实例属性与类属性、特定遮蔽关系
- 类属性与实例属性同名时,后者会遮蔽类属性:
class Demo():
des = "Class Demo attribute value One"
cash = "Class Demo attribute value Two"
def __init__(self):
self.des = "The instance attribute value"
demo = Demo()
print(demo.__dict__) # 返回一个字典,代表实例的属性集合:{'des': 'The instance attribute value'}
print(demo.des) # The instance attribute value
print(Demo.des) # Class Demo attribute value one
print(demo.cash) # Class Demo attribute value Two
- 实例属性与特性重名时,实例属性会被遮蔽:
- 特性函数:property(fget=None,fset=None,Fdel=None,doc=None)):
class C: def __init__(self): self._x=None def getx(self): return self._x def setx(self,value): self._x = value def delx(self): del self._x x = property(getx,setx,delx,"I'm the 'x' property.") # 定义托管属性 x,同时将方法getx,setx,delx等三个类方法变为类属性操作 c = C() print(c._x) # 返回None print(c.x) # 返回None c.x会调用getx函数返回_x的值 c.x =2 #set value 会调用setx函数 print(c._x) #返回经过上一步赋值以后的value - 特性 @property装饰器:
class C: def __init__(self): self._x = None @property def x(self): # 方法名均为x """I'm the 'x' property.""" print("get value is running") return self._x @x.setter def x(self, value): # 方法名均为x print('set value is running') self._x = value @x.deleter def x(self): # 方法名均为x del self._x c = C() c.x = 2 # x已变为属性或者说特性,赋值操作会调用@x.setter print(c.x) # 同理 调用 get value - 特性 @property装饰器:
class C(): value = 'the class attribute value' @property def demo(self): return "the property attribute value" c = C() print(c.value) # 打印出类属性 print(c.__dict__) # {} 显示无实例属性 c.value =20 # 给实例属性赋值,创建一个实例属性 print(c.value) #20 print(c.__dict__) #{'value': 20} print(C.value) #the class attribute value 显示类属性 c.demo =2 #尝试给类特性赋值, 报错 AttributeError: can't set attribute 因为该类特性仅有get value 只读特性 print(c.demo) # the property attribute value 打印类特性 c.__dict__['demo'] = 'instance attribute value' #虽然无法通过实例.特性 赋值,此办法可以通过 print(c.demo) # the property attribute value ,特性依然覆盖实例属性 C.demo = 1 # 销毁类特性 print(c.demo) # instance attribute value C.demo不再是特性,无法覆盖实例属性
- 特性函数:property(fget=None,fset=None,Fdel=None,doc=None)):
