@(MyBatis)[Cache]
MyBatis源码分析——Cache构建以及应用
SqlSession使用缓存流程
如果开启了二级缓存,而Executor会使用CachingExecutor来装饰,添加缓存功能,该CachingExecutor会从MappedStatement中获取对应的Cache来使用。(注:MappedStatement中有保存相关联的Cache)
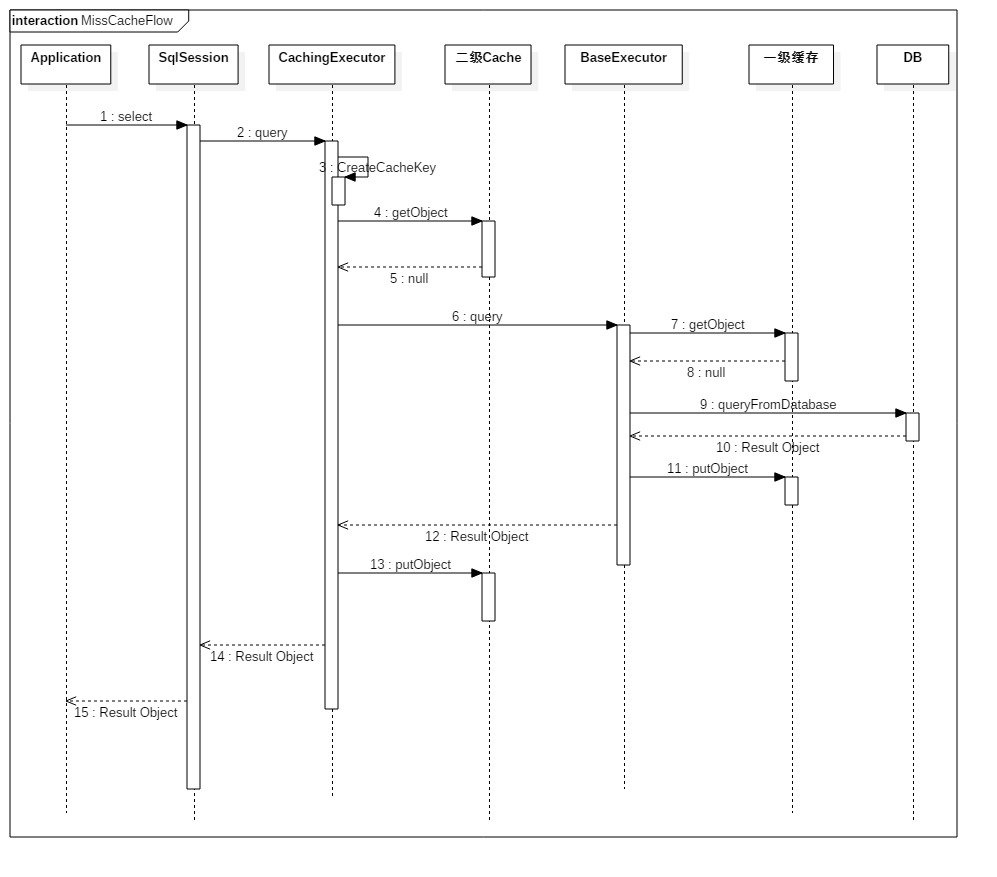
在使用SqlSession向DB查询数据时,如果开启了二级缓存,则会优先从二级缓存中获取数据,没有命中的话才会去查询一级缓存,此时,一级缓存也没有命中,则才会真正的去数据库查询数据。
没有命中缓存
下图为开启了二级缓存的查询数据时序图,其中忽略了二级缓存事务的处理(见下面二级缓存详细说明)。
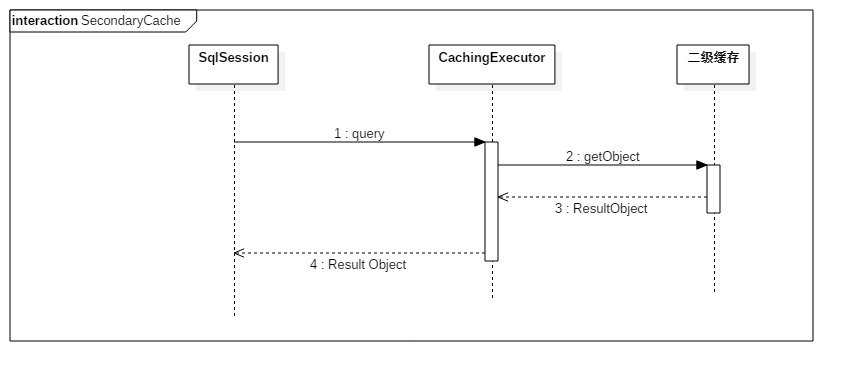
命中二级缓存
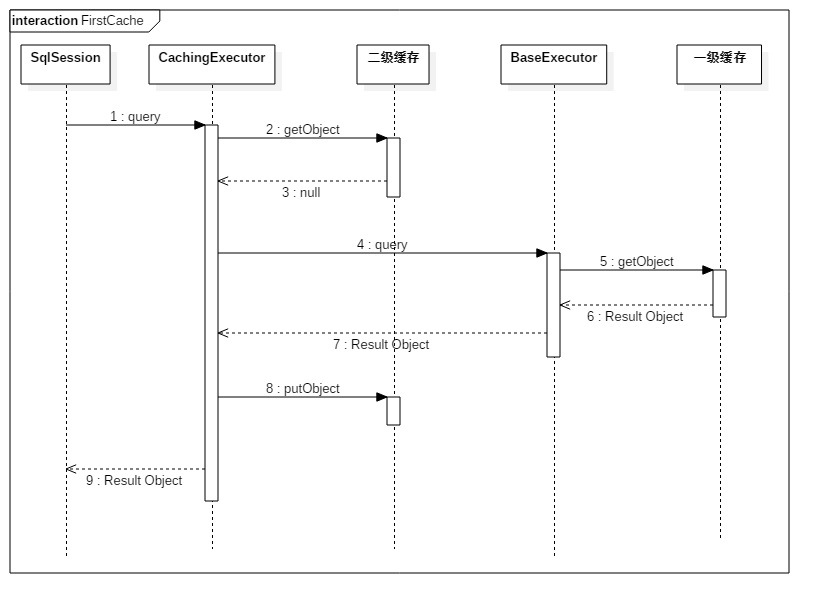
命中一级缓存
缓存键,CacheKey
下面为CacheKey的主要核心代码,省略了部分代码。在MyBatis中,是通过几个条件来判断是否同一条Sql的。
判断条件:
- Statement ID
- 结果范围
- Sql
- 所有的入参
在上面的条件中,对于需要使用JDBC查询出相同结果的来说,需要是同一条Sql以及该Sql的入参条件。
在查询数据之前,会先创建CacheKey,在BaseExecutor.createCacheKey中实现:
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
// StatementId, 即用于映射Mapper中的具体Sql的ID
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
// 结果集范围,在数据库查询出来的结果中进行过滤,并非是物理分页。
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
// 具体执行的Sql
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
// 入参变量值
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { // mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
return cacheKey;
}
CacheKey的实现:
这里将所有需要判断相等的条件都放入List中,并且更新这些条件计算出校验值和hashCode,这是为了加快比较的速度。因为只有在校验值以及HashCode相等的情况下,才会去逐一地判断每个条件是否相等。
public class CacheKey implements Cloneable, Serializable {
// 默认扩展因子
private static final int DEFAULT_MULTIPLYER = 37;
// 默认HashCdoe基值
private static final int DEFAULT_HASHCODE = 17;
private int multiplier;
private int hashcode;
private long checksum;
private int count;
private List<Object> updateList;
public CacheKey() {
this.hashcode = DEFAULT_HASHCODE;
this.multiplier = DEFAULT_MULTIPLYER;
this.count = 0;
this.updateList = new ArrayList<Object>();
}
public void update(Object object) {
if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) {
int length = Array.getLength(object);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 如果对象为数组,则根据每个数组的元素来进行计算
Object element = Array.get(object, i);
doUpdate(element);
}
} else {
doUpdate(object);
}
}
// 计算HashCode和checksum
private void doUpdate(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : object.hashCode();
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
// 扩展因子*当前的哈希值 + 对象的哈希值*扩大倍数
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
// 添加到对比条件中
updateList.add(object);
}
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (this == object)
return true;
if (!(object instanceof CacheKey))
return false;
final CacheKey cacheKey = (CacheKey) object;
if (hashcode != cacheKey.hashcode)
return false;
