摘自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhang0558/article/details/53444533
序列化和反序列化以及hadoop数据类型
1.什么是序列化和反序列化
序列化就是把内存中的对象,转换成字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)以便于存储(持久化)和网络传输。
反序列化就是将收到 字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)或者是硬盘的持久化数据,转换成内存中的对象。
2.JDK序列化和反序列化
Serialization(序列化)是一种将对象转换为字节流;反序列化deserialization是一种将这些字节流生成一个对象。
a)当你想把的内存中的对象保存到一个文件中或者数据库中时候;
b)当你想用套接字在网络上传送对象的时候;
c)当你想通过RMI传输对象的时候;
将需要序列化的类实现Serializable接口就可以了,Serializable接口中没有任何方法,可以理解为一个标记,即表明这个类可以序列化。
3.Hadoop序列化和反序列化
在hadoop中,hadoop实现了一套自己的序列化框架,hadoop的序列化相对于JDK的序列化来说是比较简洁而且更节省存储空间。在集群中信息的传递主要就是靠这些序列化的字节序列来传递的所以更快速度更小的容量就变得非常地重要了。
4.同样的数据在JDK和Hadoop中序列化的字节数比较:JDK的序列化保存对象的结构信息(继承等)、Hadoop的序列化不保存这些结构化信息。所以会见小开销。
Jdk序列化:People.java(POJO)

import java.io.Serializable; public class People implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private int age; private String name; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public People(){} public People(int age, String name) { super(); this.age = age; this.name = name; } }
运行代码和结果:

import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class TestJDKSeriable { public static void main(String[] args) { try { ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos); oos.writeObject(new People(19, "zhangsan")); System.out.println("字节大小:"+baos.size()); oos.close(); baos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //JDK Serialization //输出结果:字节大小:89
Hadoop序列化:People.java(POJO)

import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class PeopleWritable implements WritableComparable<PeopleWritable> { private IntWritable age; private Text name; public PeopleWritable(){ } public PeopleWritable(IntWritable age, Text name) { super(); this.age = age; this.name = name; } public IntWritable getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(IntWritable age) { this.age = age; } public Text getName() { return name; } public void setName(Text name) { this.name = name; } public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { age.write(out); name.write(out); } public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { age.readFields(in); name.readFields(in); } public int compareTo(PeopleWritable o) { int cmp = age.compareTo(o.getAge()); if(0 !=cmp)return cmp; return name.compareTo(o.getName()); } }
运行代码和结果:

import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.DataOutputBuffer; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; public class TestHadoopSeriable { public static void main(String[] args) { try { DataOutputBuffer dob = new DataOutputBuffer(); PeopleWritable pw = new PeopleWritable(new IntWritable(19), new Text("zhangsan")); pw.write(dob); System.out.println("字节大小:"+dob.getLength()); dob.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //Hadoop Serialization //输出 字节大小:13
由此可以看出同样的数据,在Jdk 序列化字节占用了89个,而在hadoop序列化中却只使用了13个字节。大大节省了空间和集群传输效率。
5. Hadoop序列化框架
主要有4个接口,分别是Comparator(字节比较器), Comparable(对象比较), Writable(序列化), Configurable(参数配置)。
Hadoop的序列化的特点是:
1、节省资源:由于带宽和存储是集群中的最宝贵的资源所以我们必须想法设法缩小传递信息的大小和存储大小,hadoop的序列化就为了更好地坐到这一点而设计的。
2、对象可重用:JDK的反序列化会不断地创建对象,这肯定会造成一定的系统开销,但是在hadoop的反序列化中,能重复的利用一个对象的readField方法来重新产生不同的对象。
3、可扩展性:当前hadoop的序列化有多中选择可以利用实现hadoop的WritableComparable接口。
也可使用开源的序列化框架protocol Buffers,Avro等框架。我们可以注意到的是hadoop2.X之后是实现一个YARN,所有应用(mapreduce,或者其他spark实时或者离线的计算框架都可以运行在YARN上),YARN还负责对资源的调度等等。YARN的序列化就是用Google开发的序列化框架protocol Buffers,proto目前支持支持三种语言C++,java,Python所以RPC这一层我们就可以利用其他语言来做文章,满足其他语言开发者的需求。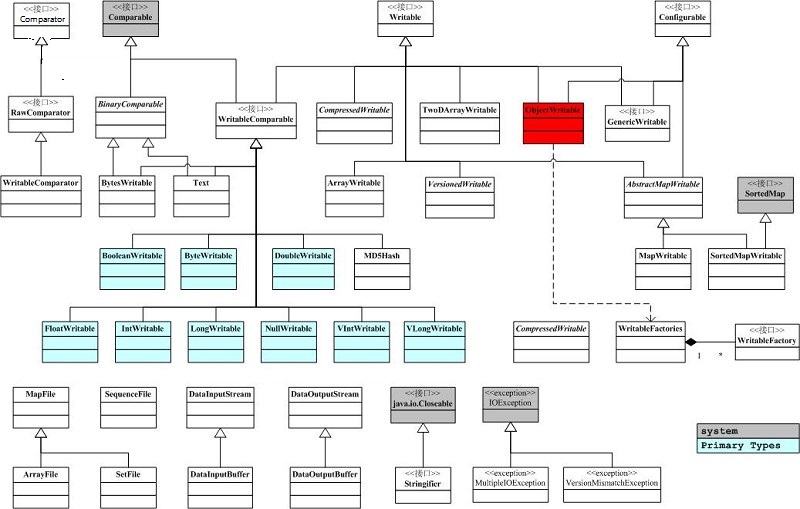
6. Hadoop Writable框架解析
序列化和反序列化只是在对象和字节转换的过程中定义了一个数据格式传输协议,只要在序列化和反序列化过程中,严格遵守这个数据格式传输协议就能成功的转换,当然也可以自行完全实现hadoop序列化框架,像avro框架一样。
Writable.java
@InterfaceAudience.Public @InterfaceStability.Stable public interface Writable { /** * 序列化一个对象,将一个对象按照某个数据传输格式写入到out流中 * Serialize the fields of this object to <code>out</code>. * @throws IOException */ void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException; /** * 反序列化,从in流中读入字节,按照某个数据传输格式读出到一个对象中 * Deserialize the fields of this object from <code>in</code>. * @throws IOException */ void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException; }
Comparable.java
public interface Comparable<T> { /** * 比较对象,这个在mapreduce中对key的对象进行比较 * Compares this object with the specified object for order. Returns a * negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as this object is less * than, equal to, or greater than the specified object. */ public int compareTo(T o); }
RawComparator.java
@InterfaceAudience.Public @InterfaceStability.Stable public interface RawComparator<T> extends Comparator<T> { /** * 在mapreduce,spill过程中,当spill的缓存达到一个值时,会将key-value写入到本地磁盘,并在此过程中sort和patition,如果实现了该接口,就可以直接以序列化的字节的状态比较key,而不需要再临时反序列化成对象再比较,这样提高了效率节省了时间。 * Compare two objects in binary. * @param b1 The first byte array. * @param s1 The position index in b1. The object under comparison's starting index. * @param l1 The length of the object in b1. * @param b2 The second byte array. * @param s2 The position index in b2. The object under comparison's starting index. * @param l2 The length of the object under comparison in b2. * @return An integer result of the comparison. */ public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2); }
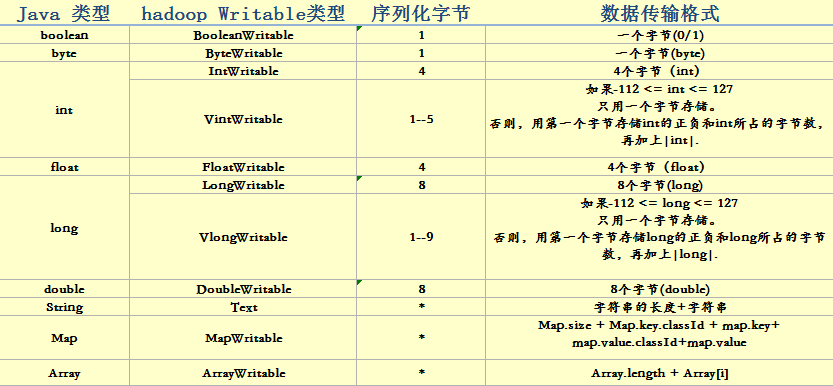
各个数据类型的数据序列化格式:
6. 利用hadoop数据传输格式序列化自定义对象
People.java

