转:https://www.cnblogs.com/hwBeta/p/6926363.html
Microsoft .Net框架SerialPort类的用法与示例
从Microsoft .Net 2.0版本以后,就默认提供了System.IO.Ports.SerialPort类,用户可以非常简单地编写少量代码就完成串口的信息收发程序。本文将介绍如何在PC端用C# .Net 来开发串口应用程序。
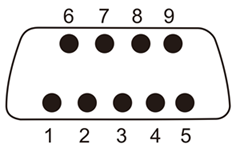
1. 串口硬件信号定义
DB9 Connector 信号定义
|
针脚
|
信号
|
定义
|
作用
|
|
1
|
DCD
|
载波检测
|
Received Line Signal Detector(Data Carrier Detect)
|
|
2
|
RXD
|
接收数据
|
Received Data
|
|
3
|
TXD
|
发送数据
|
Transmit Data
|
|
4
|
DTR
|
数据终端准备好
|
Data Terminal Ready
|
|
5
|
SGND
|
信号地
|
Signal Ground
|
|
6
|
DSR
|
数据准备好
|
Data Set Ready
|
|
7
|
RTS
|
请求发送
|
Request To Send
|
|
8
|
CTS
|
清除发送
|
Clear To Send
|
|
9
|
RI
|
振铃提示
|
Ring Indicator
|
2. 串口端口号搜索
一个最简单的办法:
string[] portList = System.IO.Ports.SerialPort.GetPortNames();
for (int i = 0; i < portList.Length; i++)
{
string name = portList[i];
comboBox.Items.Add(name);
}
还有一种通过调用API的方法来获取实现,可以获取详细的完整串口名称,对于USB-to-COM虚拟串口来说特别适用。
通过下面程序可以获取到与设备管理器中一样的名字,例如“Prolific USB-to-Serial Comm Port(COM34)”, 而上面的方法只能获取到“COM34”。
/// <summary>
/// 枚举win32 api
/// </summary>
public enum HardwareEnum
{
// 硬件
Win32_Processor, // CPU 处理器
Win32_PhysicalMemory, // 物理内存条
Win32_Keyboard, // 键盘
Win32_PointingDevice, // 点输入设备,包括鼠标。
Win32_FloppyDrive, // 软盘驱动器
Win32_DiskDrive, // 硬盘驱动器
Win32_CDROMDrive, // 光盘驱动器
Win32_BaseBoard, // 主板
Win32_BIOS, // BIOS 芯片
Win32_ParallelPort, // 并口
Win32_SerialPort, // 串口
Win32_SerialPortConfiguration, // 串口配置
Win32_SoundDevice, // 多媒体设置,一般指声卡。
Win32_SystemSlot, // 主板插槽 (ISA & PCI & AGP)
Win32_USBController, // USB 控制器
Win32_NetworkAdapter, // 网络适配器
Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration, // 网络适配器设置
Win32_Printer, // 打印机
Win32_PrinterConfiguration, // 打印机设置
Win32_PrintJob, // 打印机任务
Win32_TCPIPPrinterPort, // 打印机端口
Win32_POTSModem, // MODEM
Win32_POTSModemToSerialPort, // MODEM 端口
Win32_DesktopMonitor, // 显示器
Win32_DisplayConfiguration, // 显卡
Win32_DisplayControllerConfiguration, // 显卡设置
Win32_VideoController, // 显卡细节。
Win32_VideoSettings, // 显卡支持的显示模式。
// 操作系统
Win32_TimeZone, // 时区
Win32_SystemDriver, // 驱动程序
Win32_DiskPartition, // 磁盘分区
Win32_LogicalDisk, // 逻辑磁盘
Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition, // 逻辑磁盘所在分区及始末位置。
Win32_LogicalMemoryConfiguration, // 逻辑内存配置
Win32_PageFile, // 系统页文件信息
Win32_PageFileSetting, // 页文件设置
Win32_BootConfiguration, // 系统启动配置
Win32_ComputerSystem, // 计算机信息简要
Win32_OperatingSystem, // 操作系统信息
Win32_StartupCommand, // 系统自动启动程序
Win32_Service, // 系统安装的服务
Win32_Group, // 系统管理组
Win32_GroupUser, // 系统组帐号
Win32_UserAccount, // 用户帐号
Win32_Process, // 系统进程
Win32_Thread, // 系统线程
Win32_Share, // 共享
Win32_NetworkClient, // 已安装的网络客户端
Win32_NetworkProtocol, // 已安装的网络协议
Win32_PnPEntity,//all device
}
/// <summary>
/// WMI取硬件信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hardType"></param>
/// <param name="propKey"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string[] MulGetHardwareInfo(HardwareEnum hardType, string propKey)
{
List<string> strs = new List<string>();
try
{
