spring的主要特性是IOC,实现IOC的关键是bean,而更关键的是如何bean的管理容器,也就是BeanFactory,本文的目标是弄清楚BeanFactory具体是怎么样的存在。
先看下最简单的获取bean的案例,代码如下:
1 public static void main(String[] args){ 2 BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring-beans.xml")); 3 User user = (User) factory.getBean("user"); 4 System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(user).toString()); 5 }
首先是读取spring的配置文件,创建BeanFactory实例,如何直接从BeanFactory实例中获取指定名称的bean。接下来就从这几行简单的代码入手,分析下BeanFactory。
BeanFactory实例是通过XmlBeanFactory来创建的,很明显XmlBeanFactory是BeanFactory的子类,继承关系图如下:
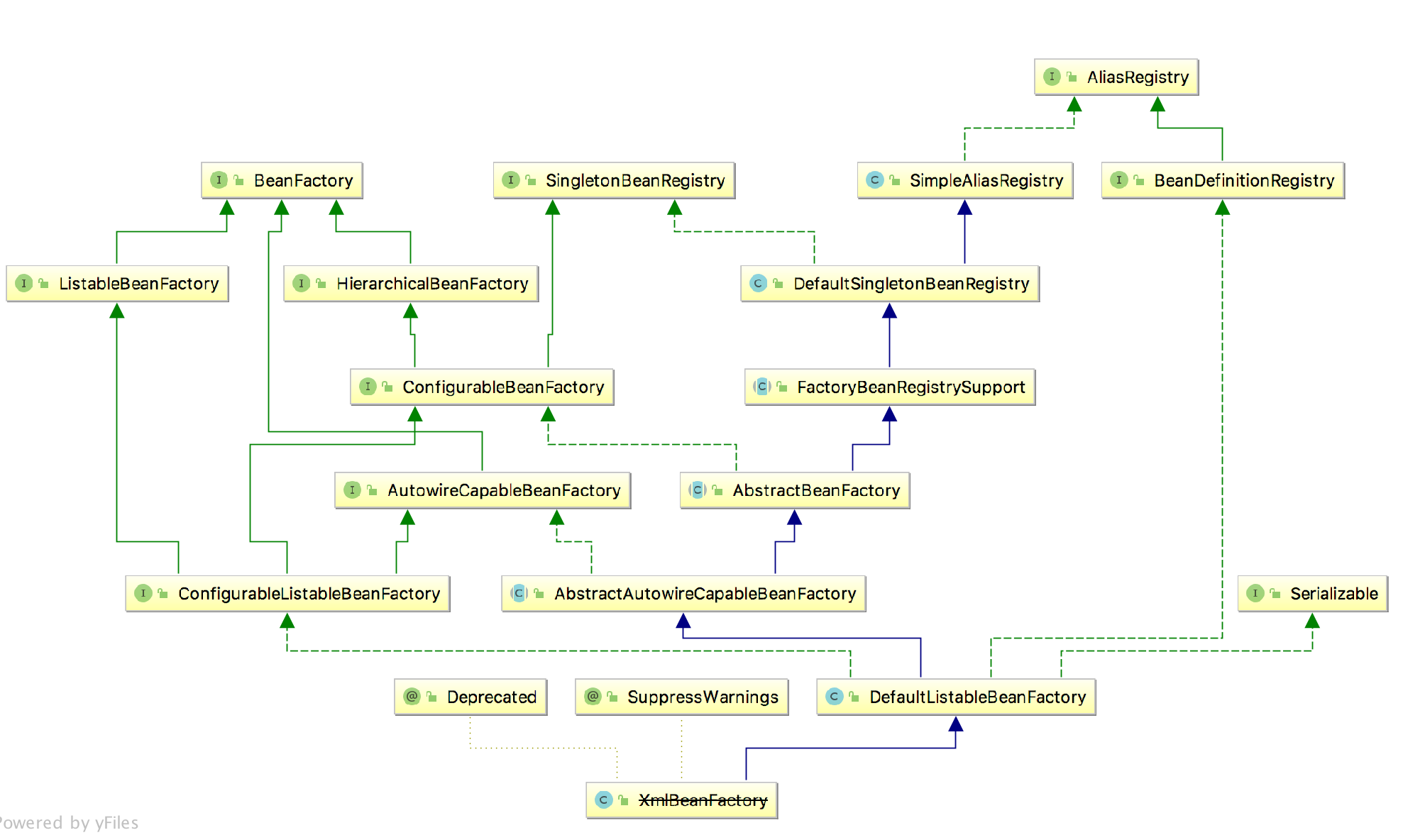
那么先就从XmlBeanFactory的构造方法开始,源码如下:
1 public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { 2 3 private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this); 4 5 public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { 6 this(resource, null); 7 } 8 9 public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { 10 super(parentBeanFactory); 11 this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 12 } 13 14 }
第5行的构造方法调用第9行的构造方法,首先是执行父类的构造方法,然后执行XmlBeanFefinitionReader的loadBeanFefinitions(resource)方法,这个方法显然就是加载bean配置文件的方法。接下来跟踪查看,源码如下:
1 @Override 2 public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 3 return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); 4 }
通过EncodeResource来封装Resource,在调用重载的方法
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); 3 //校验Resource参数 4 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 5 logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); 6 } 7 8 Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); 9 if (currentResources == null) { 10 currentResources = new HashSet<>(4); 11 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); 12 } 13 if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { 14 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 15 "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); 16 } 17 try { 18 //获取Resource的InputSteam流 19 InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); 20 try { 21 //通过InputSteam构造InputSource 22 InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); 23 if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { 24 inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); 25 } 26 //最终执行doLoadBeanDefinitions方法 27 return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); 28 } 29 finally { 30 inputStream.close(); 31 } 32 } 33 catch (IOException ex) { 34 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 35 "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); 36 } 37 finally { 38 currentResources.remove(encodedResource); 39 if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { 40 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); 41 } 42 } 43 }
这次封装的EncodedResource作用主要是对XML配置文件的编码格式进行处理,然后最终执行了doLoadBeanDefinitions方法
1 protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) 2 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 3 try { 4 //通过InputSource和Resource得到一个Document对象,然后执行注册bean的方法 5 Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); 6 return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); 7 } 8 catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { 9 throw ex; 10 } 11 catch (SAXParseException ex) { 12 throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 13 "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); 14 } 15 catch (SAXException ex) { 16 throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 17 "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); 18 } 19 catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { 20 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 21 "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); 22 } 23 catch (IOException ex) { 24 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 25 "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); 26 } 27 catch (Throwable ex) { 28 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 29 "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); 30 } 31 }
该方法只有两行有效逻辑代码,首先是加载XML文件得到一个Document对象,然后根据Document对象来注册Bean信息,一步步来看,先看如何生成Document对象。
1 private DocumentLoader documentLoader = new DefaultDocumentLoader(); 2 3 protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { 4 return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, 5 getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); 6 }
