一个 bean 经历了 createBeanInstance() 被创建出来,然后又经过一番属性注入,依赖处理,历经千辛万苦,千锤百炼,终于有点儿 bean 实例的样子,能堪大任了,只需要经历最后一步就破茧成蝶了。这最后一步就是初始化,也就是 initializeBean(),所以这篇文章我们分析 doCreateBean() 中最后一步:初始化 bean。
我回到之前的doCreateBean方法中,如下

在populateBean方法下面有一个initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd)方法,这个就是用来执行用户设定的初始化操作。我们看下方法体:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { // 激活 Aware 方法 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { // 对特殊的 bean 处理:Aware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 后处理器 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { // 激活用户自定义的 init 方法 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 后处理器 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
初始化 bean 的方法其实就是三个步骤的处理,而这三个步骤主要还是根据用户设定的来进行初始化,这三个过程为:
- 激活 Aware 方法
- 后置处理器的应用
- 激活自定义的 init 方法
激Aware方法
我们先了解一下Aware方法的使用。Spring中提供了一些Aware接口,比如BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,ResourceLoaderAware,ServletContextAware等,实现这些Aware接口的bean在被初始化后,可以取得一些相对应的资源,例如实现BeanFactoryAware的bean在初始化之后,Spring容器将会注入BeanFactory实例,而实现ApplicationContextAware的bean,在bean被初始化后,将会被注入ApplicationContext实例等。我们先通过示例方法了解下Aware的使用。
定义普通bean,如下代码:
public class HelloBean { public void say() { System.out.println("Hello"); } }
定义beanFactoryAware类型的bean
public class MyBeanAware implements BeanFactoryAware { private BeanFactory beanFactory; public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } public void testAware() { //通过hello这个bean id从beanFactory获取实例 HelloBean hello = (HelloBean)beanFactory.getBean("hello"); hello.say(); } }
进行测试
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); MyBeanAware test = (MyBeanAware)ctx.getBean("myBeanAware"); test.testAware(); } } <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="myBeanAware" class="com.chenhao.spring.MyBeanAware"> </bean> <bean id="hello" class="com.chenhao.spring.HelloBean"> </bean> </beans>
输出
Hello
上面的方法我们获取到Spring中BeanFactory,并且可以根据BeanFactory获取所有的bean,以及进行相关设置。还有其他Aware的使用都是大同小异,看一下Spring的实现方式:
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader()); } if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); } } }
处理器的应用
BeanPostPrecessor我们经常看到Spring中使用,这是Spring开放式架构的一个必不可少的亮点,给用户充足的权限去更改或者扩展Spring,而除了BeanPostProcessor外还有很多其他的PostProcessor,当然大部分都以此为基础,集成自BeanPostProcessor。BeanPostProcessor在调用用户自定义初始化方法前或者调用自定义初始化方法后分别会调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterinitialization方法,使用户可以根据自己的业务需求就行相应的处理。
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; } public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
激活自定义的init方法
客户定制的初始化方法除了我们熟知的使用配置init-method外,还有使自定义的bean实现InitializingBean接口,并在afterPropertiesSet中实现自己的初始化业务逻辑。
init-method与afterPropertiesSet都是在初始化bean时执行,执行顺序是afterPropertiesSet先执行,而init-method后执行。
在invokeInitMethods方法中就实现了这两个步骤的初始化调用。
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { // 是否实现 InitializingBean // 如果实现了 InitializingBean 接口,则只掉调用bean的 afterPropertiesSet() boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw pae.getException(); } } else { // 直接调用 afterPropertiesSet() ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { // 判断是否指定了 init-method(), // 如果指定了 init-method(),则再调用制定的init-method String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { // 利用反射机制执行 invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
首先检测当前 bean 是否实现了 InitializingBean 接口,如果实现了则调用其 afterPropertiesSet(),然后再检查是否也指定了 init-method(),如果指定了则通过反射机制调用指定的 init-method()。
init-method()
public class InitializingBeanTest { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setOtherName(){ System.out.println("InitializingBeanTest setOtherName..."); this.name = "chenhao"; } } // 配置文件 <bean id="initializingBeanTest" class="com.chenhao.spring.InitializingBeanTest" init-method="setOtherName"> <property name="name" value="chenhao123"/> </bean>
执行结果:
chenhao
我们可以使用 <beans> 标签的 default-init-method 属性来统一指定初始化方法,这样就省了需要在每个 <bean> 标签中都设置 init-method 这样的繁琐工作了。比如在 default-init-method 规定所有初始化操作全部以 initBean() 命名。如下:
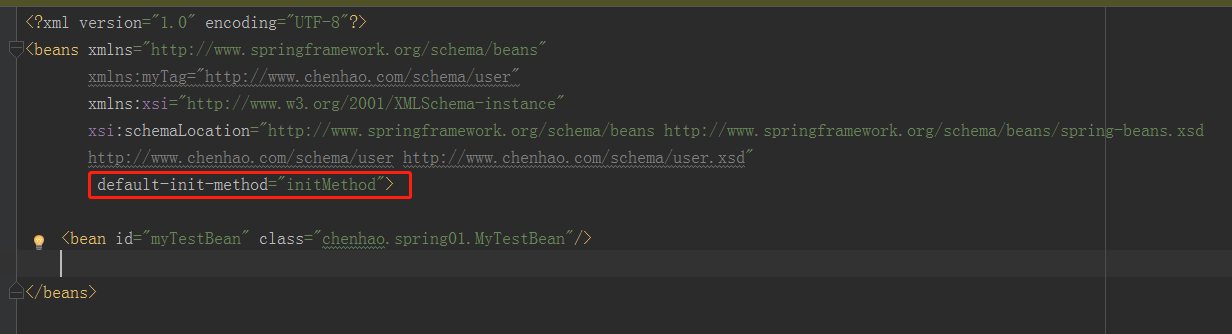
我们看看 invokeCustomInitMethod 方法:
protected void invokeCustomInitMethod(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); Assert.state(initMethodName != null, "No init method set"); Method initMethod = (mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed() ? BeanUtils.findMethod(bean.getClass(), initMethodName) : ClassUtils.getMethodIfAvailable(bean.getClass(), initMethodName)); if (initMethod == null) { if (mbd.isEnforceInitMethod()) { throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException("Could not find an init method named '" + initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No default init method named '" + initMethodName + "' found on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } // Ignore non-existent default lifecycle methods. return; } } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Invoking init method '" + initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } Method methodToInvoke = ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(initMethod); if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(methodToInvoke); return null; }); try { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> methodToInvoke.invoke(bean), getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { InvocationTargetException ex = (InvocationTargetException) pae.getException(); throw ex.getTargetException(); } } else { try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(initMethod); initMethod.invoke(bean); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw ex.getTargetException(); } } }
我们看出最后是使用反射的方式来执行初始化方法。