if (checksum != cacheKey.checksum)
return false;
if (count != cacheKey.count)
return false;
// 只有上面的检验条件都相等的情况下,才对每个条件逐一对比
for (int i = 0; i < updateList.size(); i++) {
Object thisObject = updateList.get(i);
Object thatObject = cacheKey.updateList.get(i);
if (thisObject == null) {
if (thatObject != null)
return false;
} else {
if (!thisObject.equals(thatObject))
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
一级缓存
一级缓存直接采用PerpetualCache来实现,默认为SESSION范围
刷新时机
- SESSION范围缓存失效时刻:
- SqlSession关闭,则会释放缓存
- 提交或者回滚的时候会清空对应的一级缓存。
- 在更新操作的时候,则直接清空对应的一级缓存
- 手动调用清空缓存操作
- STATEMENT范围刷新缓存
无论是查询还是更新,在执行完Sql的时候都会清空对应的一级缓存。
二级缓存
在MyBatis中,Cache都通过CachingExecutor内的TransactionalCacheManager来管理Cache,每个Cache都会使用TransactionalCache来装饰,即缓存是事务性质的,需要手动通过commit或者SqlSession的close来实现真正的将执行结果反应到Cache中,因为二级缓存是属于全局的,会有可能涉及到多个Cache的添加或者删除操作。
构建二级缓存
MapperBuilderAssistant.useNewCache调用构造CacheBuilder来构建Cache,并且将构造出来的cache注入到MappedStatement中。CacheBuilder以Builder设计模式实现,而缓存的功能添加则是通过装饰者模式来实现。
下面为CacheBuilder构建Cache的部分代码:
public Cache build() {
// 设置默认底层实现Cache,默认如果没有提供则为PerpetualCache
setDefaultImplementations();
// 创建基类,用于最底层的Cache实现
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
// 设置Cache属性
setCacheProperties(cache);
// 只有PerpetualCache才使用装饰类添加功能,自定义的Cache不添加
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
// 使用装饰类包装
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
// 设置给定的装饰类
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
}
return cache;
}
// 根据给定的Cache以及待装饰实例,创建装饰类
private Cache newCacheDecoratorInstance(Class<? extends Cache> cacheClass, Cache base) {
Constructor<? extends Cache> cacheConstructor = getCacheDecoratorConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(base);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Could not instantiate cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
metaCache.setValue("size", size);
}
// 如果开启了定时,则使用ScheduledCache装饰
if (clearInterval != null) {
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval);
}
// 读写功能,则需要序列化装饰
if (readWrite) {
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
}
// 默认会有日志以及同步
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
return cache;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
二级缓存刷新时机示例
配置:
关闭一级cache,仅仅开启二级Cache
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/>
不手动commit
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
ProductMapper productMapper = session.getMapper(ProductMapper.class);
productMapper.queryAll();
productMapper.queryAll();
}
输出结果:
可以看到,当没有手动提交,并且是同一个session时,前一次执行的结果并没有刷到缓存,两次缓存的命中率均为0