using (ManagementObjectSearcher searcher = new ManagementObjectSearcher("select * from " + hardType))
{
var hardInfos = searcher.Get();
foreach (var hardInfo in hardInfos)
{
if (hardInfo.Properties[propKey].Value.ToString().Contains("COM"))
{
strs.Add(hardInfo.Properties[propKey].Value.ToString());
}
}
searcher.Dispose();
}
return strs.ToArray();
}
catch
{
return null;
}
finally
{ strs = null; }
}
//通过WMI获取COM端口
string[] portList = MulGetHardwareInfo(HardwareEnum.Win32_PnPEntity, "Name");
3. 串口属性参数设置
参见MSDN上的帮助文件,SerialPort类所包含的属性详见下表。
| 名称 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|
 |
BaseStream |
获取 Stream 对象的基础 SerialPort 对象。 |
 |
BaudRate |
获取或设置串行波特率。 |
 |
BreakState |
获取或设置中断信号状态。 |
 |
BytesToRead |
获取接收缓冲区中数据的字节数。 |
 |
BytesToWrite |
获取发送缓冲区中数据的字节数。 |
 |
CanRaiseEvents |
获取一个值,该值指示组件是否可以引发一个事件。(继承自 Component。) |
 |
CDHolding |
获取端口的载波检测行的状态。 |
 |
Container |
获取 IContainer ,其中包含 Component。(继承自 Component。) |
 |
CtsHolding |
获取“可以发送”行的状态。 |
 |
DataBits |
获取或设置每个字节的标准数据位长度。 |
 |
DesignMode |
获取一个值,该值指示是否 Component 当前处于设计模式。(继承自 Component。) |
 |
DiscardNull |
获取或设置一个值,该值指示 null 字节在端口和接收缓冲区之间传输时是否被忽略。 |
 |
DsrHolding |
获取数据设置就绪 (DSR) 信号的状态。 |
 |
DtrEnable |
获取或设置一个值,该值在串行通信过程中启用数据终端就绪 (DTR) 信号。 |
 |
Encoding |
获取或设置传输前后文本转换的字节编码。 |
 |
Events |
获取的事件处理程序附加到此列表 Component。(继承自 Component。) |
 |
Handshake |
使用 Handshake 中的值获取或设置串行端口数据传输的握手协议。 |
 |
IsOpen |
获取一个值,该值指示 SerialPort 对象的打开或关闭状态。 |
 |
NewLine |
获取或设置用于解释 ReadLine 和 WriteLine 方法调用结束的值。 |
 |
Parity |
获取或设置奇偶校验检查协议。 |
 |
ParityReplace |
获取或设置一个字节,该字节在发生奇偶校验错误时替换数据流中的无效字节。 |
 |
PortName |
获取或设置通信端口,包括但不限于所有可用的 COM 端口。 |
 |
ReadBufferSize |
获取或设置 SerialPort 输入缓冲区的大小。 |
 |
ReadTimeout |
获取或设置读取操作未完成时发生超时之前的毫秒数。 |
 |
ReceivedBytesThreshold |
获取或设置 DataReceived 事件发生前内部输入缓冲区中的字节数。 |
 |
RtsEnable |
获取或设置一个值,该值指示在串行通信中是否启用请求发送 (RTS) 信号。 |
 |
Site |
获取或设置 ISite 的 Component。(继承自 Component。) |
 |
StopBits |
获取或设置每个字节的标准停止位数。 |
 |
WriteBufferSize |
获取或设置串行端口输出缓冲区的大小。 |
 |
WriteTimeout |
获取或设置写入操作未完成时发生超时之前的毫秒数。 |
简单初始化串口参数的示例程序:
SerialPort mySerialPort = new SerialPort("COM2");
mySerialPort.BaudRate = 9600;
mySerialPort.Parity=Parity.None;
mySerialPort.StopBits = StopBits.One;
mySerialPort.DataBits = 8;
mySerialPort.Handshake = Handshake.Non;
mySerialPort.DataReceived += new SerialDataReceivedEvenHandler(DataReceive_Method);
mySerialPort.Open();
4. 串口发送信息
SerialPort类定义了多种方法用于串口发送信息。
Write(Byte[], Int32, Int32) 使用缓冲区中的数据将指定数量的字节写入串行端口
Write(Char[], Int32, Int32) 使用缓冲区中的数据将指定数量的字符写入串行端口
Write(String) 将指定的字符串写入串行端口
WriteLine(String) 将指定的字符串和NewLine值写入输出缓冲区
下面是一个简单的例子说明如何通过串口发送字符串和字节数据:
using System.IO.Ports;
private static void SendSampleData()
{
// Instantiate the communications
// port with some basic settings
SerialPort port = new SerialPort(
"COM1", 9600, Parity.None, 8, StopBits.One);
// Open the port for communications
port.Open();
// Write a string
port.Write("Hello World");
// Write a set of bytes
port.Write(new byte[] { 0x0A, 0xE2, 0xFF }, 0, 3);
// Close the port
