1.背景知识
* 古代判官要判决number个罪犯的死刑,制定了一条荒谬的法律
* 将犯人站成一个圈,从start开始数起,每数到第distance
* 个就处决他,依照此规律直到最后剩下一个人赦免。
* 如当number=5时候,start=0,distance=2时:
* 1.假设五个人是A B C D E
* 2.从A开始每隔两个处决一个人,依次处决
* 3.原始序列A(0) B(1) C(2) D(3) E(4)
* 第一次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉B(1),从c开始
* 第二次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉D(3),从e开始
* 第三次A(0) C(2) E(4) 干掉A(0),从c开始数
* 第四次C(2) E(4) 干掉E(4)
* 第五次C(2) c是被赦免的人
2.解法1:约瑟夫问题线性表存储结构解法
a.建立sequence线性存储结构
1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 3 public class Sequence { 4 public Object[] listElem; 5 public int currentLen=0;//线性表长度 6 public Sequence(int maxSize) { 7 currentLen =0;//线性表长度置空 8 listElem = new Object[maxSize]; 9 //为顺序表分配存储空间 10 } 11 public void insert(int i, Object x) { 12 if (i<0 || i>currentLen) { 13 System.out.println("第"+i+"个元素不存在"); 14 } 15 if (currentLen==listElem.length) { 16 System.out.println("顺序表容量已满"); 17 } 18 for (int j = currentLen; j >i; j--) { 19 listElem[j]=listElem[j-1]; 20 } 21 listElem[i]=x; 22 currentLen++; 23 } 24 public int length() { 25 return currentLen; 26 } 27 public Object get(int i) { 28 if (i<0 || i>currentLen-1) { 29 System.out.println("第"+i+"个元素不存在"); 30 } 31 return listElem[i]; 32 } 33 public Object remove(int i) { 34 // 将顺序表上的第i个元素a从顺序表中删除 35 Object listRemove=listElem[i]; 36 if (i<0 ||i>=currentLen) { 37 System.out.println("删除位置不合法"); 38 } 39 for (int j = i; j < currentLen-1; j++) { 40 listElem[j]=listElem[j+1]; 41 } 42 currentLen--; 43 return listRemove; 44 } 45 public void display() { 46 for (int i = 0; i < currentLen; i++) { 47 System.out.print(listElem[i]+" "); 48 } 49 System.out.println(); 50 51 } 52 }
可点击下列代码复制

1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 3 public class Sequence { 4 public Object[] listElem; 5 public int currentLen=0;//线性表长度 6 public Sequence(int maxSize) { 7 currentLen =0;//线性表长度置空 8 listElem = new Object[maxSize]; 9 //为顺序表分配存储空间 10 } 11 public void insert(int i, Object x) { 12 if (i<0 || i>currentLen) { 13 System.out.println("第"+i+"个元素不存在"); 14 } 15 if (currentLen==listElem.length) { 16 System.out.println("顺序表容量已满"); 17 } 18 for (int j = currentLen; j >i; j--) { 19 listElem[j]=listElem[j-1]; 20 } 21 listElem[i]=x; 22 currentLen++; 23 } 24 public int length() { 25 return currentLen; 26 } 27 public Object get(int i) { 28 if (i<0 || i>currentLen-1) { 29 System.out.println("第"+i+"个元素不存在"); 30 } 31 return listElem[i]; 32 } 33 public Object remove(int i) { 34 // 将顺序表上的第i个元素a从顺序表中删除 35 Object listRemove=listElem[i]; 36 if (i<0 ||i>=currentLen) { 37 System.out.println("删除位置不合法"); 38 } 39 for (int j = i; j < currentLen-1; j++) { 40 listElem[j]=listElem[j+1]; 41 } 42 currentLen--; 43 return listRemove; 44 } 45 public void display() { 46 for (int i = 0; i < currentLen; i++) { 47 System.out.print(listElem[i]+" "); 48 } 49 System.out.println(); 50 51 } 52 }
b.约瑟夫问题代码组织(主函数)
1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 /** 3 * @author zhao-chj 4 * 古代判官要判决number个罪犯的死刑,制定了一条荒谬的法律 5 * 将犯人站成一个圈,从start开始数起,每数到第distance 6 * 个就处决他,依照此规律直到最后剩下一个人赦免。 7 * 如当number=5时候,start=0,distance=2时: 8 * 1.假设五个人是A B C D E 9 * 2.从A开始每隔两个处决一个人,依次处决 10 * 3.