一、SpringMVC简介
SpringMVC是一种基于Spring实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,使用了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进行职责解耦,并管理应用所需对象的生命周期,为简化日常开发,提供了很大便利。
二、SpringMVC核心组件
DispatcherServlet:中央控制器,统一调度其他组件的调用,是整个请求响应的控制中心,本质是一个Servlet;
Handler:业务处理器,处理客户端的具体请求和返回处理结果,通常存在形式就是各种Controller;
HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,客户端请求URL和业务处理器的映射关系,根据请求URL可以找到对应的业务处理器;
HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,负责调用业务处理器的具体方法,返回逻辑视图ModelAndView对象;
ViewResolver:视图解析器,负责将业务处理器返回的视图ModelAndView对象解析成JSP;
三、SpringMVC工作流程
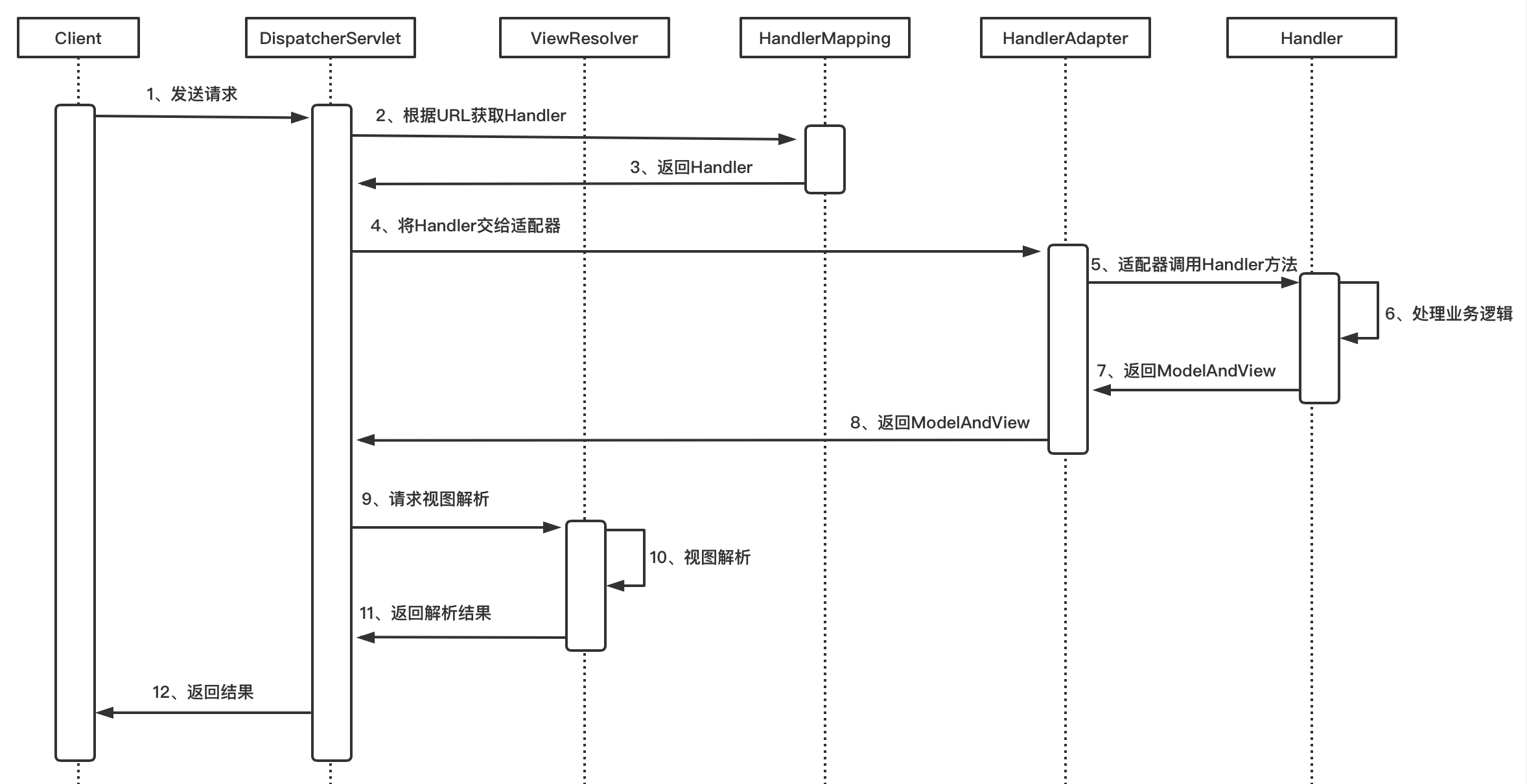
1、客户端发送请求,所有请求都有中央处理器DispatcherServlet处理;
2、DispatcherServlet通过处理器映射器HandlerMapping根据客户端请求URL获取对应的业务处理器Handler对象;
3、DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器,通知HandlerAdapter执行具体哪个Handler;
4、HandlerAdapter调用具体Handler(Controller)的方法并得到返回的结果ModelAndView,且将结果返回给DispatcherServlet;
5、DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView交给ViewReslover视图解析器解析,然后返回真正的视图;
6、DispatcherServlet将模型数据填充到视图中;
7、DispatcherServlet将结果响应给用户。
四、SpringMVC流程图
五、SpringMVC源码解析
5.1、SpringMVC启动流程
SpringMVC首先需要从web.xml配置DispatcherServlet,如下:
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
根据servlet相关知识可知所有请求都会交给DispatcherServlet处理,并且项目启动时会创建DispatcherServlet并会执行DispatcherServlet的初始化init方法。
DispatcherServlet继承之FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承之HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean实现了HttpServlet的init方法,实际是执行了initServletBean方法,该方法被子类FrameworkServlet重写,
FrameworkServlet重写initServletBean方法实现逻辑如下:
1 protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { 2 try { 3 /** 1.初始化Spring Web容器*/ 4 this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); 5 /** 2.初始化框架Servlet,空方法,交给子类扩展*/ 6 initFrameworkServlet(); 7 } 8 catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) { 9 logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); 10 throw ex; 11 } 12 }
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { /** 1. 尝试获取WebApplicationContext */ WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } /** 2.如果当前没有WebApplicationContext就初始化并刷新WebApplicationContext */ if (wac == null) { wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { /** 3.WebApplicationContext初始化并刷新后,执行onRefresh方法*/ onRefresh(wac); } } if (this.publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
通过createWebApplicationContext方法创建IOC容器WebApplicationContext并启动刷新容器,当Spring容器启动后再执行onRefresh方法刷新Servlet,Spring容器启动刷新逻辑不再细看,onRefresh方法实际是交给了
子类DispatcherServlet实现,DispatcherServlet的onRefresh方法源码如下:
/** DispatcherServlet onRefresh方法 */ protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); /** 初始化处理器映射器HandlerMapping */ initHandlerMappings(context); /** 初始化处理器适配器handlerAdapter */ initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); /** 初始化视图解析器ViewResolver */ initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
可以看出onRefresh方法主要是初始化相关组件,如初始化业务处理器映射器HandlerMapping、处理器适配器HandlerAdapter、视图解析器ViewResolver等,这里着重分析HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的初始化。
5.1.1、处理器映射器初始化
首先看处理器映射器的初始化,方法为DispatcherServlet的initHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext context), 源码如下:
1 /** 初始化处理器映射器 */ 2 private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { 3 this.handlerMappings = null; 4 /** 1.先尝试从Spring容器中获取所有HandlerMapping s*/ 5 if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { 6 Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = 7 BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); 8 if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { 9 this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); 10 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); 11 } 12 } 13 else { 14 try { 15 HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); 16 this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); 17 } 18 catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { 19 } 20 } 21 22 /** 2.如果Spring容器中没有HandlerMapping,那么就初始化默认的HandlerMapping*/ 23 if (this.handlerMappings == null) { 24 // 初始化默认HandlerMapping 25 this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); 26 } 27 } 28 29 /** 获取默认策略 */ 30 protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { 31 String key = strategyInterface.getName(); 32 /** 1.