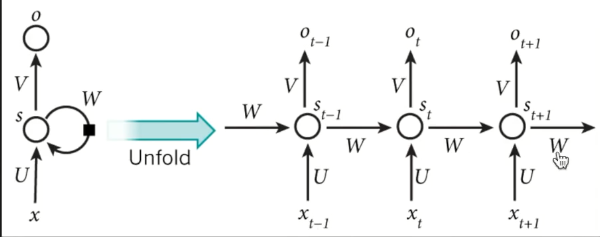
RNN
RNN无法回忆起长久的记忆
LSTM
(long short Term memory长短期记忆)解决梯度消失或弥散vanishing 和梯度爆炸explosion 0.9*n-->0 1.1*n--->无穷大
在RNN中增加了Gate
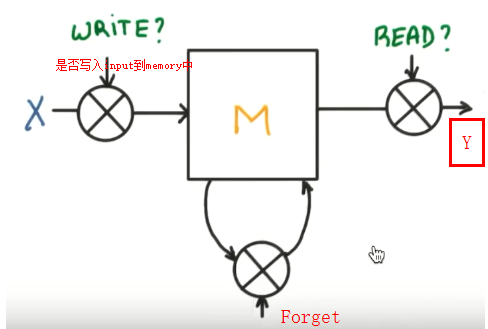
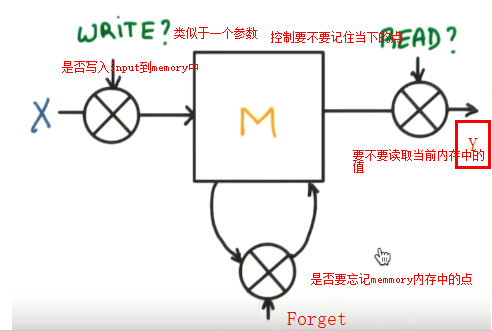
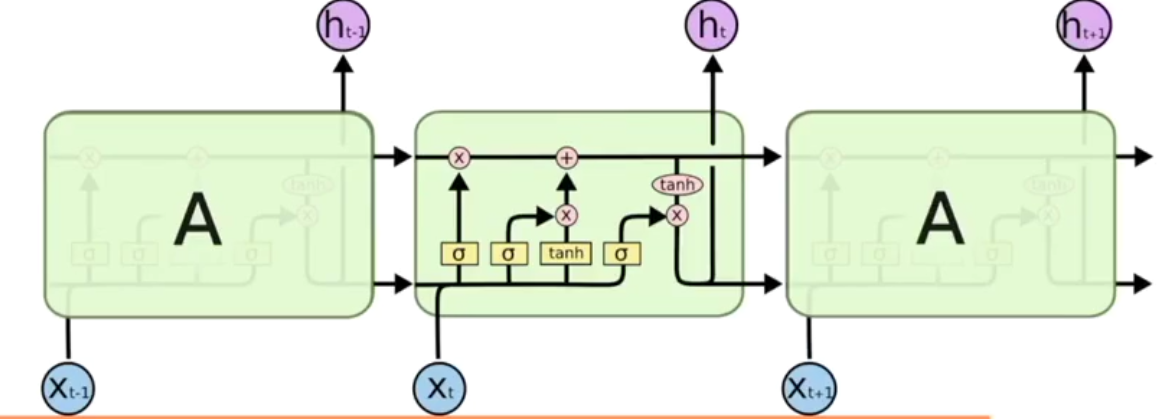
案例

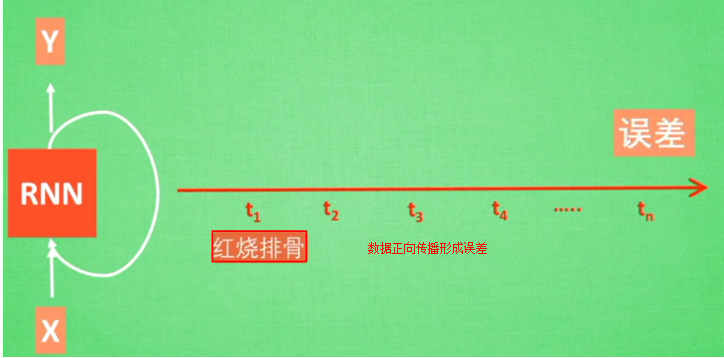


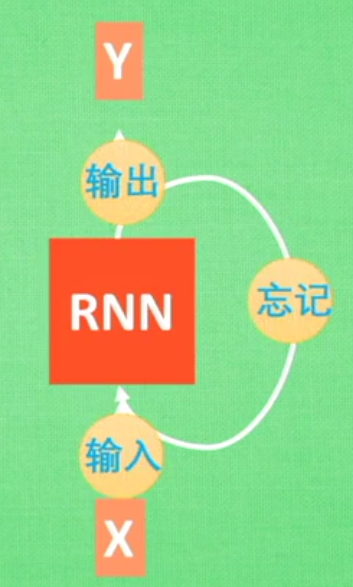
所以RNN无法回忆起长久的记忆。LSTM为了解决该问题多了三个控制器,做到了延缓记忆的功能
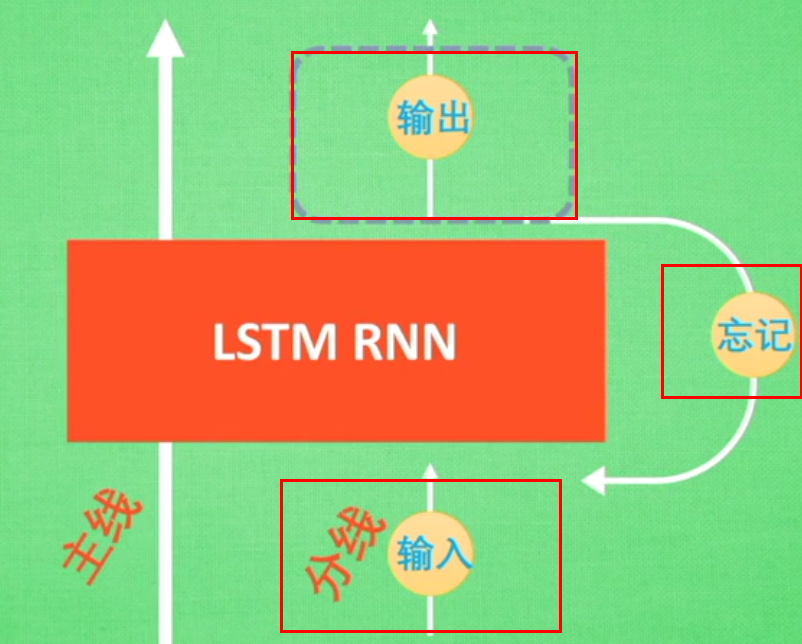
可以从主线和分线两个方面理解。LSTM可以解决延缓记忆问题
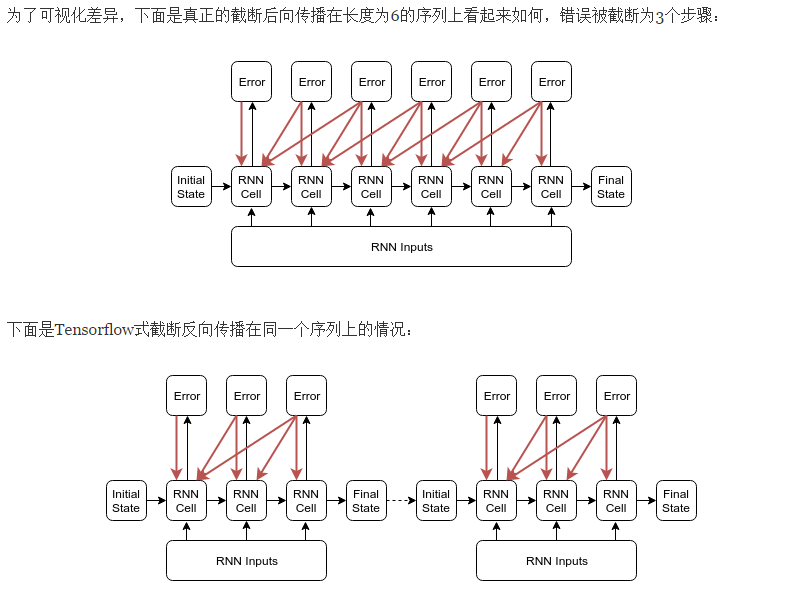
截断的反向传播BBPT
https://r2rt.com/styles-of-truncated-backpropagation.html
Tensorflow的截断反向传播(截断长度为n的子序列)的方法在定性上不同于“反向传播错误最多n步”。
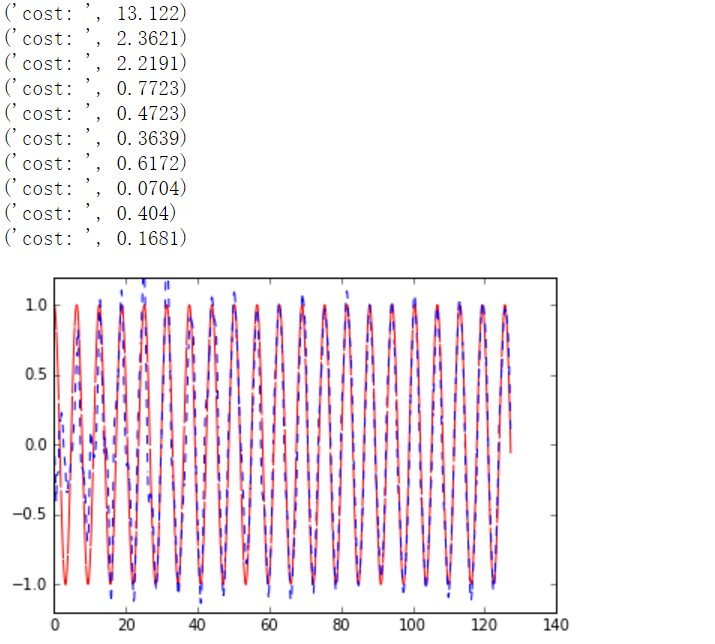
LSTM模拟sin图像解决回归问题代码
""" Please note, this code is only for python 3+. If you are using python 2+, please modify the code accordingly. Run this script on tensorflow r0.10. Errors appear when using lower versions. """ import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt BATCH_START = 0 TIME_STEPS = 20 BATCH_SIZE = 50 INPUT_SIZE = 1 OUTPUT_SIZE = 1 CELL_SIZE = 10 LR = 0.006 def get_batch(): global BATCH_START, TIME_STEPS # xs shape (50batch, 20steps) xs = np.arange(BATCH_START, BATCH_START+TIME_STEPS*BATCH_SIZE).reshape((BATCH_SIZE, TIME_STEPS)) / (10*np.pi) seq = np.sin(xs) res = np.cos(xs) BATCH_START += TIME_STEPS # plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0, :], 'r', xs[0, :], seq[0, :], 'b--') # plt.show() # returned seq, res and xs: shape (batch, step, input) return [seq[:, :, np.newaxis], res[:, :, np.newaxis], xs] class LSTMRNN(object): def __init__(self, n_steps, input_size, output_size, cell_size, batch_size): self.n_steps = n_steps self.input_size = input_size self.output_size = output_size self.cell_size = cell_size self.batch_size = batch_size with tf.name_scope('inputs'): self.xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, input_size], name='xs') self.ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, output_size], name='ys') with tf.variable_scope('in_hidden'): self.add_input_layer() with tf.variable_scope('LSTM_cell'): self.add_cell() with tf.variable_scope('out_hidden'): self.add_output_layer() with tf.name_scope('cost'): self.compute_cost() with tf.name_scope('train'): self.train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LR).minimize(self.cost) def add_input_layer(self,): l_in_x = tf.reshape(self.xs, [-1, self.input_size], name='2_2D') # (batch*n_step, in_size) # Ws (in_size, cell_size) Ws_in = self._weight_variable([self.input_size, self.cell_size]) # bs (cell_size, ) bs_in = self._bias_variable([self.cell_size,]) # l_in_y = (batch * n_steps, cell_size) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): l_in_y = tf.matmul(l_in_x, Ws_in) + bs_in # reshape l_in_y ==> (batch, n_steps, cell_size) self.l_in_y = tf.reshape(l_in_y, [-1, self.n_steps, self.cell_size], name='2_3D') def add_cell(self): lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.cell_size, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True) with tf.name_scope('initial_state'): self.cell_init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, dtype=tf.float32) self.cell_outputs, self.cell_final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn( lstm_cell, self.l_in_y, initial_state=self.cell_init_state, time_major=False) def add_output_layer(self): # shape = (batch * steps, cell_size) l_out_x = tf.reshape(self.cell_outputs, [-1, self.cell_size], name='2_2D') Ws_out = self._weight_variable([self.cell_size, self.output_size]) bs_out = self._bias_variable([self.output_size, ]) # shape = (batch * steps, output_size) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): self.pred = tf.matmul(l_out_x, Ws_out) + bs_out def compute_cost(self): losses = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example( [tf.reshape(self.pred, [-1], name='reshape_pred')], [tf.reshape(self.ys, [-1], name='reshape_target')], [tf.ones([self.batch_size * self.n_steps], dtype=tf.float32)], average_across_timesteps=True, softmax_loss_function=self.ms_error, name='losses' ) with