原始序列A(0) B(1) C(2) D(3) E(4) 11 * 第一次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉B(1),从c开始 12 * 第二次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉D(3),从e开始 13 * 第三次A(0) C(2) E(4) 干掉A(0),从c开始数 14 * 第四次C(2) E(4) 干掉E(4) 15 * 第五次C(2) c是被赦免的人 16 */ 17 public class Josephus { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 new Josephus(5, 0, 2); 20 } 21 public Josephus(int number,int start,int distance) { 22 // TODO 和类名相同的方法就是构造函数,是用于初始化变量的 23 System.out.println 24 ("Josephus("+number+","+start+","+distance+"),"); 25 Sequence list =new Sequence(number); 26 //插入罪犯的名字,以A B C D为例 27 for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) { 28 list.insert(i,(char)('A'+i)+""); 29 } 30 //输出之前输入的罪犯名字,查看是否正确 31 list.display(); 32 //计算起始位置 33 int i=start; 34 //找差别distance距离的元素或罪犯 35 while (list.length()>1) { 36 //处决间隔distance的元素或罪犯 37 i=(i+distance-1)%list.length(); 38 System.out.print("删除"+list.remove(i).toString()+" "); 39 list.display(); 40 } 41 System.out.println("被赦免者是"+list.get(0).toString()); 42 } 43 44 45 46 }
可点击下列代码复制

1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 /** 3 * @author zhao-chj 4 * 古代判官要判决number个罪犯的死刑,制定了一条荒谬的法律 5 * 将犯人站成一个圈,从start开始数起,每数到第distance 6 * 个就处决他,依照此规律直到最后剩下一个人赦免。 7 * 如当number=5时候,start=0,distance=2时: 8 * 1.假设五个人是A B C D E 9 * 2.从A开始每隔两个处决一个人,依次处决 10 * 3.原始序列A(0) B(1) C(2) D(3) E(4) 11 * 第一次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉B(1),从c开始 12 * 第二次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉D(3),从e开始 13 * 第三次A(0) C(2) E(4) 干掉A(0),从c开始数 14 * 第四次C(2) E(4) 干掉E(4) 15 * 第五次C(2) c是被赦免的人 16 */ 17 public class Josephus { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 new Josephus(5, 0, 2); 20 } 21 public Josephus(int number,int start,int distance) { 22 // TODO 和类名相同的方法就是构造函数,是用于初始化变量的 23 System.out.println 24 ("Josephus("+number+","+start+","+distance+"),"); 25 Sequence list =new Sequence(number); 26 //插入罪犯的名字,以A B C D为例 27 for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) { 28 list.insert(i,(char)('A'+i)+""); 29 } 30 //输出之前输入的罪犯名字,查看是否正确 31 list.display(); 32 //计算起始位置 33 int i=start; 34 //找差别distance距离的元素或罪犯 35 while (list.length()>1) { 36 //处决间隔distance的元素或罪犯 37 i=(i+distance-1)%list.length(); 38 System.out.print("删除"+list.remove(i).toString()+" "); 39 list.display(); 40 } 41 System.out.println("被赦免者是"+list.get(0).toString()); 42 } 43 44 45 46 }
c.测试及结果分析
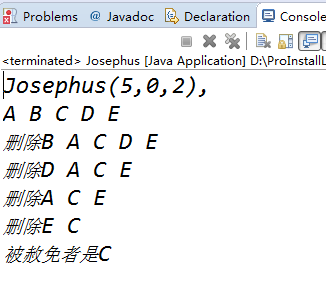
3.解法2:约瑟夫环的链表存储结构解法
a.链表Node节点定义
1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 public class Node { 3 public Object data;// 数据域 4 public Node next;// 指针域 5 public Node() { //构造空节点 6 this(null,null); 7 } 8 public Node(Object data){//构造有一个参数的数据域 9 this(data,null); 10 } 11 public Node(Object data,Node node){//构造数据域和指针域 12 this.data=data; 13 this.next=node; 14 } 15 }
展开代码可直接复制

1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 public class Node { 3 public Object data;// 数据域 4 public Node next;// 指针域 5 public Node() { //构造空节点 6 this(null,null); 7 } 8 public Node(Object data){//构造有一个参数的数据域 9 this(data,null); 10 } 11 public Node(Object data,Node node){//构造数据域和指针域 12 this.data=data; 13 this.next=node; 14 } 15 }
b.LinkList带头节点的单链表定义
