简述:
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于双链表的数据结构。
2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
一句话总结:
一、 ArrayList
1.概述:
- 以数组实现。节约空间,但数组有容量限制。超出限制时会增加50%容量,用System.arraycopy()复制到新的数组,因此最好能给出数组大小的预估值。默认第一次插入元素时创建大小为10的数组。
- 按数组下标访问元素—get(i)/set(i,e) 的性能很高,这是数组的基本优势。
- 直接在数组末尾加入元素—add(e)的性能也高,但如果按下标插入、删除元素—add(i,e), remove(i), remove(e),则要用System.arraycopy()来移动部分受影响的元素,性能就变差了,这是基本劣势。
//官方文档
Resizable-array implementation of the {@code List} interface. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including {@code null}. In addition to implementing the {@code List} interface, this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is used internally to store the list. (This class is roughly equivalent to {@code Vector}, except that it is unsynchronized.)
ArrayList是一个相对来说比较简单的数据结构,最重要的一点就是它的自动扩容,可以认为就是我们常说的“动态数组”。
2. add函数
当我们在ArrayList中增加元素的时候,会使用add函数。他会将元素放到末尾。具体实现如下:
public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
3.set和get函数
Array的set和get函数就比较简单了,先做index检查,然后执行赋值或访问操作:
public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
4.remove函数
public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) // 把后面的往前移 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); // 把最后的置null elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
二、LinkedList
1. 概述
- 以双向链表实现。链表无容量限制,但双向链表本身使用了更多空间,也需要额外的链表指针操作。
- 按下标访问元素—get(i)/set(i,e) 要悲剧的遍历链表将指针移动到位(如果i>数组大小的一半,会从末尾移起)。
- 插入、删除元素时修改前后节点的指针即可,但还是要遍历部分链表的指针才能移动到下标所指的位置,只有在链表两头的操作—add(),addFirst(),removeLast()或用iterator()上的remove()能省掉指针的移动。
LinkedList是一个简单的数据结构,与ArrayList不同的是,他是基于链表实现的。
Doubly-linked list implementation of the List and Deque interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements (including null).
2. set和get函数
public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; } public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; }
这两个函数都调用了node函数,该函数会以O(n/2)的性能去获取一个节点,具体实现如下所示:
Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
就是判断index是在前半区间还是后半区间,如果在前半区间就从head搜索,而在后半区间就从tail搜索。而不是一直从头到尾的搜索。如此设计,将节点访问的复杂度由O(n)变为O(n/2)。
三、问题
(1)删除一个ArrayList中所有值为0的元素
如果选择直接遍历删除,是有问题的
错误方法1:
private void remove(ArrayList<Integer> list) {//直接遍历删除对应索引 System.out.println("删除前: " + list); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { if (list.get(i) == 0) { list.remove(i); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); }

直接循环发现相邻的第二个0没有被删掉
ArrayList删除元素方法remove;(注意remove有两个不同参方法,这里用的是remove(int index))

然后会进入System.arraycopy,数组受影响区域会进行移动


可以发现删除一个元素之后,后面的元素就“填充”回来,而遍历的索引仍然+1,这就导致被删除元素下一个元素在下一次不被遍历;造成了上面的问题。
正确方法:
private void remove3(ArrayList<Integer> list){//倒序遍历删除对应索引元素
System.out.println("删除前: " + list);
for (int i = list.size()-1; i >=0; i--) {
if (list.get(i) == 0) {
list.remove(i);
}
}
System.out.println("删除后: " + list);
}

因为数组倒序遍历时即使发生元素删除也不影响后序元素遍历。
错误方法2:
private void remove2(ArrayList<Integer> list){//直接遍历删除对应object元素 System.out.println("删除前: " + list); for (int i :list) { if (i == 0) { list.remove((Integer) i); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); }
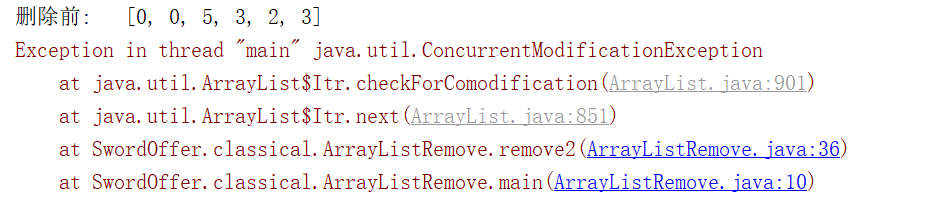
报错原因参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/huangjinyong/p/9455163.html
这种for-each写法会报出并发修改异常:java.util.ConcurrentModificationException。
这里调用的是remove(object o)方法