port.Close();
}
下面是如何发送一个文本文件的例子:
private static void SendTextFile(SerialPort port, string FileName)
{
port.Write(File.OpenText(FileName).ReadToEnd());
}
下面是如何发送一个二进制文件的例子:
private static void SendBinaryFile(SerialPort port, string FileName)
{
using (FileStream fs = File.OpenRead(FileName))
port.Write((new BinaryReader(fs)).ReadBytes((int)fs.Length), 0, (int)fs.Length);
}
5. 串口接收信息
SerialPort类定义了多种方法用于串口接收信息。
Read(Byte[], Int32, Int32) 从SerialPort输入缓冲区读取一些字节,并将那些字节写入字节数组中指定的偏移量处
Read(Byte[], Int32, Int32) 从SerialPort输入缓冲区读取一些字符,并将那些字符写入字符数组中指定的偏移量处
ReadByte() 从SerialPort输入缓冲区中同步读取一个字节
ReadChar() 从SerialPort输入缓冲区中同步读取一个字符
ReadExisting() 在编码的基础上,读取SerialPort对象的流和输入缓冲区中所有立即可用的字节
ReadLine() 一直读取到输入缓冲区中的NewLine值
ReadTo(String) 一直读取到输入缓冲区中的指定value的字符串
通常一个比较常见的用法就是将串口里面立即能用的字符或数据读取然后打印在textbox等控件中显示。
#region Namespace Inclusions
using System;
using System.IO.Ports;
using System.Windows.Forms;
#endregion
namespace SerialPortExample
{
class SerialPortProgram
{
// Create the serial port with basic settings
private SerialPort port = new SerialPort("COM1",
9600, Parity.None, 8, StopBits.One);
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Instatiate this class
new SerialPortProgram();
}
private SerialPortProgram()
{
Console.WriteLine("Incoming Data:");
// Attach a method to be called when there
// is data waiting in the port's buffer
port.DataReceived += new
SerialDataReceivedEventHandler(port_DataReceived);
// Begin communications
port.Open();
// Enter an application loop to keep this thread alive
Application.Run();
}
private void port_DataReceived(object sender, SerialDataReceivedEventArgs e)
{
// Show all the incoming data in the port's buffer
Console.WriteLine(port.ReadExisting());
}
}
}
另外还有一种应用场合是需要缓存一段串口接收数据,然后在缓存数据中查找有用信息,这时可以采用下面例子所用的办法。
using System;
using System.IO.Ports;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SerialComBuffering
{
class Program
{
SerialPort com = new SerialPort(SerialPort.GetPortNames()[0],
9600, Parity.None, 8, StopBits.One);
List<byte> bBuffer = new List<byte>();
string sBuffer = String.Empty;
static void Main(string[] args)
{ new Program(); }
Program()
{
com.DataReceived += new SerialDataReceivedEventHandler(com_DataReceived);
com.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for incoming data...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
void com_DataReceived(object sender, SerialDataReceivedEventArgs e)
{
// Use either the binary OR the string technique (but not both)
// Buffer and process binary data
while (com.BytesToRead > 0)
bBuffer.Add((byte)com.ReadByte());
ProcessBuffer(bBuffer);
// Buffer string data
sBuffer += com.ReadExisting();
ProcessBuffer(sBuffer);
}
private void ProcessBuffer(string sBuffer)
{
// Look in the string for useful information
// then remove the useful data from the buffer
}
private void ProcessBuffer(List<byte> bBuffer)
{
// Look in the byte array for useful information
// then remove the useful data from the buffer
}
}
}