1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 /** 3 * 带头结点的单链表 4 */ 5 import java.util.Scanner; 6 public class LinkedList { 7 public Node head;//链表的头指针 8 public LinkedList() { 9 head = new Node();//初始化头结点 10 } 11 public LinkedList(int n,boolean order){ 12 //如果order=1采用尾插法,如果order=2采用头插法 13 this(); 14 if (order) { 15 create1(n); 16 }else { 17 create2(n); 18 } 19 } 20 private void create1(int n) { 21 //尾插法 22 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 23 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 24 insert(length(), sc.next()); 25 } 26 } 27 private void create2(int n) { 28 //头插法 29 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 30 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 31 insert(0, sc.next()); 32 } 33 } 34 35 public int length() { 36 // 链表的长度 37 Node p = head.next; 38 int length=0; 39 while (p!=null) { 40 p=p.next; //指向后继节点 41 length++; 42 } 43 return length; 44 } 45 46 public Object get(int i) { 47 // 读取链表中第i个节点 48 Node p = head.next; 49 int j=0; 50 if (j>i||p==null) { 51 System.out.println("第"+i+"个元素不存在"); 52 } 53 while (p!=null&&j<i) {//从头结点开始查找,找到第i各节点或者p的指针域为空停止 54 p=p.next; 55 j++; 56 } 57 return p.data; 58 } 59 60 public void insert(int i, Object x) { 61 // 在第i个节点之前插入一个值为x的新节点 62 Node p = head; 63 int j=-1; 64 while (p!=null &&j<i-1) { 65 p=p.next; 66 j++; 67 } 68 if (j>i-1||p==null) { 69 System.out.println("插入位置不合法"); 70 } 71 Node s = new Node(x);//新开辟的s节点 72 //从链表中间或表尾进行插入 73 s.next=p.next; 74 p.next=s; 75 } 76 77 public Object remove(int i) { 78 // 删除单链表的第i个节点 79 Node p = head; 80 int j=-1; 81 while (p.next!=null&&j<i-1) { 82 p=p.next; 83 j++; 84 } 85 String old=(String)p.next.data;//保存要删除的值 86 if (j>i-1||p.next==null) { 87 System.out.println("删除位置不合法"); 88 } 89 p.next=p.next.next; 90 return old; 91 } 92 93 public int indexOf(Object x) { 94 // 查找值为x的位置 95 Node p = head.next; 96 int j=0; 97 while (p!=null&&!p.data.equals(x)) { 98 p= p.next; 99 j++; 100 } 101 if (p!=null) { 102 return j; 103 }else { 104 return -1; 105 } 106 } 107 108 public void display() { 109 // 输出单链表的所有节点 110 Node node = head.next; 111 while(node !=null){ 112 System.out.print(node.data+" "); 113 node=node.next; 114 } 115 System.out.println(); 116 } 117 }
展开代码可直接复制

1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 /** 3 * 带头结点的单链表 4 */ 5 import java.util.Scanner; 6 public class LinkedList { 7 public Node head;//链表的头指针 8 public LinkedList() { 9 head = new Node();//初始化头结点 10 } 11 public LinkedList(int n,boolean order){ 12 //如果order=1采用尾插法,如果order=2采用头插法 13 this(); 14 if (order) { 15 create1(n); 16 }else { 17 create2(n); 18 } 19 } 20 private void create1(int n) { 21 //尾插法 22 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 23 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 24 insert(length(), sc.next()); 25 } 26 } 27 private void create2(int n) { 28 //头插法 29 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 30 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 31 insert(0, sc.next()); 32 } 33 } 34 35 public int length() { 36 // 链表的长度 37 Node p = head.next; 38 int length=0; 39 while (p!=null) { 40 p=p.next; //指向后继节点 41 length++; 42 } 43 return length; 44 } 45 46 public Object get(int i) { 47 // 读取链表中第i个节点 48 Node p = head.next; 49 int j=0; 50 if (j>i||p==null) { 51 System.out.println("第"+i+"个元素不存在"); 52 } 53 while (p!=null&&j<i) {//从头结点开始查找,找到第i各节点或者p的指针域为空停止 54 p=p.next; 55 j++; 56 } 57 return p.data; 58 } 59 60 public void insert(int i, Object x) { 61 // 在第i个节点之前插入一个值为x的新节点 62 Node p = head; 63 int j=-1; 64 while (p!=null &&j<i-1) { 65 p=p.next; 66 j++; 67 } 68 if (j>i-1||p==null) { 69 System.out.println("插入位置不合法"); 70 } 71 Node s = new Node(x);//新开辟的s节点 72 //从链表中间或表尾进行插入 73 s.next=p.next; 74 p.next=s; 75 } 76 77 public Object remove(int i) { 78 // 删除单链表的第i个节点 79 Node p = head; 80 int j=-1; 81 while (p.next!