1、日志框架
市场上存在非常多的日志框架。JUL(java.util.logging),JCL(Apache Commons Logging),Log4j,Log4j2,Logback、SLF4j、jboss-logging等。Spring Boot在框架内容部使用JCL,spring-boot-starter-logging采用了slf4j+logback的形式,Spring Boot也能自动适配(jul、log4j2、logback)并简化配置。
| 日志门面 (日志的抽象层) | 日志实现 |
|---|---|
| Log4j JUL(java.util.logging) Log4j2 Logback |
左边选一个门面(抽象层)、右边来选一个实现;
日志门面: SLF4J;
日志实现:Logback;
SpringBoot:底层是Spring框架,Spring框架默认是用JCL;‘
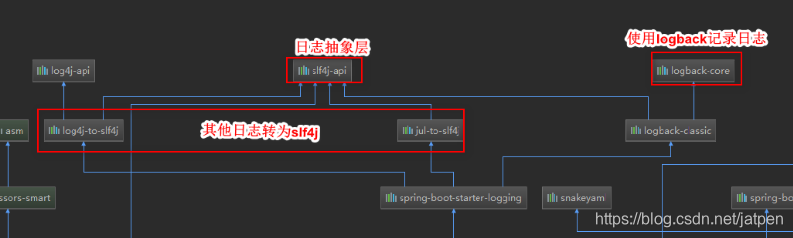
SpringBoot选用 SLF4j和logback
2、SLF4j使用
1、在系统中使用SLF4j
以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该来直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法;给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和 logback的实现jar
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}
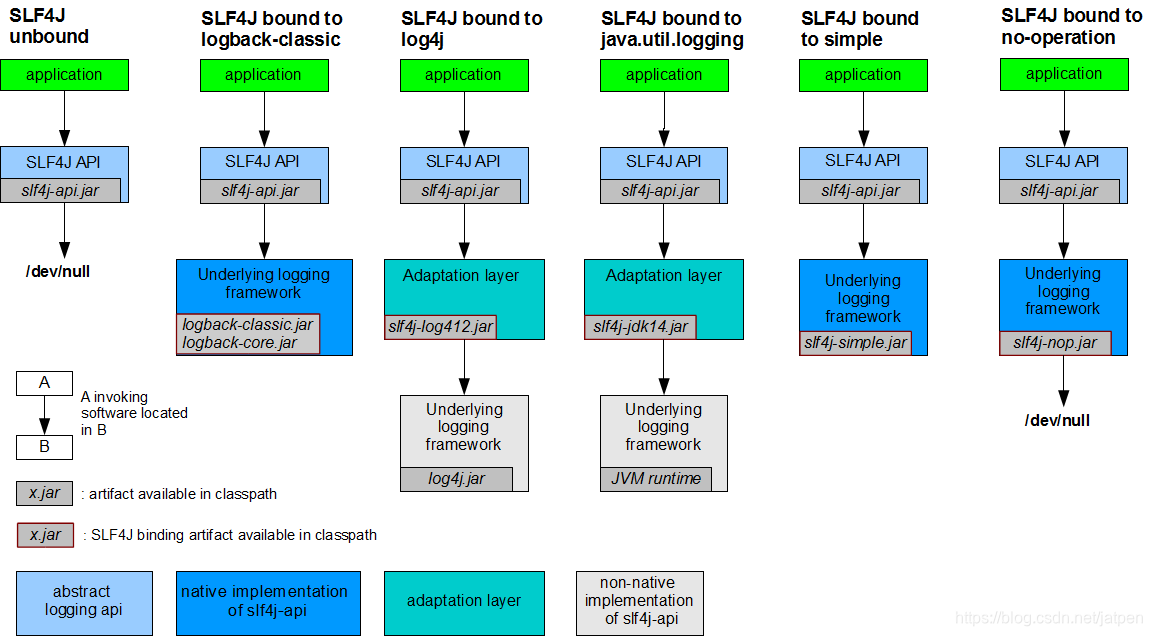
每一个日志的实现框架都有自己的配置文件。使用slf4j以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架自己本身的配置文件;
2、遗留问题
springboot(slf4j+logback): Spring(commons-logging)、Hibernate(jboss-logging)、MyBatis、xxxx
统一日志记录,怎么使用slf4j进行统一输出?
