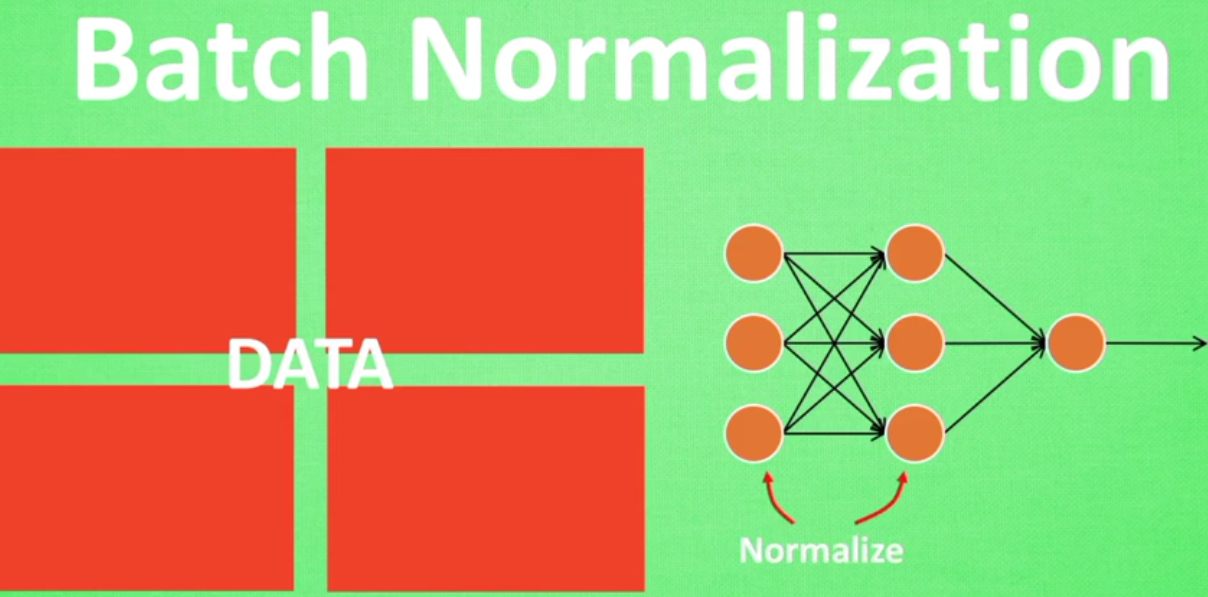
BatchNormalzation是一种解决深度神经网络层数太多,而没有办法有效前向传递的问题,因为每层的输出值都会有不同的均值和方差,所以输出数据的分布也不一样。
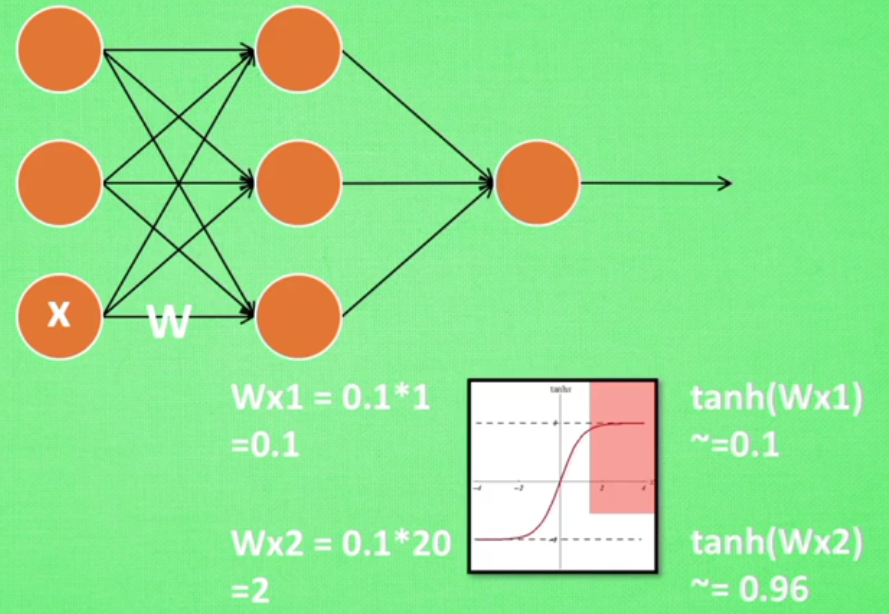
如果对于输入的X*W本身得到的值通过tanh激活函数已经输出为1,在通过下一层的神经元之后结果并没有什么改变,因为该值已经很大(神经网络过敏感问题)
对于这种情况我们可以首先做一些批处理正则化


可以看出没有BN的时候,每层的值迅速全部都变为0,也可以说,所有的神经元迅速都已经死去了,而有BN,relu之后,每层的值都能有一个比较好的分布效果
大部分神经元都还活着