2016-07-26 11:04:53 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LoggingCache.getObject()]:
Cache Hit Ratio [com.jabnih.analysis.mybatis.mapper.ProductMapper]: 0.0
2016-07-26 11:04:53 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
==> Preparing: select * from products
2016-07-26 11:04:53 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
==> Parameters:
2016-07-26 11:04:54 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
<== Total: 14
2016-07-26 11:04:54 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LoggingCache.getObject()]:
Cache Hit Ratio [com.jabnih.analysis.mybatis.mapper.ProductMapper]: 0.0
2016-07-26 11:04:54 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
==> Preparing: select * from products
2016-07-26 11:04:54 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
==> Parameters:
2016-07-26 11:04:54 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
<== Total: 14
手动commit
比上面多了一步,手动commit,刷新到缓存。
// 注:此处关闭了一级cache,仅仅开启了二级cache
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 此处设置了自动提交,但是那是JDBC中Connection的自动提交
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
ProductMapper productMapper = session.getMapper(ProductMapper.class);
List<Product> list = productMapper.queryAll();
// 这里比上面多操作一步,手动提交
session.commit();
productMapper.queryAll();
productMapper.queryAll();
}
输出结果:
可以看到下面的二级Cache命中率,第一次没有数据,故为0,第二次命中,变为0.5
2016-07-26 11:05:18 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LoggingCache.getObject()]:
Cache Hit Ratio [com.jabnih.analysis.mybatis.mapper.ProductMapper]: 0.0
2016-07-26 11:05:18 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
==> Preparing: select * from products
2016-07-26 11:05:18 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
==> Parameters:
2016-07-26 11:05:18 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.BaseJdbcLogger.debug()]:
<== Total: 14
2016-07-26 11:05:18 [DEBUG]-[Thread: main]-[org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LoggingCache.getObject()]:
Cache Hit Ratio [com.jabnih.analysis.mybatis.mapper.ProductMapper]: 0.5
MyBatis缓存使用注意点
在使用缓存的时候,需要注意如果数据缓存在本地,另一个系统修改数据库时,会出现脏数据问题。
一级缓存
Myatis的一级缓存默认为SESSION,而且由于底层采用PerpetualCache来实现,该类直接使用HashMap,并没有进行一些限制处理。
- 在MyBatis看来,SqlSession一般都是生命周期比较短的,当关闭的时候会释放缓存,但是如果使用SqlSession多次进行查询大量的数据时,会将数据缓存,那么有可能会导致OOM内存溢出。
二级缓存
MyBatis虽然全局配置开启缓存,但是还是取决于是否使用了<cache>标签,如果使用了二级缓存,需要注意:
- 每个
<cache>代表一个单独的二级缓存,如果多个Mapper需要共享同一个二级缓存,则需要使用<cache-ref> - 如果一个Mapper中查询数据时,使用了多表联查,则,当另一个Mapper更新相关数据时,如果没有共享一个Cache,那么下一次该Mapper查询时,就会出现读到脏数据。