调用了DocumentLoader的实例来进行加载,DocumentLoader接口的loadDocument方法
1 public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver, 2 ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception { 3 4 //这里显然是工厂模式+建造者模式,先创建DocumentBuilder工厂,如何得到DocumentBuilder,最终执行parse方法解析xml配置文件得到Document对象 5 DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware); 6 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 7 logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]"); 8 } 9 DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler); 10 return builder.parse(inputSource); 11 }
1 public Document parse(InputSource is) throws SAXException, IOException { 2 if (is == null) { 3 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 4 DOMMessageFormatter.formatMessage(DOMMessageFormatter.DOM_DOMAIN, 5 "jaxp-null-input-source", null)); 6 } 7 if (fSchemaValidator != null) { 8 if (fSchemaValidationManager != null) { 9 fSchemaValidationManager.reset(); 10 fUnparsedEntityHandler.reset(); 11 } 12 resetSchemaValidator(); 13 } 14 //上面的代码都是校验,核心是下面的三行,通过DomParser来获取Document对象 15 domParser.parse(is); 16 Document doc = domParser.getDocument(); 17 domParser.dropDocumentReferences(); 18 return doc; 19 }
解析配置文件得到了Document对象,接下来就是通过Document来注册beanl了。回到XmlBeanDefinitionReader的RegisterBeanDefinitions方法
1 public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 //创建BeanDefinitionDocumentReader实例 3 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); 4 //统计当前已经加载过的BeanDefinition个数 5 int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); 6 //加载及注册bean 7 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); 8 //得到本次加载的BeanFinition个数 9 return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; 10 }
核心是BeanDefinitionDocumentReader接口的registerBeanDefinitions方法,代码如下:
1 public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { 2 this.readerContext = readerContext; 3 logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); 4 Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); 5 doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); 6 }
首先是获取Document的root,然后将root元素传递给下面的方法继续执行,这里的root元素就是配置文件中的<beans>标签
1 protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { 2 //专门处理解析 3 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; 4 this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); 5 6 if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { 7 //处理<beans>标签中的profile属性 8 String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); 9 if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { 10 String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( 11 profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); 12 if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { 13 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 14 logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + 15 "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); 16 } 17 return; 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 preProcessXml(root);//代码为空(模板方法设计模式:提供给子类实现,如果需要在bean的解析前后做一些处理的话) 23 parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);//Bean的解析 24 postProcessXml(root);//代码为空 25 26 this.delegate = parent; 27 }
发现bean的注册方法应该是parseBeanDefinitions方法,继续往下
1 protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { 2 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { 3 //获取<beans>标签的子节点也就是所有的<bean>标签 4 NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); 5 for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { 6 Node node = nl.item(i); 7 if (node instanceof Element) { 8 Element ele = (Element) node; 9 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { 10 //如果是默认命名空间的bean 11 parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); 12 } 13 else { 14 //如果是自定义命名空间的bean 15 delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 else { 21 //自定义命名空间的bean 22 delegate.parseCustomElement(root); 23 } 24 }
这里是逻辑很清楚,获取root下的子节点遍历,判断是否是默认命名空间的元素来分别处理。判断是否是默认命名空间的方式是取Node的namespanceUrl来和默认命名空间的地址进行比较,默认地址为:
public static final String BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans";
像<bean id="userService" class="com.test.UserService">这种写法就是默认标签,而如<tx:annotation-driven>这种就是自定义的写法。
总结:本文从BeanFactory的初始化开始,解析XML配置文件,生成Docuemnt对象,解析Document中的标签,按标签的类型来进行区分解析,而两种的解析方式截然不同,接下来就分别解析。