import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceAudience; import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceStability; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableUtils; @InterfaceAudience.Public @InterfaceStability.Stable public class People implements WritableComparable<People> { private String name; private int age; private int deptId; public People() { } public People(String name, int age, int deptId) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.deptId = deptId; } public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { WritableUtils.writeVInt(out, this.name.length()); out.write(this.name.getBytes(), 0, this.name.length()); // out.writeUTF(name); out.writeInt(age); out.writeInt(deptId);; } public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { int newLength = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); byte[] bytes = new byte[newLength]; in.readFully(bytes, 0, newLength); this.name = new String(bytes, "UTF-8"); this.age = in.readInt(); this.deptId = in.readInt(); } public int compareTo(People o) { int cmp = this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); if(cmp !=0)return cmp; cmp = this.age - o.getAge(); if(cmp !=0)return cmp; return this.deptId - o.getDeptId(); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(obj instanceof People){ People people = (People)obj; return (this.getName().equals(people.getName()) && this.getAge()==people.getAge()&&this.getDeptId() == people.getDeptId()); } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return "People [name=" + name + ", age=" + age +"deptid"+deptId+"]"; } @Override public int hashCode() { return this.name.hashCode() *163 + this.age+this.deptId; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void setDeptId(int deptId) { this.deptId = deptId; } public int getDeptId() { return deptId; } public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator{ @Override public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) { int firstL1=0 ,firstL2 = 0; System.out.println("len:"+b1.length); int n1 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b1[s1]); //Vint所占字节数 int n2 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b2[s2]); //vint所占字节数 try { firstL1 = WritableComparator.readVInt(b1, s1); //字符串长度 firstL2 = WritableComparator.readVInt(b2, s2); //字符串长度 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } int cmp = WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, s1+n1, firstL1,b2, s2+n2, firstL2); if(0 != cmp)return cmp; int thisValue = readInt(b1, firstL1+n1); int thatValue = readInt(b2, firstL2+n2); System.out.println("value:"+thisValue); cmp = thisValue - thatValue; if(0!=cmp)return cmp; thisValue = readInt(b1, firstL1+n1+4); thatValue = readInt(b2, firstL2+n2+4); System.out.println("value:"+thisValue); return thisValue - thatValue; } } static{ WritableComparator.define(People.class, new Comparator()); } }
MainDept.java MapReduce统计部门员工数

import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser; public class MainDept { public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, People>{ private Text outKey = null; private People people = null; public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] splits = value.toString().split(" "); System.out.println("每次map:"+splits.length); people = new People(splits[0],Integer.valueOf(splits[1]),Integer.valueOf(splits[2])); outKey = new Text(String.valueOf(people.getDeptId())); context.write(outKey, people); // context.write(word, one); } } public static class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, People,Text,Text> { // private Text outKey = new Text(); private Text result = null; public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<People> values, Context context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0; for (People val : values) { System.out.println(val.getName()); sum ++; } result = new Text(); // outKey.set(String.valueOf(key)+"部门的人数:"); result.set(String.valueOf(sum)); context.write(key, result); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs(); if (otherArgs.length < 2) { System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> [<in>...] <out>"); System.exit(2); } Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(MainDept.class); job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(People.class); //job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class); job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); for (int i = 0; i < otherArgs.length - 1; ++i) { FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[i])); } FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); } }