从配置文件中获取默认策略 33 * 配置文件为DispatcherServlet.properties 34 * key为策略类全路径 35 * */ 36 String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); 37 if (value != null) { 38 String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); 39 List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length); 40 for (String className : classNames) { 41 try { 42 /** 2.反射初始化所有策略实例*/ 43 Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); 44 Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); 45 strategies.add((T) strategy); 46 } 47 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 48 } 49 catch (LinkageError err) { 50 } 51 } 52 return strategies; 53 } 54 else { 55 return new LinkedList<>(); 56 } 57 }
首先尝试从Spring容器中获取所有HandlerMapping的bean,如果不存在就加载默认处理器映射器,getDefaultStrategies方法是从配置文件DispatcherServlet.properties中加载默认配置,配置文件内容如下:
1 org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 2 3 org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver 4 5 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ 6 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\ 7 org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping 8 9 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ 10 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ 11 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\ 12 org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter 13 14 15 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\ 16 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\ 17 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 18 19 org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator 20 21 org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver 22 23 org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
可以发现默认HandlerMapping为BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping,以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例,实现了InitializingBean,
所以初始化后会执行afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法初始化属性,并调用父类AbstractHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法又执行了方法initHandlerMethods方法,AbstractHandlerMapping的
initHandlerMethods方法实质就是初始化方法映射的方法,逻辑如下:
/** 初始化路径和方法映射 */ protected void initHandlerMethods() { /** 1.遍历Spring容器中所有的bean */ for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { /** 2.处理所有后续的bean */ processCandidateBean(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); } protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { /** 1.获取bean的Class对象 */ beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { } /** 2.调用isHandler方法判断该bean是否是业务处理器*/ if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { /** 2.寻找业务处理器中映射方法 */ detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } /** 判断bean是否是业务处理器( 被Controller或RequestMapping注解修饰 )*/ protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) || AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class)); }
遍历Spring容器中所有的bean,判断bean中是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping注解,如果包含那么就是业务处理器,那么就执行detectHandlerMethods方法处理,该方法逻辑如下:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { /** 1.获取处理器Class对象 */ Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); /** 2.寻找所有映射方法集合,存入Map<Method,RequestMappingInfo>中 * RequestMappingInfo就是方法映射关系类 */ Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); /** 注册处理器、方法、映射关系, 缓存在MappingRegistry实例的Map中 */ registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
先从业务处理器中寻找所有映射方法封装成映射关系实例,然后将处理器、方法和映射关系实例注册到MappingRegistry实例中。
5.1.2、处理器适配器初始化
处理器适配器HandlerAdapter的初始化过程和处理器映射器HandlerMapping的初始化过程如出一辙,最终落实到默认的适配器RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的初始化,最终是重写了afterPropertiesSet方法。
5.2、SpringMVC工作流程
------------恢复内容开始------------
一、SpringMVC简介
SpringMVC是一种基于Spring实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,使用了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进行职责解耦,并管理应用所需对象的生命周期,为简化日常开发,提供了很大便利。
二、SpringMVC核心组件
DispatcherServlet:中央控制器,统一调度其他组件的调用,是整个请求响应的控制中心,本质是一个Servlet;
Handler:业务处理器,处理客户端的具体请求和返回处理结果,通常存在形式就是各种Controller;
HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,客户端请求URL和业务处理器的映射关系,根据请求URL可以找到对应的业务处理器;
HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,负责调用业务处理器的具体方法,返回逻辑视图ModelAndView对象;
ViewResolver:视图解析器,负责将业务处理器返回的视图ModelAndView对象解析成JSP;
三、SpringMVC工作流程
1、客户端发送请求,所有请求都有中央处理器DispatcherServlet处理;
2、DispatcherServlet通过处理器映射器HandlerMapping根据客户端请求URL获取对应的业务处理器Handler对象;
3、DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器,通知HandlerAdapter执行具体哪个Handler;
4、HandlerAdapter调用具体Handler(Controller)的方法并得到返回的结果ModelAndView,且将结果返回给DispatcherServlet;
5、DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView交给ViewReslover视图解析器解析,然后返回真正的视图;
6、DispatcherServlet将模型数据填充到视图中;
7、DispatcherServlet将结果响应给用户。
四、SpringMVC流程图

五、SpringMVC源码解析
5.1、SpringMVC启动流程
SpringMVC首先需要从web.xml配置DispatcherServlet,如下:
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
根据servlet相关知识可知所有请求都会交给DispatcherServlet处理,并且项目启动时会创建DispatcherServlet并会执行DispatcherServlet的初始化init方法。
DispatcherServlet继承之FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承之HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean实现了HttpServlet的init方法,实际是执行了initServletBean方法,该方法被子类FrameworkServlet重写,
FrameworkServlet重写initServletBean方法实现逻辑如下:
1 protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { 2 try { 3 /** 1.初始化Spring Web容器*/ 4 this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); 5 /** 2.初始化框架Servlet,空方法,交给子类扩展*/ 6 initFrameworkServlet(); 7 } 8 catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) { 9 logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); 10 throw ex; 11 } 12 }
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { /** 1. 尝试获取WebApplicationContext */ WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } /** 2.如果当前没有WebApplicationContext就初始化并刷新WebApplicationContext */ if (wac == null) { wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { /** 3.WebApplicationContext初始化并刷新后,执行onRefresh方法*/ onRefresh(wac); } } if (this.publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
通过createWebApplicationContext方法创建IOC容器WebApplicationContext并启动刷新容器,当Spring容器启动后再执行onRefresh方法刷新Servlet,Spring容器启动刷新逻辑不再细看,onRefresh方法实际是交给了
子类DispatcherServlet实现,DispatcherServlet的onRefresh方法源码如下:
/** DispatcherServlet onRefresh方法 */ protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); /** 初始化处理器映射器HandlerMapping */ initHandlerMappings(context); /** 初始化处理器适配器handlerAdapter */ initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); /** 初始化视图解析器ViewResolver */ initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
可以看出onRefresh方法主要是初始化相关组件,如初始化业务处理器映射器HandlerMapping、处理器适配器HandlerAdapter、视图解析器ViewResolver等,这里着重分析HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的初始化。
5.1.1、处理器映射器初始化
首先看处理器映射器的初始化,方法为DispatcherServlet的initHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext context), 源码如下:
1 /** 初始化处理器映射器 */ 2 private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { 3 this.handlerMappings = null; 4 /** 1.先尝试从Spring容器中获取所有HandlerMapping s*/ 5 if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { 6 Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = 7 BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); 8 if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { 9 this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); 10 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); 11 } 12 } 13 else { 14 try { 15 HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); 16 this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); 17 } 18 catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { 19 } 20 } 21 22 /** 2.如果Spring容器中没有HandlerMapping,那么就初始化默认的HandlerMapping*/ 23 if (this.handlerMappings == null) { 24 // 初始化默认HandlerMapping 25 this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); 26 } 27 } 28 29 /** 获取默认策略 */ 30 protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { 31 String key = strategyInterface.getName(); 32 /** 1.从配置文件中获取默认策略 33 * 配置文件为DispatcherServlet.properties 34 * key为策略类全路径 35 * */ 36 String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); 37 if (value != null) { 38 String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); 39 List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length); 40 for (String className : classNames) { 41 try { 42 /** 2.反射初始化所有策略实例*/ 43 Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); 44 Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); 45 strategies.add((T) strategy); 46 } 47 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 48 } 49 catch (LinkageError err) { 50 } 51 } 52 return strategies; 53 } 54 else { 55 return new LinkedList<>(); 56 } 57 }