特性工厂函数
- 为了实现对属性存取设定一定逻辑,避免不合规的数据出现,利用特性会覆盖实例属性这一特点,在取值、存储值之前可以对数据进行条件判断:例如不允许出现negative or zero :
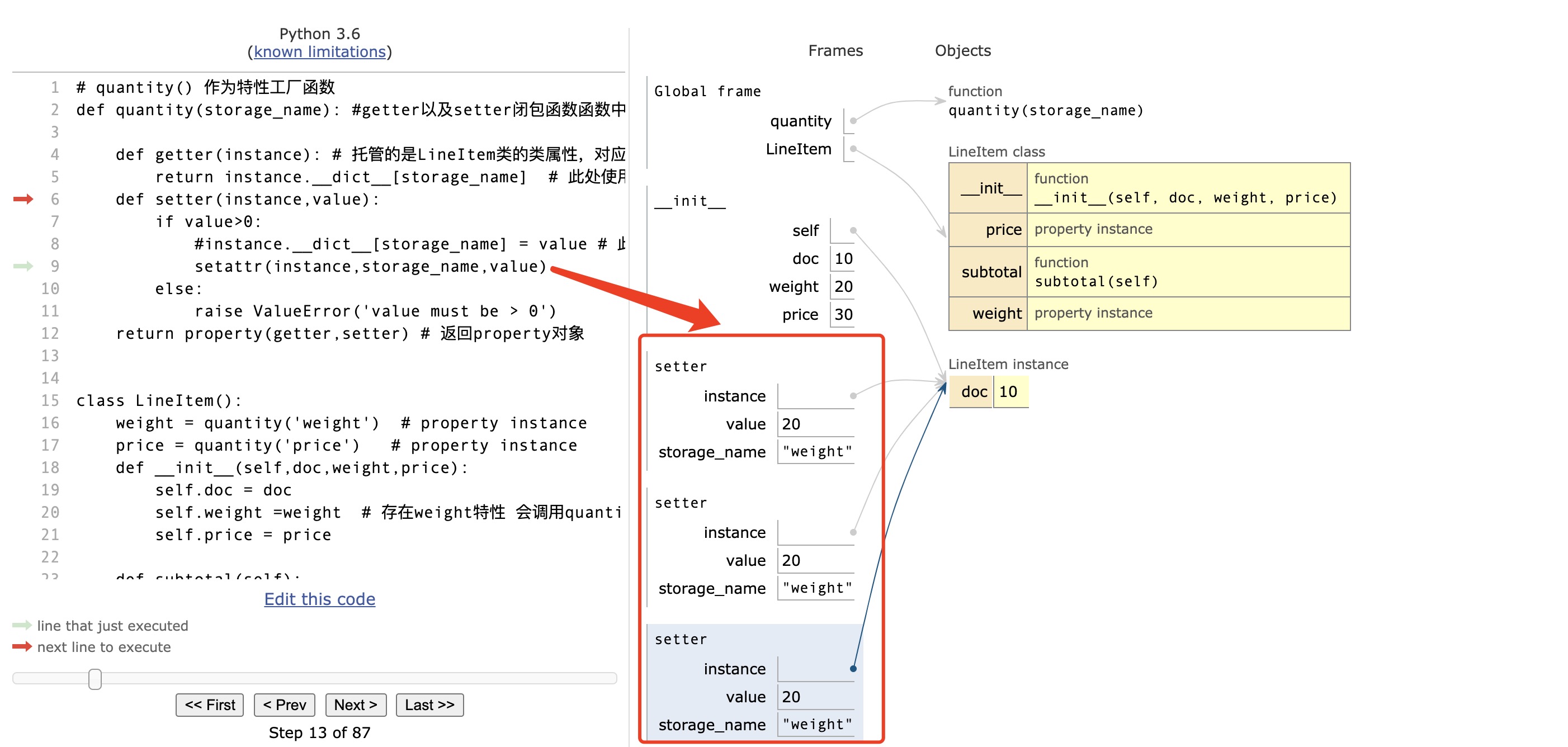
# quantity() 作为特性工厂函数
def quantity(storage_name): #getter以及setter闭包函数函数中 storage_name当作自由变量使用,会保存该变量的状态
def getter(instance): # 托管的是LineItem类的类属性,对应的instance是LineItem的实例
return instance.__dict__[storage_name] # 此处使用 instance.storage_name 会报错 ,python解释器会认为是给实例创造名为storage_name 的属性
#return getattr(instance,storage_name) # 获得instance实例中名为storage_name变量中存储的值
def setter(instance,value):
if value>0:
instance.__dict__[storage_name] = value # 此时添加实例属性。(特性管理的实际是实例属性)
#setattr(instance,storage_name,value) # 将instance实例中名为storage_name变量中存储的值 设置为value
else:
raise ValueError('value must be > 0')
return property(getter,setter) # 返回property对象
class LineItem():
weight = quantity('weight') # property instance
price = quantity('price') # property instance
def __init__(self,doc,weight,price):
self.doc = doc
self.weight =weight # 存在weight特性 会调用quantity函数中的setter函数 与类属性同名
self.price = price #与类属性同名 否则不存在特性覆盖
def subtotal(self):
return self.weight*self.price # 存在weight特性 会调用quantity函数中的getter函数
demo = LineItem(10,20,30)
print(demo.subtotal())
- 在上述get()、set()函数中调用setattr(obj,name,value)以及getattr(obj,name),因为已提到过instance.属性(属性为特性)会被特性覆盖,以下将会导致get、set被递归调用,没有穷尽:
描述符类
- 描述符可以控制属性存取的逻辑,在上述特性工厂的基础上做进一步改进:
- 描述符:言简意赅 实现了__set__、get、__delete__等方法的类
- 实现:将描述符类的实例作为控制属性存取类的类属性
class quantity(): def __init__(self,storage_name): self.storage_name =storage_name def __get__(self, instance, owner): return instance.__dict__[self.storage_name] # 防止递归 仍不能使用getattr def __set__(self, instance, value): if value>0: # 防止递归 仍不能使用setattr instance.__dict__[self.storage_name] =value # self.__dict__[self.storage_name] = value self代表的是 LineItem类属性中创建的quantity实例 else: raise ValueError('Value must > 0 ') class LineItem(): weight = quantity('weight') # property instance price = quantity('price') # property instance def __init__(self,doc,weight,price): self.doc = doc self.weight =weight # 存在weight特性 会调用quantity函数中的__set__ self.price = price def subtotal(self): return self.weight*self.price # 存在weight特性 会调用quantity函数中的__get__ demo = LineItem(10,20,30) print(demo.subtotal())-
