RedLock
- ReadWriteLock
- Semaphore
- PermitExpirableSemaphore
- CountDownLatch
四、基于注解实现的Redis缓存
4.1 Maven 和 YML配置
参考 RedisTemplate 配置。另外,还需要额外的配置类
// todo 定义序列化,解决乱码问题
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.cache.redis")
public class RedisCacheConfig {
private Duration timeToLive = Duration.ZERO;
public void setTimeToLive(Duration timeToLive) {
this.timeToLive = timeToLive;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题)
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(timeToLive)
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
4.2 使用示例
@Transactional
@Service
public class ReImpl implements RedisService {
@Resource
private CustomerRepo customerRepo;
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public static final String REDIS_CUSTOMERS_ONE = "Customers";
public static final String REDIS_CUSTOMERS_ALL = "allList";
// =====================================================================使用Spring cahce 注解方式实现缓存
// ==================================单个操作
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cache:customer", unless = "null == #result",key = "#id")
public CustomersEntity cacheOne(Integer id) {
final Optional<CustomersEntity> byId = customerRepo.findById(id);
return byId.isPresent() ? byId.get() : null;
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cache:customer", unless = "null == #result", key = "#id")
public CustomersEntity cacheOne2(Integer id) {
final Optional<CustomersEntity> byId = customerRepo.findById(id);
return byId.isPresent() ? byId.get() : null;
}
// todo 自定义redis缓存的key,
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cache:customer", unless = "null == #result", key = "#root.methodName + '.' + #id")
public CustomersEntity cacheOne3(Integer id) {
final Optional<CustomersEntity> byId = customerRepo.findById(id);
return byId.isPresent() ? byId.get() : null;
}
// todo 这里缓存到redis,还有响应页面是String(加了很多转义符\,),不是Json格式
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cache:customer", unless = "null == #result", key = "#root.methodName + '.' + #id")
public String cacheOne4(Integer id) {
final Optional<CustomersEntity> byId = customerRepo.findById(id);
return byId.map(JSONUtil::toJsonStr).orElse(null);
}
// todo 缓存json,不乱码已处理好,调整序列化和反序列化
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cache:customer", unless = "null == #result", key = "#root.methodName + '.' + #id")
public CustomersEntity cacheOne5(Integer id) {
Optional<CustomersEntity> byId = customerRepo.findById(id);
return byId.filter(obj -> !StrUtil.isBlankIfStr(obj)).orElse(null);
}
// ==================================删除缓存
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "cache:customer", key = "'cacheOne5' + '.' + #id")
public Object del(Integer id) {
// 删除缓存后的逻辑
return null;
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "cache:customer",allEntries = true)
public void del() {
}
@CacheEvict(value = "cache:all",allEntries = true)
public void delall() {
}
// ==================List操作
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cache:all")
public List<CustomersEntity> cacheList() {
List<CustomersEntity> all = customerRepo.findAll();
return all;
}
// todo 先查询缓存,再校验是否一致,然后更新操作,比较实用,要清楚缓存的数据格式(明确业务和缓存模型数据)
@Override
@CachePut(value = "cache:all",unless = "null == #result",key = "#root.methodName")
public List<CustomersEntity> cacheList2() {
List<CustomersEntity> all = customerRepo.findAll();
return all;
}
}
4.3 扩展
基于spring缓存实现
近期热文推荐:
1.1,000+ 道 Java面试题及答案整理(2021最新版)
2.别在再满屏的 if/ else 了,试试策略模式,真香!!
3.卧槽!Java 中的 xx ≠ null 是什么新语法?
4.Spring Boot 2.5 重磅发布,黑暗模式太炸了!
觉得不错,别忘了随手点赞+转发哦!