首先尝试从Spring容器中获取所有HandlerMapping的bean,如果不存在就加载默认处理器映射器,getDefaultStrategies方法是从配置文件DispatcherServlet.properties中加载默认配置,配置文件内容如下:
1 org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 2 3 org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver 4 5 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ 6 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\ 7 org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping 8 9 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ 10 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ 11 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\ 12 org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter 13 14 15 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\ 16 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\ 17 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 18 19 org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator 20 21 org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver 22 23 org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
可以发现默认HandlerMapping为BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping,以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例,实现了InitializingBean,
所以初始化后会执行afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法初始化属性,并调用父类AbstractHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法又执行了方法initHandlerMethods方法,AbstractHandlerMapping的
initHandlerMethods方法实质就是初始化方法映射的方法,逻辑如下:
/** 初始化路径和方法映射 */ protected void initHandlerMethods() { /** 1.遍历Spring容器中所有的bean */ for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { /** 2.处理所有后续的bean */ processCandidateBean(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); } protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { /** 1.获取bean的Class对象 */ beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { } /** 2.调用isHandler方法判断该bean是否是业务处理器*/ if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { /** 2.寻找业务处理器中映射方法 */ detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } /** 判断bean是否是业务处理器( 被Controller或RequestMapping注解修饰 )*/ protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) || AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class)); }
遍历Spring容器中所有的bean,判断bean中是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping注解,如果包含那么就是业务处理器,那么就执行detectHandlerMethods方法处理,该方法逻辑如下:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { /** 1.获取处理器Class对象 */ Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); /** 2.寻找所有映射方法集合,存入Map<Method,RequestMappingInfo>中 * RequestMappingInfo就是方法映射关系类 */ Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); /** 注册处理器、方法、映射关系, 缓存在MappingRegistry实例的Map中 */ registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
先从业务处理器中寻找所有映射方法封装成映射关系实例,然后将处理器、方法和映射关系实例注册到MappingRegistry实例中。
5.1.2、处理器适配器初始化
处理器适配器HandlerAdapter的初始化过程和处理器映射器HandlerMapping的初始化过程如出一辙,最终落实到默认的适配器RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的初始化,最终是重写了afterPropertiesSet方法。
5.2、SpringMVC工作流程
------------恢复内容结束------------
------------恢复内容开始------------
一、SpringMVC简介
SpringMVC是一种基于Spring实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,使用了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进行职责解耦,并管理应用所需对象的生命周期,为简化日常开发,提供了很大便利。
二、SpringMVC核心组件
DispatcherServlet:中央控制器,统一调度其他组件的调用,是整个请求响应的控制中心,本质是一个Servlet;
Handler:业务处理器,处理客户端的具体请求和返回处理结果,通常存在形式就是各种Controller;
HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,客户端请求URL和业务处理器的映射关系,根据请求URL可以找到对应的业务处理器;
HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,负责调用业务处理器的具体方法,返回逻辑视图ModelAndView对象;
ViewResolver:视图解析器,负责将业务处理器返回的视图ModelAndView对象解析成JSP;
三、SpringMVC工作流程
1、客户端发送请求,所有请求都有中央处理器DispatcherServlet处理;
2、DispatcherServlet通过处理器映射器HandlerMapping根据客户端请求URL获取对应的业务处理器Handler对象;
3、DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器,通知HandlerAdapter执行具体哪个Handler;
4、HandlerAdapter调用具体Handler(Controller)的方法并得到返回的结果ModelAndView,且将结果返回给DispatcherServlet;
5、DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView交给ViewReslover视图解析器解析,然后返回真正的视图;
