一、异常原因与异常源码分析
对集合(List、Set、Map)迭代时对其进行修改就会出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常。这里以ArrayList为例,例如下面的代码:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("1"); list.add("2"); list.add("3"); //遍历1 for (String s : list){ if (s.equals( "3")) { list.remove(s); // error } } //遍历2 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); for (; it.hasNext();) { String value = it.next(); if (value.equals("3")) { list.remove(value); // error } }
ArrayList类中包含了实现Iterator迭代器的内部类Itr,在Itr类内部维护了一个expectedModCount变量,而在ArrayList类中维护一个modCount变量(modCount是ArrayList实现AbstractList类得到成员变量)。其他集合(List、Set、Map)都与之类似。
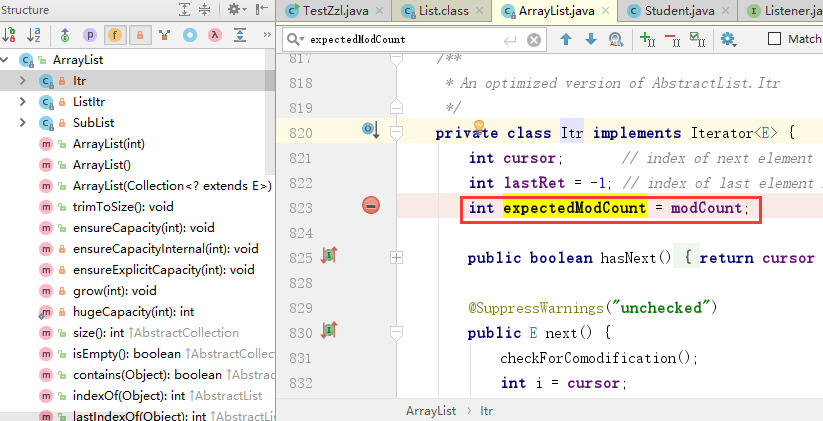
当对集合进行添加或者删除操作时modCount的值都会进行modCount++操作,例如ArrayList中的remove()方法:
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work }
当集合添加完值后,对集合进行遍历时才会创建Itr对象,这时候会执行int expectedModCount = modCount;操作,也就是说只要是在增加或删除后对集合进行遍历,那expectedModCount 与modCount永远是相等的。
但是如果在遍历的过程中进行增加或删除操作那么modCount++,但是expectedModCount保存的还是遍历前的值,也就是expectedModCount和modCount的值是不相等的。
遍历过程中会调用iterator的next()方法,next()方法方法会首先调用checkForComodification()方法来验证expectedModCount和modCount是否相等,因为之前做了增加或删除操作,modCount的值发生了变化,所以expectedModCount和modCount不相等,抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); }
二、单线程解决方案
1、迭代器删除
在Itr类中也给出了一个remove()方法,通过调用Itr类的方法就可以实现而且不报错,例如下面代码:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("1"); list.add("2"); list.add("3"); list.add("4"); list.remove("4"); //遍历2 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); for (; it.hasNext();) { String value = it.next(); if (value.equals("3")) { it.remove(); } }
在Itr类中remove()方法中,执行了expectedModCount = modCount操作,那么执行next()方法时expectedModCount和modCount肯定相等,Itr类中remove()方法的源码:
public void remove() { if (lastRet == -1) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet); if (lastRet < cursor) cursor--; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
2、其他的方式
// 2 建一个集合,记录需要删除的元素,之后统一删除 List<string> templist = new ArrayList<string>(); for (String value : myList) { if (value.equals( "3")) { templist.remove(value); } } // 可以查看removeAll源码,其中使用Iterator进行遍历 myList.removeAll(templist); System. out.println( "List Value:" + myList.toString()); // 3. 使用线程安全CopyOnWriteArrayList进行删除操作 List<string> myList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<string>(); myList.add( "1"); myList.add( "2"); myList.add( "3"); myList.add( "4"); myList.add( "5"); Iterator<string> it = myList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String value = it.next(); if (value.equals( "3")) { myList.remove( "4"); myList.add( "6"); myList.add( "7"); } } System. out.println( "List Value:" + myList.toString()); // 4. 不使用Iterator进行遍历,需要注意的是自己保证索引正常 for ( int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) { String value = myList.get(i); System. out.println( "List Value:" + value); if (value.equals( "3")) { myList.remove(value); // ok i--; // 因为位置发生改变,所以必须修改i的位置 } }
三、多线程解决方案
1、多线程下异常原因
多线程下ArrayLis用Itr类中remove()方法也是会报异常的,Vector(线程安全)也会出现这种错误,具体原因如下:
Itr是在遍历的时候创建的,也就是每个线程如果遍历都会得到一个expectedModCount ,expectedModCount 也就是每个线程私有的,假若此时有2个线程,线程1在进行遍历,线程2在进行修改,那么很有可能导致线程2修改后导致Vector中的modCount自增了,线程2的expectedModCount也自增了,但是线程1的expectedModCount没有自增,此时线程1遍历时就会出现expectedModCount不等于modCount的情况了。
2、尝试方案
(1) 在所有遍历增删地方都加上synchronized或者使用Collections.synchronizedList,虽然能解决问题但是并不推荐,因为增删造成的同步锁可能会阻塞遍历操作。
(2) 推荐使用ConcurrentHashMap或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
3、CopyOnWriteArrayList使用注意
(1) CopyOnWriteArrayList不能使用Iterator.remove()进行删除。
(2) CopyOnWriteArrayList使用Iterator且使用List.remove(Object);会出现如下异常:
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); list.add("1"); list.add("2"); list.add("3"); list.add("4"); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); for (; it.hasNext();) { String value = it.next(); if (value.equals("4")) { it.remove(); // error } } Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException at java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList$COWIterator.remove(CopyOnWriteArrayList.java:1040) at TestZzl.main(TestZzl.java:51)
4、最终解决方案
List<string> myList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<string>(); myList.add( "1"); myList.add( "2"); myList.add( "3"); myList.add( "4"); myList.add( "5"); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (String string : myList) { System.out.println("遍历集合 value = " + string); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) { String value = myList.get(i); System.out.println("删除元素 value = " + value); if (value.equals( "3")) { myList.remove(value); i--; // 注意 } try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start();
后续会具体分析一下CopyOnWriteArrayList
参考:
https://www.2cto.com/kf/201403/286536.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3933551.html