一般会走到else中的fastRemove方法
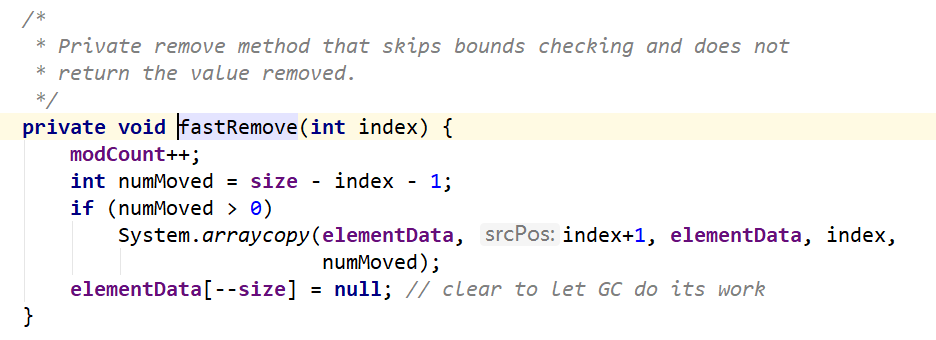
modCount进行了自增运算,
其次for((int i :list) 这句代码实质走的是Iterable接口


(具体为什么foreach走的是Iterator接口,参考这篇文章https://www.cnblogs.com/vinozly/p/5465454.html)
public E next() { checkForComodification(); try { E next = get(cursor); lastRet = cursor++; return next; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } }
第一行checkForComodification方法:
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
这里会做迭代器内部修改次数检查,因为上面的remove(Object)方法修改了modCount的值,所以才会报出并发修改异常。要避免这种情况的出现则在使用迭代器迭代时(显示或for-each的隐式)不要使用ArrayList的remove,改为用Iterator的remove即可。
接着解释一下实例二的错误原因。错误二产生的原因却是foreach写法是对实际的Iterable、hasNext、next方法的简写,问题同样处在上文的fastRemove方法中,可以看到第一行把modCount变量的值加一,但在ArrayList返回的迭代器(该代码在其父类AbstractList中):
使用迭代器:
这里会做迭代器内部修改次数检查,因为上面的remove(Object)方法修改了modCount的值,所以才会报出并发修改异常。要避免这种情况的出现则在使用迭代器迭代时(显示或for-each的隐式)不要使用ArrayList的remove,改为用Iterator的remove即可。
private void remove4(ArrayList<Integer> list){ System.out.println("删除前: " + list); Iterator<Integer> integerIterator = list.iterator(); while (integerIterator.hasNext()){ if (0==integerIterator.next()){ integerIterator.remove(); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); }

完整代码

public class ArrayListRemove { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayListRemove arrayListRemove = new ArrayListRemove(); ArrayList list = arrayListRemove.initList(); // arrayListRemove.remove(list); // arrayListRemove.remove2(list); // arrayListRemove.remove3(list); arrayListRemove.remove4(list); } private ArrayList initList() {//生成ArrayList ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(0); list.add(0); list.add(5); list.add(3); list.add(2); list.add(3); return list; } private void remove(ArrayList<Integer> list) {//直接遍历删除对应索引 System.out.println("删除前: " + list); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { if (list.get(i) == 0) { list.remove(i); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); } private void remove2(ArrayList<Integer> list){//直接遍历删除对应object元素 System.out.println("删除前: " + list); for (int i :list) { if (i == 0) { list.remove((Integer) i); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); } private void remove3(ArrayList<Integer> list){//倒序遍历删除对应索引元素 System.out.println("删除前: " + list); for (int i = list.size()-1; i >=0; i--) { if (list.get(i) == 0) { list.remove(i); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); } private void remove4(ArrayList<Integer> list){//使用迭代器 System.out.println("删除前: " + list); Iterator<Integer> integerIterator = list.iterator(); while (integerIterator.hasNext()){ if (0==integerIterator.next()){ integerIterator.remove(); } } System.out.println("删除后: " + list); } }