6、DispatcherServlet将模型数据填充到视图中;
7、DispatcherServlet将结果响应给用户。
四、SpringMVC流程图

五、SpringMVC源码解析
5.1、SpringMVC启动流程
SpringMVC首先需要从web.xml配置DispatcherServlet,如下:
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
根据servlet相关知识可知所有请求都会交给DispatcherServlet处理,并且项目启动时会创建DispatcherServlet并会执行DispatcherServlet的初始化init方法。
DispatcherServlet继承之FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承之HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean实现了HttpServlet的init方法,实际是执行了initServletBean方法,该方法被子类FrameworkServlet重写,
FrameworkServlet重写initServletBean方法实现逻辑如下:
1 protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { 2 try { 3 /** 1.初始化Spring Web容器*/ 4 this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); 5 /** 2.初始化框架Servlet,空方法,交给子类扩展*/ 6 initFrameworkServlet(); 7 } 8 catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) { 9 logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); 10 throw ex; 11 } 12 }
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { /** 1. 尝试获取WebApplicationContext */ WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } /** 2.如果当前没有WebApplicationContext就初始化并刷新WebApplicationContext */ if (wac == null) { wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { /** 3.WebApplicationContext初始化并刷新后,执行onRefresh方法*/ onRefresh(wac); } } if (this.publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
通过createWebApplicationContext方法创建IOC容器WebApplicationContext并启动刷新容器,当Spring容器启动后再执行onRefresh方法刷新Servlet,Spring容器启动刷新逻辑不再细看,onRefresh方法实际是交给了
子类DispatcherServlet实现,DispatcherServlet的onRefresh方法源码如下:
/** DispatcherServlet onRefresh方法 */ protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); /** 初始化处理器映射器HandlerMapping */ initHandlerMappings(context); /** 初始化处理器适配器handlerAdapter */ initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); /** 初始化视图解析器ViewResolver */ initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
可以看出onRefresh方法主要是初始化相关组件,如初始化业务处理器映射器HandlerMapping、处理器适配器HandlerAdapter、视图解析器ViewResolver等,这里着重分析HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的初始化。
5.1.1、处理器映射器初始化
首先看处理器映射器的初始化,方法为DispatcherServlet的initHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext context), 源码如下:
1 /** 初始化处理器映射器 */ 2 private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { 3 this.handlerMappings = null; 4 /** 1.先尝试从Spring容器中获取所有HandlerMapping s*/ 5 if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { 6 Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = 7 BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); 8 if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { 9 this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); 10 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); 11 } 12 } 13 else { 14 try { 15 HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); 16 this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); 17 } 18 catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { 19 } 20 } 21 22 /** 2.如果Spring容器中没有HandlerMapping,那么就初始化默认的HandlerMapping*/ 23 if (this.handlerMappings == null) { 24 // 初始化默认HandlerMapping 25 this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); 26 } 27 } 28 29 /** 获取默认策略 */ 30 protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { 31 String key = strategyInterface.getName(); 32 /** 1.从配置文件中获取默认策略 33 * 配置文件为DispatcherServlet.properties 34 * key为策略类全路径 35 * */ 36 String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); 37 if (value != null) { 38 String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); 39 List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length); 40 for (String className : classNames) { 41 try { 42 /** 2.反射初始化所有策略实例*/ 43 Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); 44 Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); 45 strategies.add((T) strategy); 46 } 47 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 48 } 49 catch (LinkageError err) { 50 } 51 } 52 return strategies; 53 } 54 else { 55 return new LinkedList<>(); 56 } 57 }
首先尝试从Spring容器中获取所有HandlerMapping的bean,如果不存在就加载默认处理器映射器,getDefaultStrategies方法是从配置文件DispatcherServlet.properties中加载默认配置,配置文件内容如下:
1 org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 2 3 org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver 4 5 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ 6 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\ 7 org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping 8 9 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ 10 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ 11 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\ 12 org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter 13 14 15 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\ 16 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\ 17 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 18 19 org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator 20 21 org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver 22 23 org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
可以发现默认HandlerMapping为BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping,以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例,实现了InitializingBean,
所以初始化后会执行afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法初始化属性,并调用父类AbstractHandlerMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法又执行了方法initHandlerMethods方法,AbstractHandlerMapping的
initHandlerMethods方法实质就是初始化方法映射的方法,逻辑如下:
/** 初始化路径和方法映射 */ protected void initHandlerMethods() { /** 1.遍历Spring容器中所有的bean */ for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { /** 2.处理所有后续的bean */ processCandidateBean(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); } protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { /** 1.获取bean的Class对象 */ beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { } /** 2.调用isHandler方法判断该bean是否是业务处理器*/ if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { /** 2.寻找业务处理器中映射方法 */ detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } /** 判断bean是否是业务处理器( 被Controller或RequestMapping注解修饰 )*/ protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) || AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class)); }
遍历Spring容器中所有的bean,判断bean中是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping注解,如果包含那么就是业务处理器,那么就执行detectHandlerMethods方法处理,该方法逻辑如下:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { /** 1.获取处理器Class对象 */ Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); /** 2.寻找所有映射方法集合,存入Map<Method,RequestMappingInfo>中 * RequestMappingInfo就是方法映射关系类 */ Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); /** 注册处理器、方法、映射关系, 缓存在MappingRegistry实例的Map中 */ registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
先从业务处理器中寻找所有映射方法封装成映射关系实例,然后将处理器、方法和映射关系实例注册到MappingRegistry实例中。
5.1.2、处理器适配器初始化
处理器适配器HandlerAdapter的初始化过程和处理器映射器HandlerMapping的初始化过程如出一辙,最终落实到默认的适配器RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的初始化,最终是重写了afterPropertiesSet方法。
5.2、SpringMVC工作流程
Servlet工作流程实际就是接收到客户端请求之后执行service方法,所以SpringMVC的请求处理入口就是DispatcherServlet的service方法,DispatcherServlet的service方法是执行了父类FrameworkServlet的service方法。
该方法又执行了FrameworkServlet的processRequest方法,最终调用了子类的doService方法,DispatcherServlet的doService方法就是处理业务逻辑的核心方法,源码如下:
/** DispatcherServlet 处理业务方法 */ protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { /** 1.请求参数快照,将请求参数缓存起来 */ Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } /** 2.请求参数添加配置 */ request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); if (this.flashMapManager != null) { FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); } try { /** 3.执行分配请求处理 */ doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } }
首先进行参数处理,然后调用doDispatch方法分配请求,逻辑如下:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); /** 1.根据请求从HandlerMapping中查询具体的业务处理器 */ mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } /** 2.根据业务处理器查询对应业务处理器适配器 */ HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } /** 3.调用处理器适配器的handle方法处理具体的业务逻辑 */ mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { //... } /** 4.处理请求执行结果 */ processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { //... } finally { //... } }
核心逻辑比较清晰,先从处理器映射器中查询请求对应的业务处理器,然后再根据业务处理器找到处理器适配器,然后调用适配器的handle方法处理业务,最终执行processDispatchResult方法处理请求的处理结果。
getHandler逻辑就是从集合handlerMappings中找到匹配的处理器;
getHandlerAdapter就是从集合handlerAdapters中找到对应的适配器;
handle方法就是通过反射机制执行对应处理器的方法;
processDispatchResult就是将执行结果封装成ModelAndView对象;