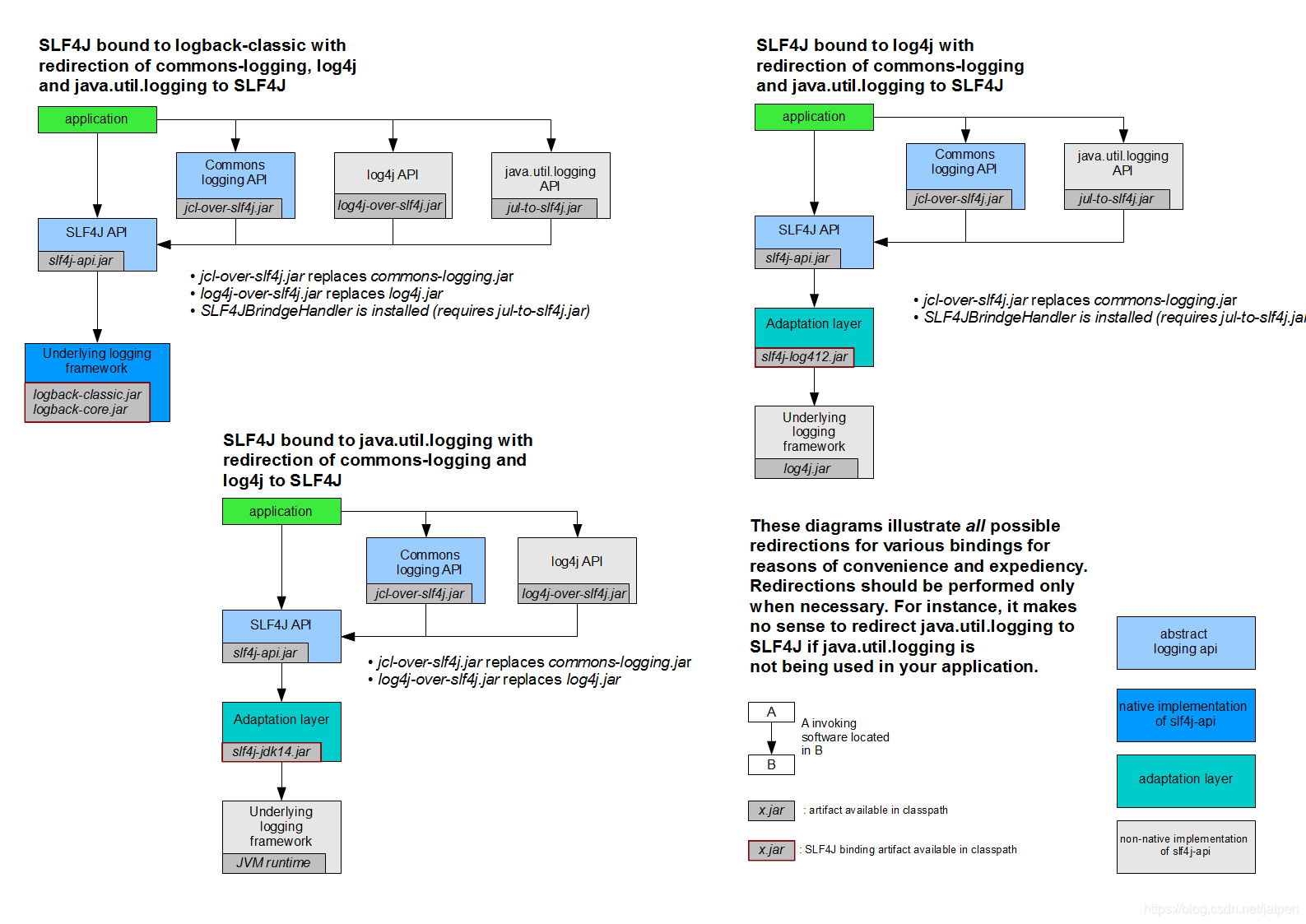
如何让系统中所有的日志都统一到slf4j;
1、将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;
2、用中间包来替换原有的日志框架;
3、我们导入slf4j其他的实现;
3、SpringBoot日志关系
SpringBoot使用它来做日志功能;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
底层依赖关系
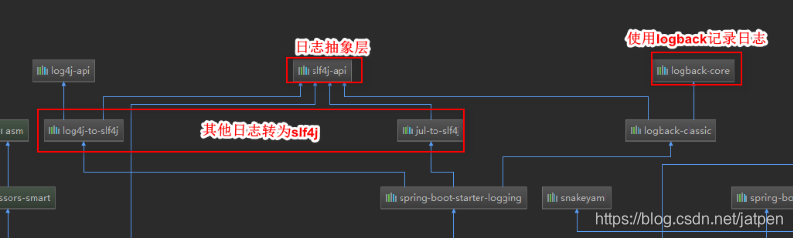
总结:
1)、SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录
2)、SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j;
3)、中间替换包?
