The Rotation Game
Time Limit : 45000/15000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 150000/150000K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 7 Accepted Submission(s) : 6
Problem Description
The rotation game uses a # shaped board, which can hold 24 pieces of square blocks (see Fig.1). The blocks are marked with symbols 1, 2 and 3, with exactly 8 pieces of each kind. 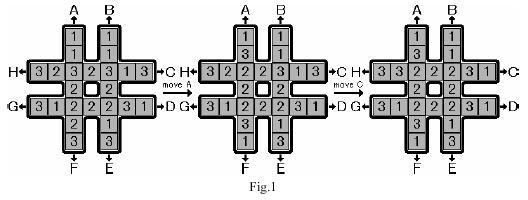

Input
The input consists of no more than 30 test cases. Each test case has only one line that contains 24 numbers, which are the symbols of the blocks in the initial configuration. The rows of blocks are listed from top to bottom. For each row the blocks are listed from left to right. The numbers are separated by spaces. For example, the first test case in the sample input corresponds to the initial configuration in Fig.1. There are no blank lines between cases. There is a line containing a single `0' after the last test case that ends the input.
Output
For each test case, you must output two lines. The first line contains all the moves needed to reach the final configuration. Each move is a letter, ranging from `A' to `H', and there should not be any spaces between the letters in the line. If no moves are needed, output `No moves needed' instead. In the second line, you must output the symbol of the blocks in the center square after these moves. If there are several possible solutions, you must output the one that uses the least number of moves. If there is still more than one possible solution, you must output the solution that is smallest in dictionary order for the letters of the moves. There is no need to output blank lines between cases.
Sample Input
1 1 1 1 3 2 3 2 3 1 3 2 2 3 1 2 2 2 3 1 2 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 0
Sample Output
AC
2
DDHH
2
Source
2004 Asia Regional Shanghai
- /*
- * POJ2286 The Rotation Game
- * 解题思路:使用迭代加深的深度搜索算法,这里非常要注意还是剪枝的问题
- * 只有较好的针对题目环境的剪枝,才能提高搜索效率
- */
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int map[25],countArray[25]; //使用数组表示游戏局面 int depth,aim; //搜索深度 , 最终的局面中心数字 char ans[110]; int isOk(int *g){ //判断是否到达了目标局面 int tmp=g[7]; if(tmp!=g[8] || tmp!=g[9] || tmp!=g[12] || tmp!=g[13] || tmp!=g[16] || tmp!=g[17] || tmp!=g[18]) return 0; return 1; } int countMaxSameNumber(const int* state){ //统计局面的中心区域含有相同数字的最大数量 memset(countArray , 0 ,sizeof(countArray) ) ; countArray[ state[7] ]++; countArray[state[8]] ++; countArray[state[9]]++; countArray[ state[12] ]++; countArray[ state[13] ]++ ; countArray[state[16]]++; countArray[state[17]] ++ ; countArray[state[18]]++; countArray[2] = (countArray[2]>countArray[1]) ? countArray[2]: countArray[1]; return max(countArray[2],countArray[3]); } void changeState(int *g,int a1,int a2,int a3,int a4,int a5,int a6,int a7){ int tmp=g[a1]; g[a1]=g[a2]; g[a2]=g[a3]; g[a3]=g[a4]; g[a4]=g[a5]; g[a5]=g[a6]; g[a6]=g[a7]; g[a7]=tmp; } //迭代加深搜索 //g:当前局面 curDepth :当前所处的搜索深度 preDir:当前搜索选择的旋转的方向 int DFS(int *g,int curDepth,int preDir){ if(depth-curDepth<8-countMaxSameNumber(g)) //剪枝 1 : 本质上使用的就是IDA*估价函数进行剪枝 return 0; if(curDepth>=depth) //超过了当前的搜索深度 return 0; int tmp[25]; for(int i=1;i<=8;i++){ //剪枝2 :前后连续的相反方向的两次旋转是没有意义的 if((i==1 && preDir==6) || (i==6 && preDir==1)) continue; if((i==2 && preDir==5) || (i==5 && preDir==2)) continue; if((i==3 && preDir==8) || (i==8 && preDir==3)) continue; if((i==4 && preDir==7) || (i==7 && preDir==4)) continue; for(int k=1;k<=24;k++) tmp[k]=g[k]; switch(i){ //记录搜索路径 case 1 : ans[curDepth] = 'A' ; changeState(tmp,1,3,7,12,16,21,23); break; case 2 : ans[curDepth] = 'B' ; changeState(tmp,2,4,9,13,18,22,24); break; case 3 : ans[curDepth] = 'C' ; changeState(tmp,11,10,9,8,7,6,5); break; case 4 : ans[curDepth] = 'D' ; changeState(tmp,20,19,18,17,16,15,14); break; case 5 : ans[curDepth] = 'E' ; changeState(tmp,24,22,18,13,9,4,2); break; case 6 : ans[curDepth] = 'F' ; changeState(tmp,23,21,16,12,7,3,1); break; case 7 : ans[curDepth] = 'G' ; changeState(tmp,14,15,16,17,18,19,20); break; case 8 : ans[curDepth] = 'H' ; changeState(tmp,5,6,7,8,9,10,11); break; default : cout<<"ERROR!"<<endl; } if(isOk(tmp)){ aim=tmp[7]; ans[curDepth+1]='\0'; return 1; } if(DFS(tmp,curDepth+1,i)) return 1; } return 0; } int main(){ //freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); while(1){ scanf("%d",&map[1]); if(map[1]==0) break; for(int i=2;i<=24;i++) scanf("%d",&map[i]); if( isOk(map)){ printf("No moves needed\n"); printf("%d\n",map[7]); }else{ depth =1 ; while(1){ if(DFS(map , 0 , -1 )) break; depth ++ ; } printf("%s\n",ans); printf("%d\n",aim); } } return 0; }