=null&&j<i-1) { 82 p=p.next; 83 j++; 84 } 85 String old=(String)p.next.data;//保存要删除的值 86 if (j>i-1||p.next==null) { 87 System.out.println("删除位置不合法"); 88 } 89 p.next=p.next.next; 90 return old; 91 } 92 93 public int indexOf(Object x) { 94 // 查找值为x的位置 95 Node p = head.next; 96 int j=0; 97 while (p!=null&&!p.data.equals(x)) { 98 p= p.next; 99 j++; 100 } 101 if (p!=null) { 102 return j; 103 }else { 104 return -1; 105 } 106 } 107 108 public void display() { 109 // 输出单链表的所有节点 110 Node node = head.next; 111 while(node !=null){ 112 System.out.print(node.data+" "); 113 node=node.next; 114 } 115 System.out.println(); 116 } 117 }
c.约瑟夫问题代码组织
1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 /** 3 * @author zhao-chj 4 * 古代判官要判决number个罪犯的死刑,制定了一条荒谬的法律 5 * 将犯人站成一个圈,从start开始数起,每数到第distance 6 * 个就处决他,依照此规律直到最后剩下一个人赦免。 7 * 如当number=5时候,start=0,distance=2时: 8 * 1.假设五个人是A B C D E 9 * 2.从A开始每隔两个处决一个人,依次处决 10 * 3.原始序列A(0) B(1) C(2) D(3) E(4) 11 * 第一次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉B(1),从c开始 12 * 第二次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉D(3),从e开始 13 * 第三次A(0) C(2) E(4) 干掉A(0),从c开始数 14 * 第四次C(2) E(4) 干掉E(4) 15 * 第五次C(2) c是被赦免的人 16 */ 17 public class Josephus_LinkList { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 new Josephus_LinkList(5, 0, 2); 20 System.out.println("**********************"); 21 new Josephus_LinkList(10, 0, 1); 22 } 23 public Josephus_LinkList(int number,int start,int distance) { 24 // TODO 和类名相同的方法就是构造函数,是用于初始化变量的 25 System.out.println 26 ("Josephus("+number+","+start+","+distance+"),"); 27 //插入罪犯的名字,以A B C D为例 28 System.out.println("请您收入"+number+"个罪犯"); 29 //采用头插法输入各个元素 30 LinkedList list =new LinkedList(number,true); 31 //输出之前输入的罪犯名字,查看是否正确 32 list.display(); 33 //计算起始位置 34 int i=start; 35 //找差别distance距离的元素或罪犯 36 while (list.length()>1) { 37 //处决间隔distance的元素或罪犯 38 i=(i+distance-1)%list.length(); 39 System.out.print("删除"+list.remove(i).toString()+": "); 40 list.display(); 41 } 42 System.out.println("被赦免者是"+list.get(0).toString());//get(0)是获得元素 43 } 44 45 46 47 }
展开并复制代码

1 package com.neusoft.chapter4.exercise; 2 /** 3 * @author zhao-chj 4 * 古代判官要判决number个罪犯的死刑,制定了一条荒谬的法律 5 * 将犯人站成一个圈,从start开始数起,每数到第distance 6 * 个就处决他,依照此规律直到最后剩下一个人赦免。 7 * 如当number=5时候,start=0,distance=2时: 8 * 1.假设五个人是A B C D E 9 * 2.从A开始每隔两个处决一个人,依次处决 10 * 3.原始序列A(0) B(1) C(2) D(3) E(4) 11 * 第一次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉B(1),从c开始 12 * 第二次A(0) C(2) D(3) E(4) 干掉D(3),从e开始 13 * 第三次A(0) C(2) E(4) 干掉A(0),从c开始数 14 * 第四次C(2) E(4) 干掉E(4) 15 * 第五次C(2) c是被赦免的人 16 */ 17 public class Josephus_LinkList { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 new Josephus_LinkList(5, 0, 2); 20 System.out.println("**********************"); 21 new Josephus_LinkList(10, 0, 1); 22 } 23 public Josephus_LinkList(int number,int start,int distance) { 24 // TODO 和类名相同的方法就是构造函数,是用于初始化变量的 25 System.out.println 26 ("Josephus("+number+","+start+","+distance+"),"); 27 //插入罪犯的名字,以A B C D为例 28 System.out.println("请您收入"+number+"个罪犯"); 29 //采用头插法输入各个元素 30 LinkedList list =new LinkedList(number,true); 31 //输出之前输入的罪犯名字,查看是否正确 32 list.display(); 33 //计算起始位置 34 int i=start; 35 //找差别distance距离的元素或罪犯 36 while (list.length()>1) { 37 //处决间隔distance的元素或罪犯 38 i=(i+distance-1)%list.length(); 39 System.out.print("删除"+list.remove(i).toString()+": "); 40 list.display(); 41 } 42 System.out.println("被赦免者是"+list.get(0).toString());//get(0)是获得元素 43 } 44 45 46 47 }
e.测试结果