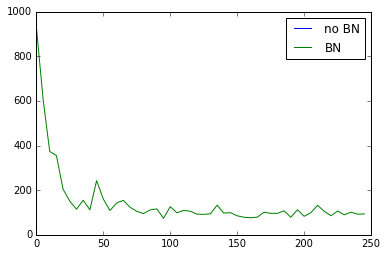
relu下的误差对比,no BN的曲线是没有的,很快消失

如果改为tanh,误差变化如下

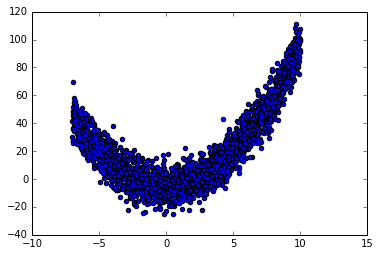
""" Build two networks. 1. Without batch normalization 2. With batch normalization Run tests on these two networks. """ # Batch Normalization import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ACTIVATION = tf.nn.relu #tf.nn.tanh N_LAYERS = 7 N_HIDDEN_UNITS = 30 def fix_seed(seed=1): # reproducible np.random.seed(seed) tf.set_random_seed(seed) def plot_his(inputs, inputs_norm): # plot histogram for the inputs of every layer for j, all_inputs in enumerate([inputs, inputs_norm]): for i, input in enumerate(all_inputs): plt.subplot(2, len(all_inputs), j*len(all_inputs)+(i+1)) plt.cla() if i == 0: the_range = (-7, 10) else: the_range = (-1, 1) plt.hist(input.ravel(), bins=15, range=the_range, color='#FF5733') plt.yticks(()) if j == 1: plt.xticks(the_range) else: plt.xticks(()) ax = plt.gca() ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') ax.spines['top'].set_color('none') plt.title("%s normalizing" % ("Without" if j == 0 else "With")) plt.draw() plt.pause(0.01) def built_net(xs, ys, norm): def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None, norm=False): # weights and biases (bad initialization for this case) Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size], mean=0., stddev=1.)) biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1) # fully connected product Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases # normalize fully connected product if norm: # Batch Normalize fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments( Wx_plus_b, axes=[0], # the dimension you wanna normalize, here [0] for batch # for image, you wanna do [0, 1, 2] for [batch, height, width] but not channel ) scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([out_size])) shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_size])) epsilon = 0.001 # apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5) def mean_var_with_update(): ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var]) with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]): return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var) mean, var = mean_var_with_update() #all parmeter batch normalization Wx_plus_b = tf.nn.batch_normalization(Wx_plus_b, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon) # similar with this two steps: # Wx_plus_b = (Wx_plus_b - fc_mean) / tf.sqrt(fc_var + 0.001) # Wx_plus_b = Wx_plus_b * scale + shift # activation if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs fix_seed(1) if norm: # BN for the first input fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments( xs, axes=[0], ) scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1])) shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1])) epsilon = 0.001 # apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5) def mean_var_with_update(): ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var]) with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]): return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var) mean, var = mean_var_with_update() xs = tf.nn.batch_normalization(xs, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon) # record inputs for every layer layers_inputs = [xs] # build hidden layers for l_n in range(N_LAYERS): layer_input = layers_inputs[l_n] in_size = layers_inputs[l_n].get_shape()[1].value output = add_layer( layer_input, # input in_size, # input size N_HIDDEN_UNITS, # output size ACTIVATION, # activation function norm, # normalize before activation ) layers_inputs.append(output) # add output for next run # build output layer prediction = add_layer(layers_inputs[-1], 30, 1, activation_function=None) cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost) return [train_op, cost, layers_inputs] # make up data fix_seed(1) x_data = np.linspace(-7, 10, 2500)[:, np.newaxis] np.random.shuffle(x_data) noise = np.random.normal(0, 8, x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data) - 5 + noise # plot input data plt.scatter(x_data, y_data) plt.show() xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) # [num_samples, num_features] ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) #create 2 neuralnetwork train_op, cost, layers_inputs = built_net(xs, ys, norm=False) # without BN train_op_norm, cost_norm, layers_inputs_norm = built_net(xs, ys, norm=True) # with BN sess = tf.Session() if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # record cost cost_his = [] cost_his_norm = [] record_step = 5 plt.ion() plt.figure(figsize=(7, 3)) for i in range(250): if i % 50 == 0: # plot histogram all_inputs, all_inputs_norm = sess.run([layers_inputs, layers_inputs_norm], feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) plot_his(all_inputs, all_inputs_norm) # train on batch sess.run([train_op, train_op_norm], feed_dict={xs: x_data[i*10:i*10+10], ys: y_data[i*10:i*10+10]}) if i % record_step == 0: # record cost cost_his.append(sess.run(cost, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})) cost_his_norm.append(sess.run(cost_norm, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})) plt.ioff() plt.figure() plt.plot(np.arange(len(cost_his))*record_step, np.array(cost_his), label='no BN') # no norm plt.plot(np.arange(len(cost_his))*record_step, np.array(cost_his_norm), label='BN') # norm plt.legend() plt.show()
数据集图示