/**
* Create an actual {@link Log} instance for the selected API.
* @param name the logger name
*/
public static Log createLog(String name) {
switch (logApi) {
case LOG4J:
return Log4jAdapter.createLog(name);
case SLF4J_LAL:
return Slf4jAdapter.createLocationAwareLog(name);
case SLF4J:
return Slf4jAdapter.createLog(name);
default:
// Defensively use lazy-initializing adapter class here as well since the
// java.logging module is not present by default on JDK 9. We are requiring
// its presence if neither Log4j nor SLF4J is available; however, in the
// case of Log4j or SLF4J, we are trying to prevent early initialization
// of the JavaUtilLog adapter - e.g. by a JVM in debug mode - when eagerly
// trying to parse the bytecode for all the cases of this switch clause.
return JavaUtilAdapter.createLog(name);
}
}
中间转换包:
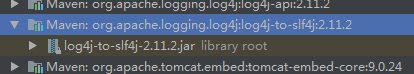
4)、如果我们要引入其他框架?一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉?
Spring框架用的是commons-logging;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉即可.
4、日志使用
1、默认配置
SpringBoot默认帮我们配置好了日志;
package com.spboot.springboot;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot03LoggingApplicationTests {
//logger 记录器
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//System.out.println("ss");
//日志级别 由低到高 trace>debug>info>warn>error
//可以调整日志输出级别,日志只会在这个级别和高级别生效
/*
*springboot默认使用的info级别,没有指定级别的就用springboot默认规定的级别
* */
logger.trace("这是trace日志");
logger.debug("这是debug信息");
logger.info("这是info日志");
logger.warn("这是警告日志");
logger.error("这是错误日志");
}
}
日志文件格式:
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符
-->
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
SpringBoot修改日志的默认配置
logging.level.com.spboot=trace
#spring.profiles.active=dev
#不指定的话就在当前项目下生成日志文件
#可以指定完整的路径
#logging.file=d:/spring.log
#在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹,日志文件是spring.log
logging.path=/spring/log
#咱控制台输出的格式
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd} [%thread] %‐5level %logger{50} ‐ %msg%n
#在文件中输出日志的格式
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd}===[%thread]=== %‐5level=== %logger{50} ‐ %msg%n
| logging.file | logging.path | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| (none) | (none) | 只在控制台输出 | |
| 指定文件名 | (none) | my.log | 输出日志到my.log文件 |
| (none) | 指定目录 | /var/log | 输出到指定目录的 spring.log 文件中 |
2、指定配置
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可;SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置的了
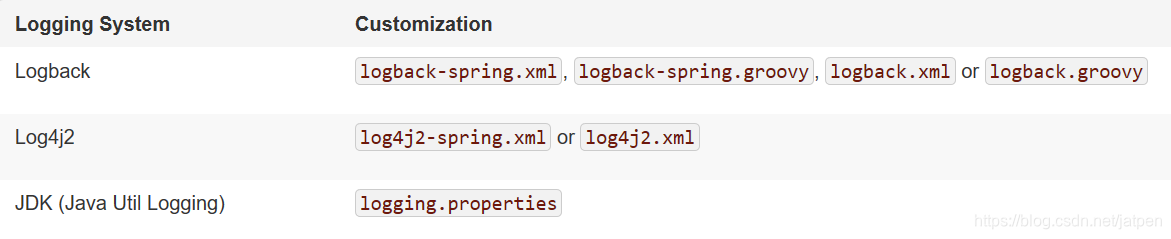
| Logging System | Customization |
|---|---|
| Logback | logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml or logback.groovy |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml or log4j2.xml |
| JDK (Java Util Logging) | logging.properties |
logback.xml:直接就被日志框架识别了;
logback-spring.xml:日志框架就不直接加载日志的配置项,由SpringBoot解析日志配置,可以使用SpringBoot的高级Profile功能
<springProfile name="staging">
<!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active -->
可以指定某段配置只在某个环境下生效
</springProfile>
如:
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!--
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符
-->
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<springProfile name="dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ----> [%thread] ---> %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="!dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
</layout>
</appender>
如果使用logback.xml作为日志配置文件,还要使用profile功能,会有以下错误
no applicable action for [springProfile]
5、切换日志框架
可以按照slf4j的日志适配图,进行相关的切换;
slf4j+log4j的方式;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</dependency>
切换为log4j2
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>