tf.name_scope('average_cost'): self.cost = tf.div( tf.reduce_sum(losses, name='losses_sum'), self.batch_size, name='average_cost') tf.summary.scalar('cost', self.cost) @staticmethod def ms_error(labels, logits): return tf.square(tf.subtract(labels, logits)) def _weight_variable(self, shape, name='weights'): initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0., stddev=1.,) return tf.get_variable(shape=shape, initializer=initializer, name=name) def _bias_variable(self, shape, name='biases'): initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1) return tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, initializer=initializer) if __name__ == '__main__': model = LSTMRNN(TIME_STEPS, INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE) sess = tf.Session() merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs", sess.graph) # tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from # 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12 if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # relocate to the local dir and run this line to view it on Chrome (http://0.0.0.0:6006/): # $ tensorboard --logdir='logs' plt.ion() plt.show() for i in range(200): seq, res, xs = get_batch() if i == 0: feed_dict = { model.xs: seq, model.ys: res, # create initial state } else: feed_dict = { model.xs: seq, model.ys: res, model.cell_init_state: state # use last state as the initial state for this run } _, cost, state, pred = sess.run( [model.train_op, model.cost, model.cell_final_state, model.pred], feed_dict=feed_dict) # plotting 绘制训练sin图像的过程 plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0].flatten(), 'r', xs[0, :], pred.flatten()[:TIME_STEPS], 'b--') plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2)) plt.draw() plt.pause(0.3) #每隔3秒运行一次 if i % 20 == 0: print('cost: ', round(cost, 4)) result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict) writer.add_summary(result, i)
程序运行结果
下面的图像是拟合正弦曲线的过程