以下图表反映了在描述符类quantity方法中 self 与instance的代表着什么:self quantity描述类实例,instance代表LineItem托管类实例:
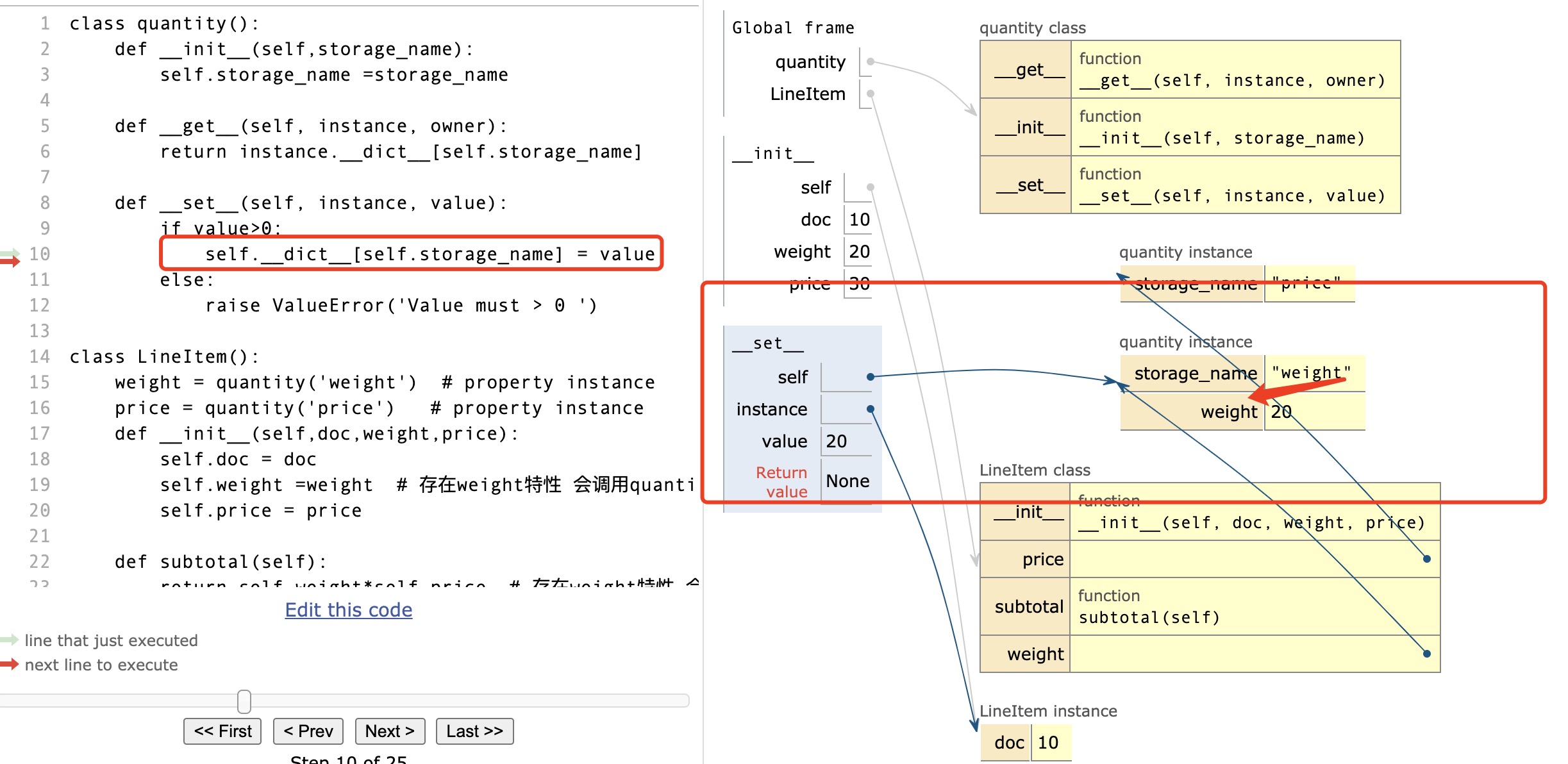
-
在托管类LineItem中因为需要在创建描述符实例的时候填入对应的列属性对应的名称,以下做一个改进:
class quantity(): __counter = 0 # 作为类变量 为quantity所有实例共享 def __init__(self): cls= self.__class__ prefix = cls.__name__ index = cls.__counter self.storage_name = '__{}_{}'.format(prefix,index) cls.__counter +=1 #每创建一个quantity实例 计数器自增1 def __get__(self, instance, owner): return instance.__dict__[self.storage_name] #可以使用getattr函数 因为托管的weight、price属性与存储的storage_name名称不同 def __set__(self, instance, value): if value>0: instance.__dict__[self.storage_name] =value #可以使用setattr函数 因为托管的weight、price属性与存储的storage_name名称不同 else: raise ValueError('value must be > 0') class LineItem(): weight = quantity() # property instance price = quantity() # property instance def __init__(self,doc,weight,price): self.doc = doc self.weight =weight self.price = price def subtotal(self): return self.weight*self.price demo = LineItem(10,20,30) print(demo.subtotal()) -
特性工厂函数同步改进:
def quantity(): try: quantity._counter +=1 except AttributeError: quantity._counter =0 storage_name = '__{}#{}'.format('quantity',quantity._counter) def getter(instance): return getattr(instance,storage_name) def setter(instance, value): if value>0: setattr(instance,storage_name,value) else: raise ValueError('value must be > 0') return property(getter,setter) class LineItem(): weight = quantity() # property instance price = quantity() # property instance def __init__(self,doc,weight,price): self.doc = doc self.weight =weight self.price = price def subtotal(self): return self.weight*self.price demo = LineItem(10,20,30)
上述例子中实现了__set__方法的描述符 可以遮盖实例特性,成为覆盖型描述符,只实现了__get__方法的类则为非覆盖型描述符,无法完成实例属性遮蔽,且只读属性。